Dados tres puntos de coordenadas A, B y C, encuentre el punto D que falta tal que ABCD pueda ser un paralelogramo.
Ejemplos:
Input : A = (1, 0)
B = (1, 1)
C = (0, 1)
Output : 0, 0
Explanation:
The three input points form a unit
square with the point (0, 0)
Input : A = (5, 0)
B = (1, 1)
C = (2, 5)
Output : 6, 4
Como se muestra en el siguiente diagrama, puede haber múltiples salidas posibles, necesitamos imprimir cualquiera de ellas.
Se dice que un cuadrilátero es un paralelogramo si sus lados opuestos son paralelos y de igual longitud.
Como nos dan tres puntos del paralelogramo, podemos encontrar la pendiente de los lados que faltan, así como sus longitudes.
El algoritmo se puede explicar de la siguiente manera
Sea R el punto que falta. Ahora por definición, tenemos
- Longitud de PR = Longitud de QS = L1 (Los lados opuestos son iguales)
- Pendiente de PR = Pendiente de QS = M1 (Los lados opuestos son paralelos)
- Longitud de PQ = Longitud de RS = L2 (Los lados opuestos son iguales)
- Pendiente de PQ= Pendiente de RS = M2 (Los lados opuestos son paralelos)
Así podemos encontrar los puntos a una distancia L1 de P que tienen una pendiente M1 como se menciona en el siguiente artículo:
Encuentra puntos a una distancia dada en una línea de pendiente dada .
Ahora uno de los puntos satisfará las condiciones anteriores que se pueden verificar fácilmente (usando la condición 3 o 4)
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to find missing point of a
// parallelogram
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// struct to represent a co-ordinate point
struct Point {
float x, y;
Point()
{
x = y = 0;
}
Point(float a, float b)
{
x = a, y = b;
}
};
// given a source point, slope(m) of line
// passing through it this function calculates
// and return two points at a distance l away
// from the source
pair<Point, Point> findPoints(Point source,
float m, float l)
{
Point a, b;
// slope is 0
if (m == 0) {
a.x = source.x + l;
a.y = source.y;
b.x = source.x - l;
b.y = source.y;
}
// slope if infinity
else if (m == std::numeric_limits<float>::max()) {
a.x = source.x;
a.y = source.y + l;
b.x = source.x;
b.y = source.y - l;
}
// normal case
else {
float dx = (l / sqrt(1 + (m * m)));
float dy = m * dx;
a.x = source.x + dx, a.y = source.y + dy;
b.x = source.x - dx, b.y = source.y - dy;
}
return pair<Point, Point>(a, b);
}
// given two points, this function calculates
// the slope of the line/ passing through the
// points
float findSlope(Point p, Point q)
{
if (p.y == q.y)
return 0;
if (p.x == q.x)
return std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
return (q.y - p.y) / (q.x - p.x);
}
// calculates the distance between two points
float findDistance(Point p, Point q)
{
return sqrt(pow((q.x - p.x), 2) + pow((q.y - p.y), 2));
}
// given three points, it prints a point such
// that a parallelogram is formed
void findMissingPoint(Point a, Point b, Point c)
{
// calculate points originating from a
pair<Point, Point> d = findPoints(a, findSlope(b, c),
findDistance(b, c));
// now check which of the two points satisfy
// the conditions
if (findDistance(d.first, c) == findDistance(a, b))
cout << d.first.x << ", " << d.first.y << endl;
else
cout << d.second.x << ", " << d.second.y << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
findMissingPoint(Point(1, 0), Point(1, 1), Point(0, 1));
findMissingPoint(Point(5, 0), Point(1, 1), Point(2, 5));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find missing point of a
// parallelogram
import java.util.*;
// struct to represent a co-ordinate point
class Point {
public double x, y;
public Point()
{
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
public Point(double a, double b)
{
x = a;
y = b;
}
};
class GFG {
// given a source point, slope(m) of line
// passing through it this function calculates
// and return two points at a distance l away
// from the source
static Point[] findPoints(Point source, double m,
double l)
{
Point a = new Point();
Point b = new Point();
// slope is 0
if (m == 0) {
a.x = source.x + l;
a.y = source.y;
b.x = source.x - l;
b.y = source.y;
}
// slope if infinity
else if (m == Double.MAX_VALUE) {
a.x = source.x;
a.y = source.y + l;
b.x = source.x;
b.y = source.y - l;
}
// normal case
else {
double dx = (l / Math.sqrt(1 + (m * m)));
double dy = m * dx;
a.x = source.x + dx;
a.y = source.y + dy;
b.x = source.x - dx;
b.y = source.y - dy;
}
Point[] res = { a, b };
return res;
}
// given two points, this function calculates
// the slope of the line/ passing through the
// points
static double findSlope(Point p, Point q)
{
if (p.y == q.y)
return 0;
if (p.x == q.x)
return Double.MAX_VALUE;
return (q.y - p.y) / (q.x - p.x);
}
// calculates the distance between two points
static double findDistance(Point p, Point q)
{
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((q.x - p.x), 2)
+ Math.pow((q.y - p.y), 2));
}
// given three points, it prints a point such
// that a parallelogram is formed
static void findMissingPoint(Point a, Point b, Point c)
{
// calculate points originating from a
Point[] d = findPoints(a, findSlope(b, c),
findDistance(b, c));
// now check which of the two points satisfy
// the conditions
if (findDistance(d[0], c) == findDistance(a, b))
System.out.println(d[0].x + ", " + d[0].y);
else
System.out.println(d[1].x + ", " + d[1].y);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
findMissingPoint(new Point(1, 0), new Point(1, 1),
new Point(0, 1));
findMissingPoint(new Point(5, 0), new Point(1, 1),
new Point(2, 5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by phasing17
Python3
# Python program to find missing point of a
# parallelogram
import math as Math
FLOAT_MAX = 3.40282e+38
# given a source point, slope(m) of line
# passing through it this function calculates
# and return two points at a distance l away
# from the source
def findPoints(source, m, l):
a = [0] * (2)
b = [0] * (2)
# slope is 0
if (m == 0):
a[0] = source[0] + l
a[1] = source[1]
b[0] = source[0] - l
b[1] = source[1]
# slope if infinity
elif (m == FLOAT_MAX):
a[0] = source[0]
a[1] = source[1] + l
b[0] = source[0]
b[1] = source[1] - l
# normal case
else:
dx = (l / ((1 + (m * m)) ** 0.5))
dy = m * dx
a[0] = source[0] + dx
a[1] = source[1] + dy
b[0] = source[0] - dx
b[1] = source[1] - dy
return [a, b]
# given two points, this function calculates
# the slope of the line/ passing through the
# points
def findSlope(p, q):
if (p[1] == q[1]):
return 0
if (p[0] == q[0]):
return FLOAT_MAX
return (q[1] - p[1]) / (q[0] - p[0])
# calculates the distance between two points
def findDistance(p, q):
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((q[0] - p[0]), 2) + Math.pow((q[1] - p[1]), 2))
# given three points, it prints a point such
# that a parallelogram is formed
def findMissingPoint(a, b, c):
# calculate points originating from a
d = findPoints(a, findSlope(b, c), findDistance(b, c))
# now check which of the two points satisfy
# the conditions
if (findDistance(d[0], c) == findDistance(a, b)):
print(f"{(int)(d[0][0])}, {(int)(d[0][1])}")
else:
print(f"{(int)(d[1][0])}, {(int)(d[1][1])}")
# Driver code
Point1 = [1, 0]
Point2 = [1, 1]
Point3 = [0, 1]
findMissingPoint(Point1, Point2, Point3)
Point1 = [5, 0]
Point2 = [1, 1]
Point3 = [2, 5]
findMissingPoint(Point1, Point2, Point3)
# The code is contributed by Saurabh Jaiswal
Javascript
// JavaScript program to find missing point of a
// parallelogram
const FLOAT_MAX = 3.40282e+38;
// given a source point, slope(m) of line
// passing through it this function calculates
// and return two points at a distance l away
// from the source
function findPoints(source, m, l)
{
let a = new Array(2);
let b = new Array(2);
// slope is 0
if (m == 0) {
a[0] = source[0] + l;
a[1] = source[1];
b[0] = source[0] - l;
b[1] = source[1];
}
// slope if infinity
else if (m == FLOAT_MAX) {
a[0] = source[0];
a[1] = source[1] + l;
b[0] = source[0];
b[1] = source[1] - l;
}
// normal case
else {
let dx = (l / Math.sqrt(1 + (m * m)));
let dy = m * dx;
a[0] = source[0] + dx, a[1] = source[1] + dy;
b[0] = source[0] - dx, b[1] = source[1] - dy;
}
return [a, b];
}
// given two points, this function calculates
// the slope of the line/ passing through the
// points
function findSlope(p, q)
{
if (p[1] == q[1]){
return 0;
}
if (p[0] == q[0]){
return FLOAT_MAX;
}
return (q[1] - p[1]) / (q[0] - p[0]);
}
// calculates the distance between two points
function findDistance(p, q)
{
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((q[0] - p[0]), 2) + Math.pow((q[1] - p[1]), 2));
}
// given three points, it prints a point such
// that a parallelogram is formed
function findMissingPoint(a, b, c)
{
// calculate points originating from a
let d = findPoints(a, findSlope(b, c), findDistance(b, c));
// now check which of the two points satisfy
// the conditions
if (findDistance(d[0], c) === findDistance(a, b)){
console.log(d[0][0], ",", d[0][1]);
}
else{
console.log(d[1][0], ",", d[1][1]);
}
}
// Driver code
{
let Point1 = [1, 0];
let Point2 = [1, 1];
let Point3 = [0, 1];
findMissingPoint(Point1, Point2, Point3);
Point1 = [5, 0];
Point2 = [1, 1];
Point3 = [2, 5];
findMissingPoint(Point1, Point2, Point3);
}
// The code is contributed by Gautam goel (gautamgoel962)
Producción :
0, 0 6, 4
Complejidad de tiempo: O(log(log n)) desde el uso de las funciones sqrt y log incorporadas
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Enfoque alternativo:
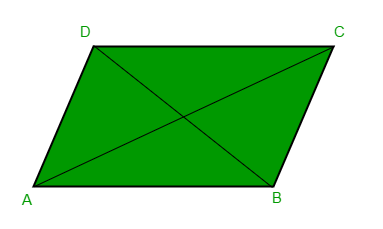
Dado que los lados opuestos son iguales, AD = BC y AB = CD, podemos calcular las coordenadas del punto que falta (D) como:
AD = BC (Dx - Ax, Dy - Ay) = (Cx - Bx, Cy - By) Dx = Ax + Cx - Bx Dy = Ay + Cy - By
Referencias: https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/887095/find-the-4th-vertex-of-the-parallelogram
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to find missing point
// of a parallelogram
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// main method
int main()
{
int ax = 5, ay = 0; //coordinates of A
int bx = 1, by = 1; //coordinates of B
int cx = 2, cy = 5; //coordinates of C
cout << ax + cx - bx << ", "
<< ay + cy - by;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to
// find missing point
// of a parallelogram
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int ax = 5, ay = 0; //coordinates of A
int bx = 1, by = 1; //coordinates of B
int cx = 2, cy = 5; //coordinates of C
System.out.println(ax + (cx - bx) + ", " +
ay + (cy - by));
}
}
// This code is contributed by m_kit
Python 3
# Python 3 program to find missing point # of a parallelogram # Main method if __name__ == "__main__": # coordinates of A ax, ay = 5, 0 # coordinates of B bx ,by = 1, 1 # coordinates of C cx ,cy = 2, 5 print(ax + cx - bx , ",", ay + cy - by) # This code is contributed by Smitha
C#
// C# program to
// find missing point
// of a parallelogram
using System;
class GFG
{
static public void Main ()
{
int ax = 5, ay = 0; //coordinates of A
int bx = 1, by = 1; //coordinates of B
int cx = 2, cy = 5; //coordinates of C
Console.WriteLine(ax + (cx - bx) + ", " +
ay + (cy - by));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajit
PHP
<?php // PHP program to find missing // point of a parallelogram // Driver Code $ax = 5; $ay = 0; //coordinates of A $bx = 1; $by = 1; //coordinates of B $cx = 2; $cy = 5; //coordinates of C echo $ax + $cx - $bx , ", ", $ay + $cy - $by; // This code is contributed by aj_36 ?>
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to find missing point of a parallelogram let ax = 5, ay = 0; //coordinates of A let bx = 1, by = 1; //coordinates of B let cx = 2, cy = 5; //coordinates of C document.write((ax + (cx - bx)) + ", " + (ay + (cy - by))); </script>
Producción:
6, 4
Tiempo Complejidad: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Este artículo es una contribución de Aarti_Rathi y Ashutosh Kumar 😀 y Abhishek Sharma . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA