Dado un número entero N , la tarea es verificar si el límite del cubo de dígitos de un número entero llega a un punto fijo o en un ciclo límite.
Un límite de cubo de dígitos es un número que llega repetidamente a un punto si su valor se calcula como la suma de los cubos de sus dígitos, es decir, tienen las siguientes propiedades:
- Llegar a un punto fijo si es un número de Armstrong .
- Llegar a un ciclo límite si se está repitiendo en un ciclo.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 3
Salida: Alcanzado al punto fijo 153
Explicación:
F(3) = 3 * 3 * 3 = 27
F(27) = 2*2*2 + 7*7*7 = 351
F(351) = 3 *3*3 + 5*5*5 + 1*1*1 = 153
F(153) = 1*1*1 + 5*5*5 + 3*3*3 = 153
Desde un punto fijo(= 153) se obtuvo, que es un número de Armstrong de orden 3. A continuación se muestra la ilustración:
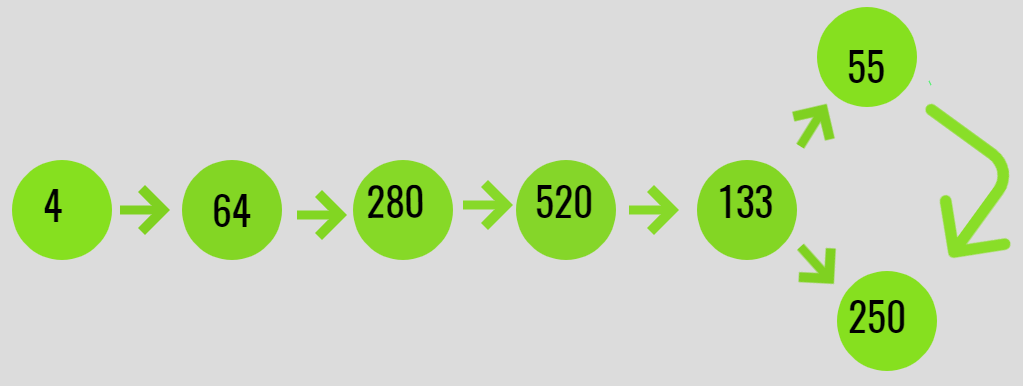
Entrada: N = 4
Salida: Llegó al ciclo
Explicación:
F(4) = 4 * 4 * 4 = 64
F(64) = 6 * 6 * 6 + 4 * 4 * 4 = 280
F(280) = 2 * 2 * 2 + 8 * 8 * 8 + 0 * 0 * 0 = 520
F(520) = 5 * 5 * 5 + 2 * 2 * 2 + 0*0*0 = 133
F(133) = 1*1*1 + 3*3*3 + 3*3*3 = 55
F(55) = 5*5*5 + 5*5*5 = 250
F(250) = 5*5*5 + 2*2*2 + 0 *0*0 = 133
Se obtiene un ciclo entre
133 -> 55 -> 250 -> 133.
A continuación se muestra la ilustración del mismo:
Enfoque: siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Cree un hashMap para almacenar la suma del cubo de dígitos del número durante la iteración.
- Iterar para los siguientes valores para la suma del cubo de dígitos de un número y verificar si la siguiente suma del cubo de dígitos ya está presente en el hashMap o no.
- Si el número ya está en el mapa hash, verifique si el número es un número de Armstrong o no. Si se encuentra que es cierto, entonces el número llega a un punto fijo.
- De lo contrario, si el número no es el número de Armstrong, continúe.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// Define the limit
#define limit 1000000000
using namespace std;
// Function to get the sum of cube
// of digits of a number
long long F(long long N)
{
// Convert to string to get sum
// of the cubes of its digits
string str = to_string(N);
long long sum = 0;
for (long long i = 0;
i < str.size(); i++) {
long long val
= int(str[i] - '0');
sum += val * val * val;
}
// return sum
return sum;
}
// Function to check if the number
// arrives at a fixed point or a cycle
long long findDestination(long long N)
{
// Stores the values obtained
set<long long> s;
long long prev = N, next;
// Insert N to set s
s.insert(N);
while (N <= limit) {
// Get the next number using F(N)
next = F(N);
// Check if the next number is
// repeated or not
auto it = s.find(next);
if (it != s.end()) {
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.insert(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
// Function to check if digit cube
// limit of an integer arrives at
// fixed point or in a limit cycle
void digitCubeLimit(long long N)
{
// N is a non negative integer
if (N < 0)
cout << "N cannot be negative\n";
else {
// Function Call
long long ans
= findDestination(N);
// If the value received is
// greater than limit
if (ans > limit)
cout << "Limit exceeded\n";
// If the value received is
// an Armstrong number
else if (ans == F(ans)) {
cout << N;
cout << " reaches to a"
<< " fixed point: ";
cout << ans;
}
else {
cout << N;
cout << " reaches to a"
<< " limit cycle: ";
cout << ans;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
long long N = 3;
// Function Call
digitCubeLimit(N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the
// above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Define the limit
static final int limit = 1000000000;
// Function to get the sum of cube
// of digits of a number
static int F(int N)
{
// Convert to String to get sum
// of the cubes of its digits
String str = String.valueOf(N);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0;
i < str.length(); i++)
{
int val = (int)(str.charAt(i) - '0');
sum += val * val * val;
}
// return sum
return sum;
}
// Function to check if the number
// arrives at a fixed point or a cycle
static int findDestination(int N)
{
// Stores the values obtained
HashSet<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
int prev = N, next =0;
// Insert N to set s
s.add(N);
while (N <= limit)
{
// Get the next number
// using F(N)
next = F(N);
// Check if the next number is
// repeated or not
if (s.contains(next))
{
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.add(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
// Function to check if digit cube
// limit of an integer arrives at
// fixed point or in a limit cycle
static void digitCubeLimit(int N)
{
// N is a non negative integer
if (N < 0)
System.out.print("N cannot be negative\n");
else
{
// Function Call
int ans = findDestination(N);
// If the value received is
// greater than limit
if (ans > limit)
System.out.print("Limit exceeded\n");
// If the value received is
// an Armstrong number
else if (ans == F(ans))
{
System.out.print(N);
System.out.print(" reaches to a" +
" fixed point: ");
System.out.print(ans);
}
else
{
System.out.print(N);
System.out.print(" reaches to a" +
" limit cycle: ");
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3;
// Function Call
digitCubeLimit(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Define the limit
LIMIT = 1000000000
# Function to get the sum of cube
# of digits of a number
def F(N: int) -> int:
# Convert to string to get sum
# of the cubes of its digits
string = str(N)
sum = 0
for i in range(len(string)):
val = int(ord(string[i]) - ord('0'))
sum += val * val * val
# Return sum
return sum
# Function to check if the number
# arrives at a fixed point or a cycle
def findDestination(N: int) -> int:
# Stores the values obtained
s = set()
prev = N
next = 0
# Insert N to set s
s.add(N)
while (N <= LIMIT):
# Get the next number using F(N)
next = F(N)
# Check if the next number is
# repeated or not
if next in s:
return next
prev = next
s.add(prev)
N = next
return next
# Function to check if digit cube
# limit of an integer arrives at
# fixed point or in a limit cycle
def digitCubeLimit(N: int) -> int:
# N is a non negative integer
if (N < 0):
print("N cannot be negative")
else:
# Function Call
ans = findDestination(N)
# If the value received is
# greater than limit
if (ans > LIMIT):
print("Limit exceeded")
# If the value received is
# an Armstrong number
elif (ans == F(ans)):
print("{} reaches to a fixed point: {}".format(
N, ans))
else:
print("{} reaches to a limit cycle: {}".format(
N, ans))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 3
# Function Call
digitCubeLimit(N)
# This code is contributed by sanjeev2552
C#
// C# program for the
// above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Define the limit
static readonly int limit =
1000000000;
// Function to get the sum
// of cube of digits of a
// number
static int F(int N)
{
// Convert to String to get sum
// of the cubes of its digits
String str = String.Join("", N);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0;
i < str.Length; i++)
{
int val = (int)(str[i] - '0');
sum += val * val * val;
}
// return sum
return sum;
}
// Function to check if the
// number arrives at a fixed
// point or a cycle
static int findDestination(int N)
{
// Stores the values
// obtained
HashSet<int> s =
new HashSet<int>();
int prev = N, next = 0;
// Insert N to set s
s.Add(N);
while (N <= limit)
{
// Get the next number
// using F(N)
next = F(N);
// Check if the next
// number is repeated
// or not
if (s.Contains(next))
{
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.Add(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
// Function to check if digit cube
// limit of an integer arrives at
// fixed point or in a limit cycle
static void digitCubeLimit(int N)
{
// N is a non negative integer
if (N < 0)
Console.Write("N cannot be negative\n");
else
{
// Function Call
int ans = findDestination(N);
// If the value received is
// greater than limit
if (ans > limit)
Console.Write("Limit exceeded\n");
// If the value received is
// an Armstrong number
else if (ans == F(ans))
{
Console.Write(N);
Console.Write(" reaches to a" +
" fixed point: ");
Console.Write(ans);
}
else
{
Console.Write(N);
Console.Write(" reaches to a" +
" limit cycle: ");
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3;
// Function Call
digitCubeLimit(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the
// above approach
// Define the limit
let limit = 1000000000;
// Function to get the sum of cube
// of digits of a number
function F(N)
{
// Convert to String to get sum
// of the cubes of its digits
let str = (N).toString();
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0;
i < str.length; i++)
{
let val = (str[i].charCodeAt(0) - '0'.charCodeAt(0));
sum += val * val * val;
}
// return sum
return sum;
}
// Function to check if the number
// arrives at a fixed point or a cycle
function findDestination(N)
{
// Stores the values obtained
let s = new Set();
let prev = N, next =0;
// Insert N to set s
s.add(N);
while (N <= limit)
{
// Get the next number
// using F(N)
next = F(N);
// Check if the next number is
// repeated or not
if (s.has(next))
{
return next;
}
prev = next;
s.add(prev);
N = next;
}
return next;
}
// Function to check if digit cube
// limit of an integer arrives at
// fixed point or in a limit cycle
function digitCubeLimit(N)
{
// N is a non negative integer
if (N < 0)
document.write("N cannot be negative\n");
else
{
// Function Call
let ans = findDestination(N);
// If the value received is
// greater than limit
if (ans > limit)
document.write("Limit exceeded\n");
// If the value received is
// an Armstrong number
else if (ans == F(ans))
{
document.write(N);
document.write(" reaches to a" +
" fixed point: ");
document.write(ans);
}
else
{
document.write(N);
document.write(" reaches to a" +
" limit cycle: ");
document.write(ans);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
let N = 3;
// Function Call
digitCubeLimit(N);
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
3 reaches to a fixed point: 153
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shuklarishabh356 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA