El artículo se centra en el uso de un algoritmo para resolver un sistema de ecuaciones lineales. Nos ocuparemos de la array de coeficientes. La eliminación gaussiana no funciona en arrays singulares (conducen a la división por cero).
Input: For N unknowns, input is an augmented
matrix of size N x (N+1). One extra
column is for Right Hand Side (RHS)
mat[N][N+1] = {{3.0, 2.0,-4.0, 3.0},
{2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 15.0},
{5.0, -3, 1.0, 14.0}
};
Output: Solution to equations is:
3.000000
1.000000
2.000000
Explanation:
Given matrix represents following equations
3.0X1 + 2.0X2 - 4.0X3 = 3.0
2.0X1 + 3.0X2 + 3.0X3 = 15.0
5.0X1 - 3.0X2 + X3 = 14.0
There is a unique solution for given equations,
solutions is, X1 = 3.0, X2 = 1.0, X3 = 2.0,

Forma escalonada por filas: se dice que la array está en referencia si se cumplen las siguientes condiciones:
- El primer elemento distinto de cero en cada fila, llamado coeficiente principal, es 1.
- Cada coeficiente principal está en una columna a la derecha del coeficiente principal de la fila anterior.
- Las filas con todos ceros están debajo de las filas con al menos un elemento distinto de cero.
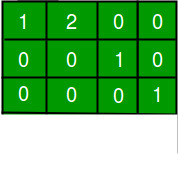
Forma escalonada de fila reducida: se dice que Matrix está en rref si se cumplen las siguientes condiciones:
- Todas las condiciones para ref.
- El coeficiente principal en cada fila es la única entrada distinta de cero en su columna.
El algoritmo consiste principalmente en realizar una secuencia de operaciones en las filas de la array. Lo que nos gustaría tener en cuenta al realizar estas operaciones es que queremos convertir la array en una array triangular superior en forma escalonada por filas. Las operaciones pueden ser:
- Intercambio de dos filas
- Multiplicar una fila por un escalar distinto de cero
- Sumar a una fila un múltiplo de otra
El proceso:
- Eliminación hacia adelante: reducción a la forma escalonada por filas. Utilizándolo, uno puede decir si no hay soluciones, o una solución única, o infinitas soluciones.
- Sustitución posterior: reducción adicional a la forma escalonada de fila reducida.
Algoritmo:
- Pivote parcial: encuentre el k-ésimo pivote intercambiando filas, para mover la entrada con el valor absoluto más grande a la posición de pivote. Esto imparte estabilidad computacional al algoritmo.
- Para cada fila debajo del pivote, calcule el factor f que hace que la entrada k-ésima sea cero, y para cada elemento de la fila reste el quinto múltiplo del elemento correspondiente en la fila k-ésima.
- Repita los pasos anteriores para cada incógnita. Nos quedaremos con una array de referencia parcial.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del algoritmo anterior.
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate working of Gaussian Elimination
// method
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 3 // Number of unknowns
// function to reduce matrix to r.e.f. Returns a value to
// indicate whether matrix is singular or not
int forwardElim(double mat[N][N+1]);
// function to calculate the values of the unknowns
void backSub(double mat[N][N+1]);
// function to get matrix content
void gaussianElimination(double mat[N][N+1])
{
/* reduction into r.e.f. */
int singular_flag = forwardElim(mat);
/* if matrix is singular */
if (singular_flag != -1)
{
printf("Singular Matrix.\n");
/* if the RHS of equation corresponding to
zero row is 0, * system has infinitely
many solutions, else inconsistent*/
if (mat[singular_flag][N])
printf("Inconsistent System.");
else
printf("May have infinitely many "
"solutions.");
return;
}
/* get solution to system and print it using
backward substitution */
backSub(mat);
}
// function for elementary operation of swapping two rows
void swap_row(double mat[N][N+1], int i, int j)
{
//printf("Swapped rows %d and %d\n", i, j);
for (int k=0; k<=N; k++)
{
double temp = mat[i][k];
mat[i][k] = mat[j][k];
mat[j][k] = temp;
}
}
// function to print matrix content at any stage
void print(double mat[N][N+1])
{
for (int i=0; i<N; i++, printf("\n"))
for (int j=0; j<=N; j++)
printf("%lf ", mat[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
// function to reduce matrix to r.e.f.
int forwardElim(double mat[N][N+1])
{
for (int k=0; k<N; k++)
{
// Initialize maximum value and index for pivot
int i_max = k;
int v_max = mat[i_max][k];
/* find greater amplitude for pivot if any */
for (int i = k+1; i < N; i++)
if (abs(mat[i][k]) > v_max)
v_max = mat[i][k], i_max = i;
/* if a principal diagonal element is zero,
* it denotes that matrix is singular, and
* will lead to a division-by-zero later. */
if (!mat[k][i_max])
return k; // Matrix is singular
/* Swap the greatest value row with current row */
if (i_max != k)
swap_row(mat, k, i_max);
for (int i=k+1; i<N; i++)
{
/* factor f to set current row kth element to 0,
* and subsequently remaining kth column to 0 */
double f = mat[i][k]/mat[k][k];
/* subtract fth multiple of corresponding kth
row element*/
for (int j=k+1; j<=N; j++)
mat[i][j] -= mat[k][j]*f;
/* filling lower triangular matrix with zeros*/
mat[i][k] = 0;
}
//print(mat); //for matrix state
}
//print(mat); //for matrix state
return -1;
}
// function to calculate the values of the unknowns
void backSub(double mat[N][N+1])
{
double x[N]; // An array to store solution
/* Start calculating from last equation up to the
first */
for (int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
/* start with the RHS of the equation */
x[i] = mat[i][N];
/* Initialize j to i+1 since matrix is upper
triangular*/
for (int j=i+1; j<N; j++)
{
/* subtract all the lhs values
* except the coefficient of the variable
* whose value is being calculated */
x[i] -= mat[i][j]*x[j];
}
/* divide the RHS by the coefficient of the
unknown being calculated */
x[i] = x[i]/mat[i][i];
}
printf("\nSolution for the system:\n");
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
printf("%lf\n", x[i]);
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
/* input matrix */
double mat[N][N+1] = {{3.0, 2.0,-4.0, 3.0},
{2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 15.0},
{5.0, -3, 1.0, 14.0}
};
gaussianElimination(mat);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to demonstrate working of Gaussian Elimination
// method
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
public static int N = 3; // Number of unknowns
// function to get matrix content
static void gaussianElimination(double mat[][])
{
/* reduction into r.e.f. */
int singular_flag = forwardElim(mat);
/* if matrix is singular */
if (singular_flag != -1)
{
System.out.println("Singular Matrix.");
/* if the RHS of equation corresponding to
zero row is 0, * system has infinitely
many solutions, else inconsistent*/
if (mat[singular_flag][N] != 0)
System.out.print("Inconsistent System.");
else
System.out.print(
"May have infinitely many solutions.");
return;
}
/* get solution to system and print it using
backward substitution */
backSub(mat);
}
// function for elementary operation of swapping two
// rows
static void swap_row(double mat[][], int i, int j)
{
// printf("Swapped rows %d and %d\n", i, j);
for (int k = 0; k <= N; k++)
{
double temp = mat[i][k];
mat[i][k] = mat[j][k];
mat[j][k] = temp;
}
}
// function to print matrix content at any stage
static void print(double mat[][])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++, System.out.println())
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j++)
System.out.print(mat[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
// function to reduce matrix to r.e.f.
static int forwardElim(double mat[][])
{
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
// Initialize maximum value and index for pivot
int i_max = k;
int v_max = (int)mat[i_max][k];
/* find greater amplitude for pivot if any */
for (int i = k + 1; i < N; i++)
if (Math.abs(mat[i][k]) > v_max)
{
v_max = (int)mat[i][k];
i_max = i;
}
/* if a principal diagonal element is zero,
* it denotes that matrix is singular, and
* will lead to a division-by-zero later. */
if (mat[k][i_max] == 0)
return k; // Matrix is singular
/* Swap the greatest value row with current row
*/
if (i_max != k)
swap_row(mat, k, i_max);
for (int i = k + 1; i < N; i++)
{
/* factor f to set current row kth element
* to 0, and subsequently remaining kth
* column to 0 */
double f = mat[i][k] / mat[k][k];
/* subtract fth multiple of corresponding
kth row element*/
for (int j = k + 1; j <= N; j++)
mat[i][j] -= mat[k][j] * f;
/* filling lower triangular matrix with
* zeros*/
mat[i][k] = 0;
}
// print(mat); //for matrix state
}
// print(mat); //for matrix state
return -1;
}
// function to calculate the values of the unknowns
static void backSub(double mat[][])
{
double x[]
= new double[N]; // An array to store solution
/* Start calculating from last equation up to the
first */
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
/* start with the RHS of the equation */
x[i] = mat[i][N];
/* Initialize j to i+1 since matrix is upper
triangular*/
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
/* subtract all the lhs values
* except the coefficient of the variable
* whose value is being calculated */
x[i] -= mat[i][j] * x[j];
}
/* divide the RHS by the coefficient of the
unknown being calculated */
x[i] = x[i] / mat[i][i];
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Solution for the system:");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
System.out.format("%.6f", x[i]);
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* input matrix */
double mat[][] = { { 3.0, 2.0, -4.0, 3.0 },
{ 2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 15.0 },
{ 5.0, -3, 1.0, 14.0 } };
gaussianElimination(mat);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.
Python3
# Python3 program to demonstrate working of
# Gaussian Elimination method
N = 3
# function to get matrix content
def gaussianElimination(mat):
# reduction into r.e.f.
singular_flag = forwardElim(mat)
# if matrix is singular
if (singular_flag != -1):
print("Singular Matrix.")
# if the RHS of equation corresponding to
# zero row is 0, * system has infinitely
# many solutions, else inconsistent*/
if (mat[singular_flag][N]):
print("Inconsistent System.")
else:
print("May have infinitely many solutions.")
return
# get solution to system and print it using
# backward substitution
backSub(mat)
# function for elementary operation of swapping two rows
def swap_row(mat, i, j):
for k in range(N + 1):
temp = mat[i][k]
mat[i][k] = mat[j][k]
mat[j][k] = temp
# function to reduce matrix to r.e.f.
def forwardElim(mat):
for k in range(N):
# Initialize maximum value and index for pivot
i_max = k
v_max = mat[i_max][k]
# find greater amplitude for pivot if any
for i in range(k + 1, N):
if (abs(mat[i][k]) > v_max):
v_max = mat[i][k]
