Dada una array de elementos únicos , tenemos que encontrar todas las permutaciones de longitud L usando los elementos de la array. Se permite la repetición de elementos.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr = { 1, 2 }, L=3
Salida:
111
211
121
221
112
212
122
222
Entrada: arr = { 1, 2, 3 }, L=2
Salida:
11
21
31
12
22
32
13
23
33
Acercarse:
- Para formar una secuencia de longitud L con N número de elementos, se sabe que el i-ésimo elemento de la secuencia se puede llenar de N formas. Entonces habrá
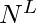 secuencias
secuencias - Ejecutaremos un ciclo de 0 a
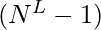 , para cada i convertiremos i de base 10 a base N . Los dígitos del número convertido representarán los índices de la array.
, para cada i convertiremos i de base 10 a base N . Los dígitos del número convertido representarán los índices de la array. - Podemos imprimir todas las
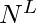 secuencias de esta manera.
secuencias de esta manera.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque:
C++
// C++ implementation
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Convert the number to Lth
// base and print the sequence
void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n,
int arr[],
int len,
int L)
{
// Sequence is of length L
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
// Print the ith element
// of sequence
cout << arr[n % len];
n /= len;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Print all the permuataions
void print(int arr[],
int len,
int L)
{
// There can be (len)^l
// permutations
for (int i = 0; i < (int)pow(len, L); i++) {
// Convert i to len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int L = 2;
// function call
print(arr, len, L);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation for above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Convert the number to Lth
// base and print the sequence
static void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n, int arr[],
int len, int L)
{
// Sequence is of length L
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
// Print the ith element
// of sequence
System.out.print(arr[n % len]);
n /= len;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Print all the permuataions
static void print(int arr[], int len, int L)
{
// There can be (len)^l
// permutations
for (int i = 0;
i < (int)Math.pow(len, L); i++)
{
// Convert i to len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = arr.length;
int L = 2;
// function call
print(arr, len, L);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajit.
Python3
# Python3 implementation for the above approach # Convert the number to Lth # base and print the sequence def convert_To_Len_th_base(n, arr, Len, L): # Sequence is of Length L for i in range(L): # Print the ith element # of sequence print(arr[n % Len], end = "") n //= Len print() # Print all the permuataions def printf(arr, Len, L): # There can be (Len)^l permutations for i in range(pow(Len, L)): # Convert i to Len th base convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, Len, L) # Driver code arr = [1, 2, 3] Len = len(arr) L = 2 # function call printf(arr, Len, L) # This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar
C#
// C# implementation for above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Convert the number to Lth
// base and print the sequence
static void convert_To_Len_th_base(int n, int []arr,
int len, int L)
{
// Sequence is of length L
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
// Print the ith element
// of sequence
Console.Write(arr[n % len]);
n /= len;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Print all the permuataions
static void print(int []arr, int len, int L)
{
// There can be (len)^l
// permutations
for (int i = 0;
i < (int)Math.Pow(len, L); i++)
{
// Convert i to len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
int len = arr.Length;
int L = 2;
// function call
print(arr, len, L);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation
// Convert the number to Lth
// base and print the sequence
function convert_To_Len_th_base( n, arr, len, L)
{
// Sequence is of length L
for ( i = 0; i < L; i++) {
// Print the ith element
// of sequence
document.write(parseInt(arr[n % len]));
n = parseInt(n / len);
}
document.write("<br>");
}
// Print all the permuataions
function print( arr, len, L)
{
// There can be (len)^l
// permutations
for (var i = 0; i < parseInt(Math.pow(len, L)); i++) {
// Convert i to len th base
convert_To_Len_th_base(i, arr, len, L);
}
}
var arr = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
var len = arr.length;
var L = 2;
// function call
print(arr, len, L);
//This code is contributed by SoumikModnal
</script>
11 21 31 12 22 32 13 23 33
Complejidad de tiempo: O(L*len L ), ya que estamos usando un ciclo para recorrer pow(len,L) tiempos y en cada recorrido, estamos llamando a la función convert_To_Len_th_base que costará O(L). Donde L es el número de elementos de la array.
Espacio auxiliar: O(1), ya que no estamos utilizando ningún espacio adicional.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por andrew1234 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA