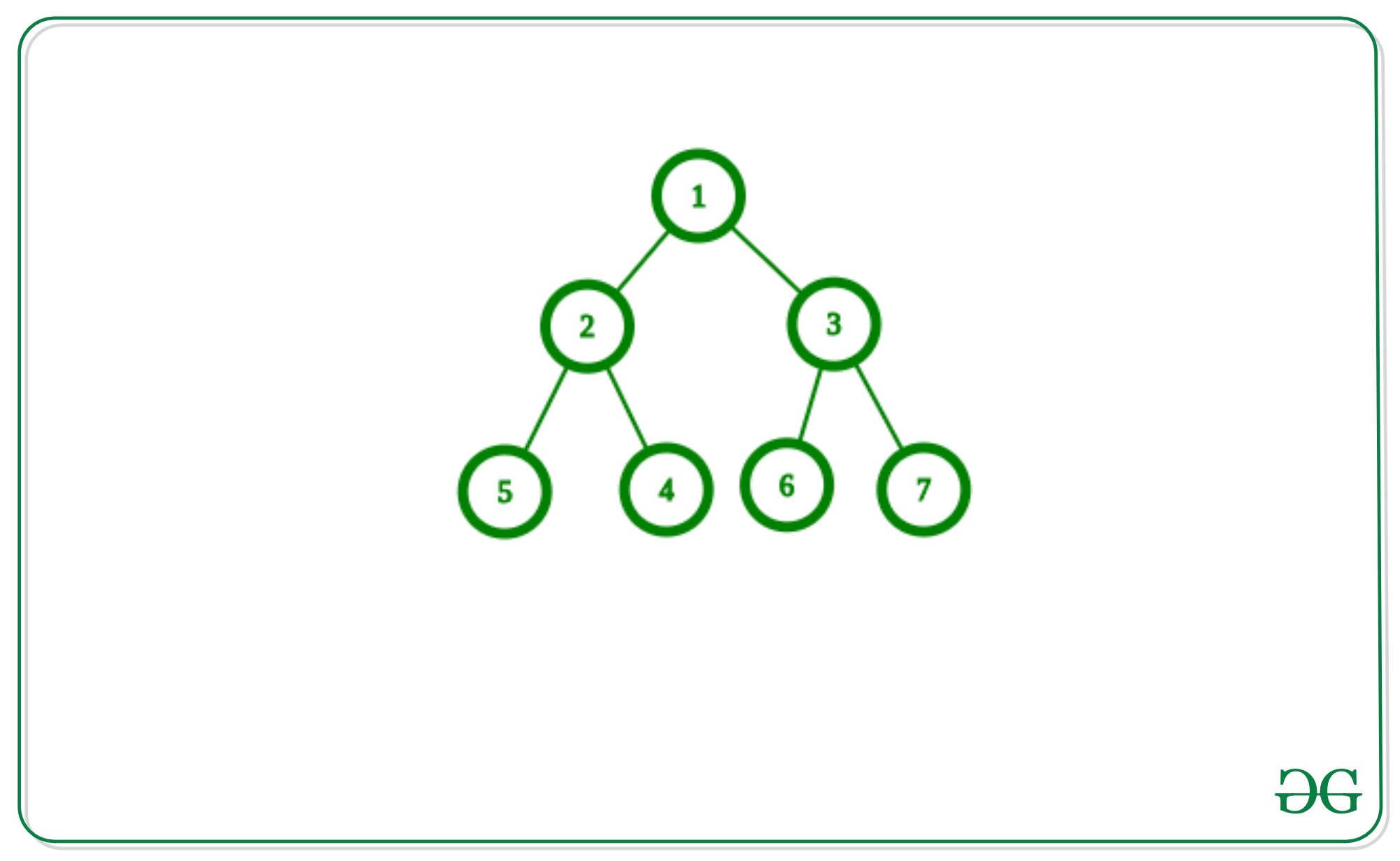
Dado un árbol , la tarea es encontrar el Node más lejano de cada Node a otro Node en este árbol.
Ejemplo:
Entrada: Lista de adyacencia dada del siguiente árbol:
Salida:
Node más lejano del Node 1: 6
Node más lejano del Node 2: 6 Node más lejano del Node
3: 6
Node más lejano del Node 4: 6
Node más lejano del Node 5: 1
Node más lejano del Node 6: 1Aporte:
Salida:
Node más lejano del Node 1: 4
Node más lejano del Node 2: 7
Node más lejano del Node 3: 4
Node más lejano del Node 4: 7
Node más lejano del Node 5: 7
Node más lejano del Node 6: 4
Node más lejano del Node 7: 4
Enfoque:
Primero, tenemos que encontrar dos vértices extremos del diámetro y para encontrar eso, elegiremos un vértice arbitrario y encontraremos el Node más alejado de este vértice arbitrario y este Node será un extremo del diámetro y luego lo convertiremos en raíz. encuentre el Node más alejado de él, que será el otro extremo del diámetro. Ahora, para cada Node, el Node más lejano será uno de estos dos vértices finales del diámetro del árbol.
¿Por qué funciona?
Sean x e y los dos vértices extremos del diámetro del árbol y un vértice aleatorio es u. Deje que el vértice más alejado de u sea v, no x o y. Como v es el más alejado de u, entonces se formará un nuevo diámetro con vértices extremos como x, v o y, v que tiene mayor longitud pero un árbol tiene una longitud única del diámetro, por lo que no es posible y el vértice más alejado de u debe ser x o y.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// farthest node from each vertex
// of the tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 10000
// Adjacency list to store edges
vector<int> adj[N];
int lvl[N], dist1[N], dist2[N];
// Add edge between
// U and V in tree
void AddEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Edge from U to V
adj[u].push_back(v);
// Edge from V to U
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
int end1, end2, maxi;
// DFS to find the first
// End Node of diameter
void findFirstEnd(int u, int p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi) {
maxi = lvl[u];
end1 = u;
}
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u][i] != p) {
findFirstEnd(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to clear the levels
// of the nodes
void clear(int n)
{
// set all value of lvl[]
// to 0 for next dfs
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
lvl[i] = 0;
}
// Set maximum with 0
maxi = 0;
dist1[0] = dist2[0] = -1;
}
// DFS will calculate second
// end of the diameter
void findSecondEnd(int u, int p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi) {
maxi = lvl[u];
// Store the node with
// maximum depth from end1
end2 = u;
}
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u][i] != p) {
findSecondEnd(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of the farthest distant node
void findDistancefromFirst(int u, int p)
{
// Storing distance from
// end1 to node u
dist1[u] = 1 + dist1[p];
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
if (adj[u][i] != p) {
findDistancefromFirst(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of nodes from second end of diameter
void findDistancefromSecond(int u, int p)
{
// storing distance from end2 to node u
dist2[u] = 1 + dist2[p];
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
if (adj[u][i] != p) {
findDistancefromSecond(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
void findNodes(){
int n = 5;
// Joining Edge between two
// nodes of the tree
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(1, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 5);
// Find the one end of
// the diameter of tree
findFirstEnd(1, 0);
clear(n);
// Find the other end
// of the diameter of tree
findSecondEnd(end1, 0);
// Find the distance
// to each node from end1
findDistancefromFirst(end1, 0);
// Find the distance to
// each node from end2
findDistancefromSecond(end2, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x = dist1[i];
int y = dist2[i];
// Comparing distance between
// the two ends of diameter
if (x >= y) {
cout << end1 << ' ';
}
else {
cout << end2 << ' ';
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Function Call
findNodes();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find the
// farthest node from each vertex
// of the tree
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int N = 10000;
// Adjacency list to store edges
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector<Integer>[] adj = new Vector[N];
static int[] lvl = new int[N],
dist1 = new int[N],
dist2 = new int[N];
// Add edge between
// U and V in tree
static void AddEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Edge from U to V
adj[u].add(v);
// Edge from V to U
adj[v].add(u);
}
static int end1, end2, maxi;
// DFS to find the first
// End Node of diameter
static void findFirstEnd(int u, int p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi)
{
maxi = lvl[u];
end1 = u;
}
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++)
{
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u].elementAt(i) != p)
{
findFirstEnd(adj[u].elementAt(i), u);
}
}
}
// Function to clear the levels
// of the nodes
static void clear(int n)
{
// Set all value of lvl[]
// to 0 for next dfs
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
lvl[i] = 0;
}
// Set maximum with 0
maxi = 0;
dist1[0] = dist2[0] = -1;
}
// DFS will calculate second
// end of the diameter
static void findSecondEnd(int u, int p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi)
{
maxi = lvl[u];
// Store the node with
// maximum depth from end1
end2 = u;
}
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++)
{
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u].elementAt(i) != p)
{
findSecondEnd(adj[u].elementAt(i), u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of the farthest distant node
static void findDistancefromFirst(int u, int p)
{
// Storing distance from
// end1 to node u
dist1[u] = 1 + dist1[p];
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++)
{
if (adj[u].elementAt(i) != p)
{
findDistancefromFirst(
adj[u].elementAt(i), u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of nodes from second end of diameter
static void findDistancefromSecond(int u, int p)
{
// Storing distance from end2 to node u
dist2[u] = 1 + dist2[p];
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++)
{
if (adj[u].elementAt(i) != p)
{
findDistancefromSecond(
adj[u].elementAt(i), u);
}
}
}
static void findNodes()
{
int n = 5;
// Joining Edge between two
// nodes of the tree
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(1, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 5);
// Find the one end of
// the diameter of tree
findFirstEnd(1, 0);
clear(n);
// Find the other end
// of the diameter of tree
findSecondEnd(end1, 0);
// Find the distance
// to each node from end1
findDistancefromFirst(end1, 0);
// Find the distance to
// each node from end2
findDistancefromSecond(end2, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = dist1[i];
int y = dist2[i];
// Comparing distance between
// the two ends of diameter
if (x >= y)
{
System.out.print(end1 + " ");
}
else
{
System.out.print(end2 + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
adj[i] = new Vector<>();
}
// Function call
findNodes();
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552
Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the # farthest node from each vertex # of the tree # Add edge between # U and V in tree def AddEdge(u, v): global adj # Edge from U to V adj[u].append(v) # Edge from V to U adj[v].append(u) # DFS to find the first # End Node of diameter def findFirstEnd(u, p): global lvl, adj, end1, maxi # Calculating level of nodes lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p] if (lvl[u] > maxi): maxi = lvl[u] end1 = u for i in range(len(adj[u])): # Go in opposite # direction of parent if (adj[u][i] != p): findFirstEnd(adj[u][i], u) # Function to clear the levels # of the nodes def clear(n): global lvl, dist1, dist2 # Set all value of lvl[] # to 0 for next dfs for i in range(n + 1): lvl[i] = 0 # Set maximum with 0 maxi = 0 dist1[0] = dist2[0] = -1 # DFS will calculate second # end of the diameter def findSecondEnd(u, p): global lvl, adj, maxi, end2 # Calculating level of nodes lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p] if (lvl[u] > maxi): maxi = lvl[u] # Store the node with # maximum depth from end1 end2 = u for i in range(len(adj[u])): # Go in opposite # direction of parent if (adj[u][i] != p): findSecondEnd(adj[u][i], u) # Function to find the distance # of the farthest distant node def findDistancefromFirst(u, p): global dist1, adj # Storing distance from # end1 to node u dist1[u] = 1 + dist1[p] for i in range(len(adj[u])): if (adj[u][i] != p): findDistancefromFirst(adj[u][i], u) # Function to find the distance # of nodes from second end of diameter def findDistancefromSecond(u, p): global dist2, adj # Storing distance from end2 to node u dist2[u] = 1 + dist2[p] for i in range(len(adj[u])): if (adj[u][i] != p): findDistancefromSecond(adj[u][i], u) def findNodes(): global adj, lvl, dist1, dist2, end1, end2, maxi n = 5 # Joining Edge between two # nodes of the tree AddEdge(1, 2) AddEdge(1, 3) AddEdge(3, 4) AddEdge(3, 5) # Find the one end of # the diameter of tree findFirstEnd(1, 0) clear(n) # Find the other end # of the diameter of tree findSecondEnd(end1, 0) # Find the distance # to each node from end1 findDistancefromFirst(end1, 0) # Find the distance to # each node from end2 findDistancefromSecond(end2, 0) for i in range(1, n + 1): x = dist1[i] y = dist2[i] # Comparing distance between # the two ends of diameter if (x >= y): print(end1, end = " ") else: print(end2, end = " ") # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': adj = [[] for i in range(10000)] lvl = [0 for i in range(10000)] dist1 = [-1 for i in range(10000)] dist2 = [-1 for i in range(10000)] end1, end2, maxi = 0, 0, 0 # Function Call findNodes() # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# implementation to find the
// farthest node from each vertex
// of the tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int N = 10000;
// Adjacency list to store edges
static List<int>[] adj = new List<int>[N];
static int[] lvl = new int[N],
dist1 = new int[N],
dist2 = new int[N];
// Add edge between
// U and V in tree
static void AddEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Edge from U to V
adj[u].Add(v);
// Edge from V to U
adj[v].Add(u);
}
static int end1, end2, maxi;
// DFS to find the first
// End Node of diameter
static void findFirstEnd(int u, int p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi)
{
maxi = lvl[u];
end1 = u;
}
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].Count; i++)
{
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findFirstEnd(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to clear the levels
// of the nodes
static void clear(int n)
{
// Set all value of lvl[]
// to 0 for next dfs
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
lvl[i] = 0;
}
// Set maximum with 0
maxi = 0;
dist1[0] = dist2[0] = -1;
}
// DFS will calculate second
// end of the diameter
static void findSecondEnd(int u, int p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi)
{
maxi = lvl[u];
// Store the node with
// maximum depth from end1
end2 = u;
}
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].Count; i++)
{
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findSecondEnd(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of the farthest distant node
static void findDistancefromFirst(int u, int p)
{
// Storing distance from
// end1 to node u
dist1[u] = 1 + dist1[p];
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].Count; i++)
{
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findDistancefromFirst(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of nodes from second end of diameter
static void findDistancefromSecond(int u, int p)
{
// Storing distance from end2 to node u
dist2[u] = 1 + dist2[p];
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].Count; i++)
{
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findDistancefromSecond(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
static void findNodes()
{
int n = 5;
// Joining Edge between two
// nodes of the tree
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(1, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 5);
// Find the one end of
// the diameter of tree
findFirstEnd(1, 0);
clear(n);
// Find the other end
// of the diameter of tree
findSecondEnd(end1, 0);
// Find the distance
// to each node from end1
findDistancefromFirst(end1, 0);
// Find the distance to
// each node from end2
findDistancefromSecond(end2, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = dist1[i];
int y = dist2[i];
// Comparing distance between
// the two ends of diameter
if (x >= y)
{
Console.Write(end1 + " ");
}
else
{
Console.Write(end2 + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
// Function call
findNodes();
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to find the
// farthest node from each vertex
// of the tree
let N = 10000;
// Adjacency list to store edges
let adj = new Array(N);
let lvl = new Array(N);
let dist1 = new Array(N);
let dist2 = new Array(N);
let end = 0, end2 = 0, maxi = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
lvl[i] = 0;
dist1[i] = -1;
dist2[i] = -1;
}
// Add edge between
// U and V in tree
function AddEdge(u,v)
{
// Edge from U to V
adj[u].push(v);
// Edge from V to U
adj[v].push(u);
}
// DFS to find the first
// End Node of diameter
function findFirstEnd(u,p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi)
{
maxi = lvl[u];
end1 = u;
}
for(let i = 0; i < adj[u].length; i++)
{
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findFirstEnd(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to clear the levels
// of the nodes
function clear(n)
{
// Set all value of lvl[]
// to 0 for next dfs
for(let i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
lvl[i] = 0;
}
// Set maximum with 0
maxi = 0;
dist1[0] = dist2[0] = -1;
}
// DFS will calculate second
// end of the diameter
function findSecondEnd(u,p)
{
// Calculating level of nodes
lvl[u] = 1 + lvl[p];
if (lvl[u] > maxi)
{
maxi = lvl[u];
// Store the node with
// maximum depth from end1
end2 = u;
}
for(let i = 0; i < adj[u].length; i++)
{
// Go in opposite
// direction of parent
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findSecondEnd(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of the farthest distant node
function findDistancefromFirst(u,p)
{
// Storing distance from
// end1 to node u
dist1[u] = 1 + dist1[p];
for(let i = 0; i < adj[u].length; i++)
{
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findDistancefromFirst(
adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
// Function to find the distance
// of nodes from second end of diameter
function findDistancefromSecond(u,p)
{
// Storing distance from end2 to node u
dist2[u] = 1 + dist2[p];
for(let i = 0; i < adj[u].length; i++)
{
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
findDistancefromSecond(
adj[u][i], u);
}
}
}
function findNodes()
{
let n = 5;
// Joining Edge between two
// nodes of the tree
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(1, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 5);
// Find the one end of
// the diameter of tree
findFirstEnd(1, 0);
clear(n);
// Find the other end
// of the diameter of tree
findSecondEnd(end1, 0);
// Find the distance
// to each node from end1
findDistancefromFirst(end1, 0);
// Find the distance to
// each node from end2
findDistancefromSecond(end2, 0);
for(let i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
let x = dist1[i];
let y = dist2[i];
// Comparing distance between
// the two ends of diameter
if (x >= y)
{
document.write(end1 + " ");
}
else
{
document.write(end2 + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
adj[i] = [];
}
// Function call
findNodes();
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
4 4 2 2 2
Complejidad temporal: O(V+E), donde V es el número de vértices y E es el número de aristas.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V + E).