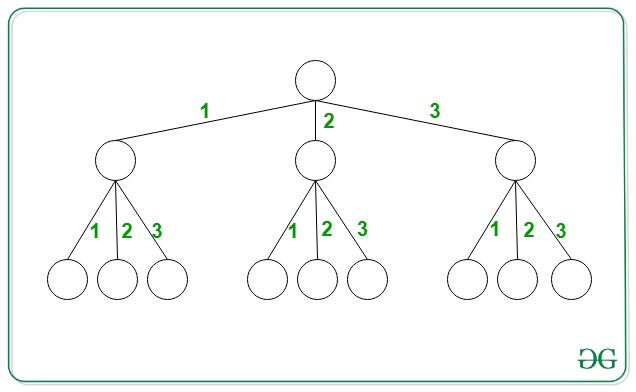
Dado un número entero X y un número entero N , la tarea es encontrar el número de rutas únicas que comienzan desde la raíz en un árbol N-ario tal que la suma de todas estas rutas sea igual a X. El árbol N -ario satisface las siguientes condiciones:
- Todos los Nodes tienen N hijos y el peso de cada borde es distinto y se encuentra en el rango [1, N] .
- El árbol se extiende hasta el infinito.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 3, X = 2
Salida: 2
Explicación: los dos caminos que tienen una suma de caminos igual a 2 son {1, 1} y {2}.Entrada: N = 3, X = 6
Salida: 24
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque más simple es encontrar recursivamente todas las formas posibles de obtener una suma de ruta igual a X e imprimir el conteo obtenido.
Complejidad temporal: O(N * X)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Enfoque Eficiente: Para optimizar el enfoque anterior, la idea es utilizar Programación Dinámica . Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice una array dp[] que, para cada i -ésimo índice, almacene el recuento de rutas que se suman a i .
- Para cada vértice, itere desde strong>1 hasta min(X, N), es decir, todos los valores posibles de sus hijos y encuentre el número de caminos posibles con la suma dada de cada Node considerado.
- Agregue todos los caminos hechos usando los bordes 1 a N y verifique si el conteo ya se calculó o no. Si ya se calculó, devuelve el valor. De lo contrario, cuente recursivamente el número de rutas con una suma igual al valor actual considerando todas las formas posibles de extender el árbol desde el vértice actual.
- Actualice la array dp[] y devuelva el recuento obtenido.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
// Function for counting total
// no of paths possible with
// the sum is equal to X
ll findTotalPath(int X, int n,
vector<int>& dp)
{
// If the path of the sum
// from the root to current
// node is stored in sum
if (X == 0) {
return 1;
}
ll ans = 0;
// If already computed
if (dp[X] != -1) {
return dp[X];
}
// Count different no of paths
// using all possible ways
for (int i = 1; i <= min(X, n); ++i) {
ans += findTotalPath(
X - i, n, dp)
% mod;
ans %= mod;
}
// Return total no of paths
return dp[X] = ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
// Stores the number of ways
// to obtains sums 0 to X
vector<int> dp(X + 1, -1);
// Function call
cout << findTotalPath(X, n, dp);
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
// Function for counting total
// no of paths possible with
// the sum is equal to X
static int findTotalPath(int X, int n,
ArrayList<Integer> dp)
{
// If the path of the sum
// from the root to current
// node is stored in sum
if (X == 0)
{
return 1;
}
int ans = 0;
// If already computed
if (dp.get(X) != -1)
{
return dp.get(X);
}
// Count different no of paths
// using all possible ways
for(int i = 1; i <= Math.min(X, n); ++i)
{
ans += findTotalPath(X - i, n, dp) % mod;
ans %= mod;
}
// Return total no of paths
dp.set(X, ans);
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
// Stores the number of ways
// to obtains sums 0 to X
ArrayList<Integer> dp = new ArrayList<Integer>(
Collections.nCopies(X + 1, -1));
// Function call
System.out.print(findTotalPath(X, n, dp));
}
}
// This code is contributed by akhilsaini
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach mod = int(1e9 + 7) # Function for counting total # no of paths possible with # the sum is equal to X def findTotalPath(X, n, dp): # If the path of the sum # from the root to current # node is stored in sum if (X == 0): return 1 ans = 0 # If already computed if (dp[X] != -1): return dp[X] # Count different no of paths # using all possible ways for i in range(1, min(X, n) + 1): ans = ans + findTotalPath(X - i, n, dp) % mod; ans %= mod; # Return total no of paths dp[X] = ans return ans # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': n = 3 X = 2 # Stores the number of ways # to obtains sums 0 to X dp = [-1] * (X + 1) # Function call print(findTotalPath(X, n, dp)) # This code is contributed by akhilsaini
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
// Function for counting total
// no of paths possible with
// the sum is equal to X
static int findTotalPath(int X, int n, int[] dp)
{
// If the path of the sum
// from the root to current
// node is stored in sum
if (X == 0)
{
return 1;
}
int ans = 0;
// If already computed
if (dp[X] != -1)
{
return dp[X];
}
// Count different no of paths
// using all possible ways
for(int i = 1; i <= Math.Min(X, n); ++i)
{
ans += findTotalPath(X - i, n, dp) % mod;
ans %= mod;
}
// Return total no of paths
dp[X] = ans;
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
// Stores the number of ways
// to obtains sums 0 to X
int[] dp = new int[X + 1];
Array.Fill(dp, -1);
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(findTotalPath(X, n, dp));
}
}
// This code is contributed by akhilsaini
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
var mod = 1000000007;
// Function for counting total
// no of paths possible with
// the sum is equal to X
function findTotalPath(X, n, dp)
{
// If the path of the sum
// from the root to current
// node is stored in sum
if (X == 0) {
return 1;
}
var ans = 0;
// If already computed
if (dp[X] != -1) {
return dp[X];
}
// Count different no of paths
// using all possible ways
for (var i = 1; i <= Math.min(X, n); ++i) {
ans += findTotalPath(
X - i, n, dp)
% mod;
ans %= mod;
}
// Return total no of paths
return dp[X] = ans;
}
// Driver Code
var n = 3, X = 2;
// Stores the number of ways
// to obtains sums 0 to X
var dp = Array(X + 1).fill(-1);
// Function call
document.write( findTotalPath(X, n, dp));
</script>
2
Complejidad temporal: O(min (N, X))
Espacio auxiliar: O(X)