i_max = i
# if a principal diagonal element is zero,
# it denotes that matrix is singular, and
# will lead to a division-by-zero later.
if not mat[k][i_max]:
return k # Matrix is singular
# Swap the greatest value row with current row
if (i_max != k):
swap_row(mat, k, i_max)
for i in range(k + 1, N):
# factor f to set current row kth element to 0,
# and subsequently remaining kth column to 0 */
f = mat[i][k]/mat[k][k]
# subtract fth multiple of corresponding kth
# row element*/
for j in range(k + 1, N + 1):
mat[i][j] -= mat[k][j]*f
# filling lower triangular matrix with zeros*/
mat[i][k] = 0
# print(mat); //for matrix state
# print(mat); //for matrix state
return -1
# function to calculate the values of the unknowns
def backSub(mat):
x = [None for _ in range(N)] # An array to store solution
# Start calculating from last equation up to the
# first */
for i in range(N-1, -1, -1):
# start with the RHS of the equation */
x[i] = mat[i][N]
# Initialize j to i+1 since matrix is upper
# triangular*/
for j in range(i + 1, N):
# subtract all the lhs values
# except the coefficient of the variable
# whose value is being calculated */
x[i] -= mat[i][j]*x[j]
# divide the RHS by the coefficient of the
# unknown being calculated
x[i] = (x[i]/mat[i][i])
print("\nSolution for the system:")
for i in range(N):
print("{:.8f}".format(x[i]))
# Driver program
# input matrix
mat = [[3.0, 2.0, -4.0, 3.0], [2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 15.0], [5.0, -3, 1.0, 14.0]]
gaussianElimination(mat)
# This code is contributed by phasing17
C#
// C# program to demonstrate working
// of Gaussian Elimination method
using System;
class GFG{
// Number of unknowns
public static int N = 3;
// Function to get matrix content
static void gaussianElimination(double [,]mat)
{
/* reduction into r.e.f. */
int singular_flag = forwardElim(mat);
/* if matrix is singular */
if (singular_flag != -1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Singular Matrix.");
/* if the RHS of equation corresponding to
zero row is 0, * system has infinitely
many solutions, else inconsistent*/
if (mat[singular_flag,N] != 0)
Console.Write("Inconsistent System.");
else
Console.Write("May have infinitely " +
"many solutions.");
return;
}
/* get solution to system and print it using
backward substitution */
backSub(mat);
}
// Function for elementary operation of swapping two
// rows
static void swap_row(double [,]mat, int i, int j)
{
// printf("Swapped rows %d and %d\n", i, j);
for(int k = 0; k <= N; k++)
{
double temp = mat[i, k];
mat[i, k] = mat[j, k];
mat[j, k] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print matrix content at any stage
static void print(double [,]mat)
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++, Console.WriteLine())
for(int j = 0; j <= N; j++)
Console.Write(mat[i, j]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to reduce matrix to r.e.f.
static int forwardElim(double [,]mat)
{
for(int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
// Initialize maximum value and index for pivot
int i_max = k;
int v_max = (int)mat[i_max, k];
/* find greater amplitude for pivot if any */
for(int i = k + 1; i < N; i++)
{
if (Math.Abs(mat[i, k]) > v_max)
{
v_max = (int)mat[i, k];
i_max = i;
}
/* If a principal diagonal element is zero,
* it denotes that matrix is singular, and
* will lead to a division-by-zero later. */
if (mat[k, i_max] == 0)
return k; // Matrix is singular
/* Swap the greatest value row with
current row
*/
if (i_max != k)
swap_row(mat, k, i_max);
for(int i = k + 1; i < N; i++)
{
/* factor f to set current row kth element
* to 0, and subsequently remaining kth
* column to 0 */
double f = mat[i, k] / mat[k, k];
/* subtract fth multiple of corresponding
kth row element*/
for(int j = k + 1; j <= N; j++)
mat[i, j] -= mat[k, j] * f;
/* filling lower triangular matrix with
* zeros*/
mat[i, k] = 0;
}
}
// print(mat); //for matrix state
}
// print(mat); //for matrix state
return -1;
}
// Function to calculate the values of the unknowns
static void backSub(double [,]mat)
{
// An array to store solution
double []x = new double[N];
/* Start calculating from last equation up to the
first */
for(int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
/* start with the RHS of the equation */
x[i] = mat[i,N];
/* Initialize j to i+1 since matrix is upper
triangular*/
for(int j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
/* subtract all the lhs values
* except the coefficient of the variable
* whose value is being calculated */
x[i] -= mat[i,j] * x[j];
}
/* divide the RHS by the coefficient of the
unknown being calculated */
x[i] = x[i] / mat[i,i];
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Solution for the system:");
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Console.Write("{0:F6}", x[i]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* input matrix */
double [,]mat = { { 3.0, 2.0, -4.0, 3.0 },
{ 2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 15.0 },
{ 5.0, -3, 1.0, 14.0 } };
gaussianElimination(mat);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
PHP
<?php
// PHP program to demonstrate working
// of Gaussian Elimination method
$N = 3; // Number of unknowns
// function to get matrix content
function gaussianElimination($mat)
{
global $N;
/* reduction into r.e.f. */
$singular_flag = forwardElim($mat);
/* if matrix is singular */
if ($singular_flag != -1)
{
print("Singular Matrix.\n");
/* if the RHS of equation corresponding to
zero row is 0, * system has infinitely
many solutions, else inconsistent*/
if ($mat[$singular_flag][$N])
print("Inconsistent System.");
else
print("May have infinitely many solutions.");
return;
}
/* get solution to system and print it using
backward substitution */
backSub($mat);
}
// function for elementary operation
// of swapping two rows
function swap_row(&$mat, $i, $j)
{
global $N;
//printf("Swapped rows %d and %d\n", i, j);
for ($k = 0; $k <= $N; $k++)
{
$temp = $mat[$i][$k];
$mat[$i][$k] = $mat[$j][$k];
$mat[$j][$k] = $temp;
}
}
// function to print matrix content at any stage
function print1($mat)
{
global $N;
for ($i=0; $i<$N; $i++, print("\n"))
for ($j=0; $j<=$N; $j++)
print($mat[$i][$j]);
print("\n");
}
// function to reduce matrix to r.e.f.
function forwardElim(&$mat)
{
global $N;
for ($k=0; $k<$N; $k++)
{
// Initialize maximum value and index for pivot
$i_max = $k;
$v_max = $mat[$i_max][$k];
/* find greater amplitude for pivot if any */
for ($i = $k+1; $i < $N; $i++)
if (abs($mat[$i][$k]) > $v_max)
{
$v_max = $mat[$i][$k];
$i_max = $i;
}
/* if a principal diagonal element is zero,
* it denotes that matrix is singular, and
* will lead to a division-by-zero later. */
if (!$mat[$k][$i_max])
return $k; // Matrix is singular
/* Swap the greatest value row with current row */
if ($i_max != $k)
swap_row($mat, $k, $i_max);
for ($i = $k + 1; $i < $N; $i++)
{
/* factor f to set current row kth element to 0,
* and subsequently remaining kth column to 0 */
$f = $mat[$i][$k]/$mat[$k][$k];
/* subtract fth multiple of corresponding kth
row element*/
for ($j = $k + 1; $j <= $N; $j++)
$mat[$i][$j] -= $mat[$k][$j] * $f;
/* filling lower triangular matrix with zeros*/
$mat[$i][$k] = 0;
}
//print(mat); //for matrix state
}
//print(mat); //for matrix state
return -1;
}
// function to calculate the values of the unknowns
function backSub(&$mat)
{
global $N;
$x = array_fill(0, $N, 0); // An array to store solution
/* Start calculating from last equation up to the
first */
for ($i = $N - 1; $i >= 0; $i--)
{
/* start with the RHS of the equation */
$x[$i] = $mat[$i][$N];
/* Initialize j to i+1 since matrix is upper
triangular*/
for ($j = $i + 1; $j < $N; $j++)
{
/* subtract all the lhs values
* except the coefficient of the variable
* whose value is being calculated */
$x[$i] -= $mat[$i][$j] * $x[$j];
}
/* divide the RHS by the coefficient of the
unknown being calculated */
$x[$i] = $x[$i] / $mat[$i][$i];
}
print("\nSolution for the system:\n");
for ($i = 0; $i < $N; $i++)
print(number_format(strval($x[$i]), 6)."\n");
}
// Driver program
/* input matrix */
$mat = array(array(3.0, 2.0,-4.0, 3.0),
array(2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 15.0),
array(5.0, -3, 1.0, 14.0));
gaussianElimination($mat);
// This code is contributed by mits
?>
Javascript
// JavaScript program to demonstrate working of Gaussian Elimination
// method
let N = 3;
// function to get matrix content
function gaussianElimination(mat)
{
/* reduction into r.e.f. */
let singular_flag = forwardElim(mat);
/* if matrix is singular */
if (singular_flag != -1)
{
console.log("Singular Matrix.");
/* if the RHS of equation corresponding to
zero row is 0, * system has infinitely
many solutions, else inconsistent*/
if (mat[singular_flag][N])
console.log("Inconsistent System.");
else
console.log("May have infinitely many solutions.");
return;
}
/* get solution to system and print it using
backward substitution */
backSub(mat);
}
// function for elementary operation of swapping two rows
function swap_row(mat, i, j)
{
//printf("Swapped rows %d and %d\n", i, j);
for (var k=0; k<=N; k++)
{
let temp = mat[i][k];
mat[i][k] = mat[j][k];
mat[j][k] = temp;
}
}
// function to print matrix content at any stage
function print(mat)
{
for (var i=0; i<N; i++, console.log(""))
for (var j=0; j<=N; j++)
process.stdout.write("" + mat[i][j]);
console.log("");
}
// function to reduce matrix to r.e.f.
function forwardElim(mat)
{
for (var k=0; k<N; k++)
{
// Initialize maximum value and index for pivot
var i_max = k;
var v_max = mat[i_max][k];
/* find greater amplitude for pivot if any */
for (var i = k+1; i < N; i++)
if (Math.abs(mat[i][k]) > v_max)
v_max = mat[i][k], i_max = i;
/* if a principal diagonal element is zero,
* it denotes that matrix is singular, and
* will lead to a division-by-zero later. */
if (!mat[k][i_max])
return k; // Matrix is singular
/* Swap the greatest value row with current row */
if (i_max != k)
swap_row(mat, k, i_max);
for (var i=k+1; i<N; i++)
{
/* factor f to set current row kth element to 0,
* and subsequently remaining kth column to 0 */
let f = mat[i][k]/mat[k][k];
/* subtract fth multiple of corresponding kth
row element*/
for (var j=k+1; j<=N; j++)
mat[i][j] -= mat[k][j]*f;
/* filling lower triangular matrix with zeros*/
mat[i][k] = 0;
}
//print(mat); //for matrix state
}
//print(mat); //for matrix state
return -1;
}
// function to calculate the values of the unknowns
function backSub(mat)
{
let x = new Array(N); // An array to store solution
/* Start calculating from last equation up to the
first */
for (var i = N-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
/* start with the RHS of the equation */
x[i] = mat[i][N];
/* Initialize j to i+1 since matrix is upper
triangular*/
for (var j=i+1; j<N; j++)
{
/* subtract all the lhs values
* except the coefficient of the variable
* whose value is being calculated */
x[i] -= mat[i][j]*x[j];
}
/* divide the RHS by the coefficient of the
unknown being calculated */
x[i] = Math.round(x[i]/mat[i][i]);
}
console.log("\nSolution for the system:");
for (var i=0; i<N; i++)
console.log(x[i].toFixed(8));
}
// Driver program
/* input matrix */
let mat = [[3.0, 2.0,-4.0, 3.0],
[2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 15.0],
[5.0, -3, 1.0, 14.0]];
gaussianElimination(mat);
// This code is contributed by phasing17
Producción:
Solution for the system: 3.000000 1.000000 2.000000
Ilustración:

Complejidad de tiempo: dado que para cada pivote recorremos la parte a su derecha para cada fila debajo de él, O(n)*(O(n)*O(n)) = O(n 3 ).
También podemos aplicar la Eliminación Gaussiana para calcular:
- Rango de una array
- Determinante de una array
- Inversa de una array cuadrada invertible
Este artículo es una contribución de Yash Varyani . Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA