Dada una array arr[] que consta de N enteros, la tarea es encontrar el número de pares tal que el GCD de cualquier par de elementos de la array sea el elemento mínimo de ese par.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[ ] = {2, 3, 1, 2}
Salida: 4
Explicación:
A continuación se muestran todos los pares posibles de la array dada:
- (0, 1): El MCD del par formado por el elemento en los índices 0 y 2 es mcd(2, 1) = 1, que es igual a su valor mínimo del par {2, 1}.
- (0, 3): El MCD del par formado por el elemento en los índices 0 y 3 es mcd(2, 2) = 2, que es igual a su valor mínimo del par {2, 2}.
- (1, 2): El MCD del par formado tomando elementos en los índices 1 y 2 es mcd(3, 1) = 1, que es igual a su valor mínimo del par {3, 1}.
- (2, 3): El MCD del par formado tomando elementos en los índices 2 y 3 es mcd(1, 2) = 1, que es igual a su valor mínimo del par {1, 2}.
Por lo tanto, hay un total de 4 pares posibles cuyo MCD es igual a su elemento mínimo del par.
Entrada: arr[] = {4, 6}
Salida: 0
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque más simple para resolver el problema dado es generar todos los pares posibles a partir de la array dada y, si existe algún par cuyo GCD sea igual a los elementos mínimos de ese par, cuente ese par. Después de verificar todos los pares, imprima el valor de conteo obtenido como resultado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
int countPairs(int arr[], int N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
int count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N - 2]
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
// Iterate over the range [i + 1, N]
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
// If arr[i] % arr[j] is 0
// or arr[j] % arr[i] is 0
if (arr[i] % arr[j] == 0
|| arr[j] % arr[i] == 0) {
// Increment count by 1
count++;
}
}
}
// Return the resultant count
return count;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 1, 2 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << countPairs(arr, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
static int countPairs(int arr[], int N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
int count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N - 2]
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
// Iterate over the range [i + 1, N]
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
// If arr[i] % arr[j] is 0
// or arr[j] % arr[i] is 0
if (arr[i] % arr[j] == 0
|| arr[j] % arr[i] == 0) {
// Increment count by 1
count++;
}
}
}
// Return the resultant count
return count;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 1, 2 };
int N = arr.length;
System.out.print(countPairs(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash.
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to count pairs from an # array having GCD equal to # minimum element of that pair def countPairs(arr, N): # Stores the resultant count count = 0 # Iterate over the range [0, N - 2] for i in range(N - 1): # Iterate over the range [i + 1, N] for j in range(i + 1, N): # If arr[i] % arr[j] is 0 # or arr[j] % arr[i] is 0 if (arr[i] % arr[j] == 0 or arr[j] % arr[i] == 0): # Increment count by 1 count += 1 # Return the resultant count return count # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [2, 3, 1, 2] N = len(arr) print (countPairs(arr, N)) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG {
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
static int countPairs(int[] arr, int N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
int count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N - 2]
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
// Iterate over the range [i + 1, N]
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
// If arr[i] % arr[j] is 0
// or arr[j] % arr[i] is 0
if (arr[i] % arr[j] == 0
|| arr[j] % arr[i] == 0) {
// Increment count by 1
count++;
}
}
}
// Return the resultant count
return count;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 1, 2 };
int N = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(countPairs(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the above approach
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
function countPairs(arr, N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
let count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N - 2]
for (let i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
// Iterate over the range [i + 1, N]
for (let j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
// If arr[i] % arr[j] is 0
// or arr[j] % arr[i] is 0
if (arr[i] % arr[j] == 0
|| arr[j] % arr[i] == 0) {
// Increment count by 1
count++;
}
}
}
// Return the resultant count
return count;
}
// Driver Code
let arr = [ 2, 3, 1, 2 ];
let N = arr.length;
document.write(countPairs(arr, N));
</script>
4
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(N 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Enfoque eficiente: el enfoque anterior se puede optimizar en función de las siguientes observaciones:
- El elemento mínimo del par debe dividir al elemento máximo del par, y se puede observar que el elemento 1 puede formar un total de (N – 1) pares .
- Cada elemento puede formar un
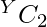 par consigo mismo, donde Y es el recuento de un elemento de array .
par consigo mismo, donde Y es el recuento de un elemento de array . - La idea es atravesar los divisores de cada elemento del arreglo e incrementar el conteo de pares que se pueden formar por las frecuencias de los divisores.
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice una variable, digamos res , que almacene el conteo resultante.
- Inicialice un mapa , digamos mp , que almacene el conteo de cada elemento de la array.
- Recorra la array arr[] e incremente el conteo de arr[i] en mp .
- Iterar sobre los pares de map mp y realizar las siguientes operaciones:
- Almacene el valor del elemento de array en una variable, por ejemplo, X y la frecuencia de ese número en una variable Y.
- Si el valor de X es 1 , aumente el valor de res en (N – 1) y continúe .
- Incremente el valor de res por (Y*(Y – 1))/2 .
- Ahora, trato sobre los divisores del entero X usando una variable j e incremento la res por mp[j] .
- Después de completar los pasos anteriores, imprima el valor de res como el recuento total obtenido.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
int CountPairs(int arr[], int N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
int res = 0;
// Stores the frequency of
// each array element
map<int, int> mp;
// Traverse the array arr[]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
mp[arr[i]]++;
}
// Iterate over the Map mp
for (auto p : mp) {
// Stores the array element
int x = p.first;
// Stores the count
// of array element x
int y = p.second;
// If x is 1
if (x == 1) {
// Increment res by N-1
res += N - 1;
continue;
}
// Increment res by yC2
res += (y * (y - 1)) / 2;
// Iterate over the
// range [2, sqrt(x)]
for (int j = 2;
j <= sqrt(x); j++) {
// If x is divisible by j
if (x % j == 0) {
// Increment the value
// of res by mp[j]
res += mp[j];
// If j is not equal to x/j
if (j != x / j)
// Increment res
// by mp[x/j]
res += mp[x / j];
}
}
}
// Return the resultant count
return res;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 1, 2 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << CountPairs(arr, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
static int CountPairs(int arr[], int N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
int res = 0;
// Stores the frequency of
// each array element
Map<Integer, Integer> mp = new HashMap<>();
// Traverse the array arr[]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Integer c = mp.get(arr[i]);
mp.put(arr[i], (c == null) ? 1 : c + 1);
}
// Iterate over the Map mp
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> itr = mp.entrySet().iterator();
while(itr.hasNext())
{
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = itr.next();
// Stores the array element
int x = (int)entry.getKey();
// Stores the count
// of array element x
int y = (int)entry.getValue();
// If x is 1
if (x == 1) {
// Increment res by N-1
res += N - 1;
continue;
}
// Increment res by yC2
res += (y * (y - 1)) / 2;
// Iterate over the
// range [2, sqrt(x)]
for (int j = 2; j <= Math.sqrt(x); j++) {
// If x is divisible by j
if (x % j == 0) {
// Increment the value
// of res by mp[j]
res += mp.get(j);
// If j is not equal to x/j
if (j != x / j)
// Increment res
// by mp[x/j]
res += mp.get((int)x / j);
}
}
}
// Return the resultant count
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 1, 2 };
int N = arr.length;
System.out.println(CountPairs(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
from math import sqrt
# Function to count pairs from an
# array having GCD equal to
# minimum element of that pair
def CountPairs(arr, N):
# Stores the resultant count
res = 0
# Stores the frequency of
# each array element
mp = {}
# Traverse the array arr[]
for i in range(N):
if (arr[i] in mp):
mp[arr[i]] += 1
else:
mp[arr[i]] = 1
# Iterate over the Map mp
for key, value in mp.items():
# Stores the array element
x = key
# Stores the count
# of array element x
y = value
# If x is 1
if (x == 1):
# Increment res by N-1
res += N - 1
continue
# Increment res by yC2
res += (y * (y - 1)) // 2
# Iterate over the
# range [2, sqrt(x)]
for j in range(2, int(sqrt(x)) + 1, 1):
# If x is divisible by j
if (x % j == 0):
# Increment the value
# of res by mp[j]
res += mp[j]
# If j is not equal to x/j
if (j != x // j):
# Increment res
# by mp[x/j]
res += mp[x // j]
# Return the resultant count
return res
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [ 2, 3, 1, 2 ]
N = len(arr)
print(CountPairs(arr, N))
# This code is contributed by SURENDRA_GANGWAR
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
static int CountPairs(int []arr, int N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
int res = 0;
// Stores the frequency of
// each array element
Dictionary<int,
int> mp = new Dictionary<int,
int>();
// Traverse the array arr[]
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (mp.ContainsKey(arr[i]))
mp[arr[i]]++;
else
mp.Add(arr[i], 1);
}
// Iterate over the Map mp
foreach(KeyValuePair<int, int> kvp in mp)
{
// Stores the array element
int x = kvp.Key;
// Stores the count
// of array element x
int y = kvp.Value;
// If x is 1
if (x == 1)
{
// Increment res by N-1
res += N - 1;
continue;
}
// Increment res by yC2
res += (y * (y - 1)) / 2;
// Iterate over the
// range [2, sqrt(x)]
for(int j = 2;
j <= Math.Sqrt(x); j++)
{
// If x is divisible by j
if (x % j == 0)
{
// Increment the value
// of res by mp[j]
res += mp[j];
// If j is not equal to x/j
if (j != x / j)
// Increment res
// by mp[x/j]
res += mp[x / j];
}
}
}
// Return the resultant count
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = { 2, 3, 1, 2 };
int N = arr.Length;
Console.Write(CountPairs(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by bgangwar59
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Function to count pairs from an
// array having GCD equal to
// minimum element of that pair
function CountPairs(arr, N)
{
// Stores the resultant count
var res = 0;
// Stores the frequency of
// each array element
var mp = new Map();
// Traverse the array arr[]
for (var i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if(mp.has(arr[i]))
{
mp.set(arr[i], mp.get(arr[i])+1);
}
else{
mp.set(arr[i], 1);
}
}
// Iterate over the Map mp
mp.forEach((value, key) => {
// Stores the array element
var x = key;
// Stores the count
// of array element x
var y = value;
// If x is 1
if (x == 1) {
// Increment res by N-1
res += N - 1;
}
// Increment res by yC2
res += parseInt((y * (y - 1)) / 2);
// Iterate over the
// range [2, sqrt(x)]
for (var j = 2;
j <= parseInt(Math.sqrt(x)); j++) {
// If x is divisible by j
if (x % j == 0) {
// Increment the value
// of res by mp[j]
res += mp.get(j);
// If j is not equal to x/j
if (j != parseInt(x / j))
// Increment res
// by mp[x/j]
res += mp.get(parseInt(x / j));
}
}
});
// Return the resultant count
return res;
}
// Driver Code
var arr = [2, 3, 1, 2 ];
var N = arr.length;
document.write( CountPairs(arr, N));
</script>
4
Complejidad temporal: O(N*√M), donde M es el elemento máximo del arreglo .
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por santhoshcharan y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA