El algoritmo de Floyd Warshall es para resolver el problema de la ruta más corta de todos los pares. El problema es encontrar las distancias más cortas entre cada par de vértices en un gráfico dirigido ponderado de borde dado.
Ejemplo:
Input:
graph[][] = { {0, 5, INF, 10},
{INF, 0, 3, INF},
{INF, INF, 0, 1},
{INF, INF, INF, 0} }
which represents the following graph
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3
Note that the value of graph[i][j] is 0 if i is equal to j
And graph[i][j] is INF (infinite) if there is no edge from vertex i to j.
Output:
Shortest distance matrix
0 5 8 9
INF 0 3 4
INF INF 0 1
INF INF INF 0
Algoritmo de Floyd Warshall
Inicializamos la array de solución igual que la array del gráfico de entrada como primer paso. Luego actualizamos la array solución considerando todos los vértices como un vértice intermedio. La idea es elegir uno por uno todos los vértices y actualizar todos los caminos más cortos que incluyen el vértice elegido como un vértice intermedio en el camino más corto. Cuando elegimos el vértice número k como vértice intermedio, ya hemos considerado los vértices {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} como vértices intermedios. Para cada par (i, j) de los vértices de origen y destino respectivamente, hay dos casos posibles.
1) k no es un vértice intermedio en el camino más corto de i a j. Mantenemos el valor de dist[i][j] como está.
2)k es un vértice intermedio en el camino más corto de i a j. Actualizamos el valor de dist[i][j] como dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] si dist[i][j] > dist[i][k] + dist[k][ j]
La siguiente figura muestra la propiedad de subestructura óptima anterior en el problema del camino más corto de todos los pares.
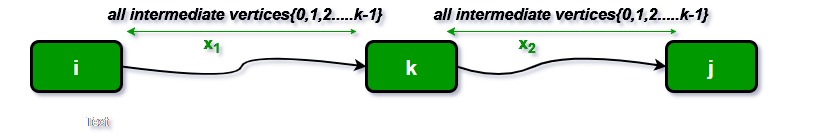
A continuación se muestran las implementaciones del algoritmo Floyd Warshall.
C++
// C++ Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Number of vertices in the graph
#define V 4
/* Define Infinite as a large enough
value.This value will be used for
vertices not connected to each other */
#define INF 99999
// A function to print the solution matrix
void printSolution(int dist[][V]);
// Solves the all-pairs shortest path
// problem using Floyd Warshall algorithm
void floydWarshall(int graph[][V])
{
/* dist[][] will be the output matrix
that will finally have the shortest
distances between every pair of vertices */
int dist[V][V], i, j, k;
/* Initialize the solution matrix same
as input graph matrix. Or we can say
the initial values of shortest distances
are based on shortest paths considering
no intermediate vertex. */
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
dist[i][j] = graph[i][j];
/* Add all vertices one by one to
the set of intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of an iteration,
we have shortest distances between all
pairs of vertices such that the
shortest distances consider only the
vertices in set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as
intermediate vertices.
----> After the end of an iteration,
vertex no. k is added to the set of
intermediate vertices and the set becomes {0, 1, 2, ..
k} */
for (k = 0; k < V; k++) {
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// Pick all vertices as destination for the
// above picked source
for (j = 0; j < V; j++) {
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of
// dist[i][j]
if (dist[i][j] > (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j])
&& (dist[k][j] != INF
&& dist[i][k] != INF))
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
// Print the shortest distance matrix
printSolution(dist);
}
/* A utility function to print solution */
void printSolution(int dist[][V])
{
cout << "The following matrix shows the shortest "
"distances"
" between every pair of vertices \n";
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (dist[i][j] == INF)
cout << "INF"
<< " ";
else
cout << dist[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3 */
int graph[V][V] = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 },
{ INF, 0, 3, INF },
{ INF, INF, 0, 1 },
{ INF, INF, INF, 0 } };
// Print the solution
floydWarshall(graph);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Mythri J L
C
// C Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm
#include<stdio.h>
// Number of vertices in the graph
#define V 4
/* Define Infinite as a large enough
value. This value will be used
for vertices not connected to each other */
#define INF 99999
// A function to print the solution matrix
void printSolution(int dist[][V]);
// Solves the all-pairs shortest path
// problem using Floyd Warshall algorithm
void floydWarshall (int graph[][V])
{
/* dist[][] will be the output matrix
that will finally have the shortest
distances between every pair of vertices */
int dist[V][V], i, j, k;
/* Initialize the solution matrix
same as input graph matrix. Or
we can say the initial values of
shortest distances are based
on shortest paths considering no
intermediate vertex. */
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
dist[i][j] = graph[i][j];
/* Add all vertices one by one to
the set of intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of an iteration, we
have shortest distances between all
pairs of vertices such that the shortest
distances consider only the
vertices in set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as
intermediate vertices.
----> After the end of an iteration,
vertex no. k is added to the set of
intermediate vertices and the set
becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination for the
// above picked source
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j])
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
// Print the shortest distance matrix
printSolution(dist);
}
/* A utility function to print solution */
void printSolution(int dist[][V])
{
printf ("The following matrix shows the shortest distances"
" between every pair of vertices \n");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
if (dist[i][j] == INF)
printf("%7s", "INF");
else
printf ("%7d", dist[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3 */
int graph[V][V] = { {0, 5, INF, 10},
{INF, 0, 3, INF},
{INF, INF, 0, 1},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
// Print the solution
floydWarshall(graph);
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program for Floyd Warshall All Pairs Shortest
// Path algorithm.
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class AllPairShortestPath
{
final static int INF = 99999, V = 4;
void floydWarshall(int graph[][])
{
int dist[][] = new int[V][V];
int i, j, k;
/* Initialize the solution matrix
same as input graph matrix.
Or we can say the initial values
of shortest distances
are based on shortest paths
considering no intermediate
vertex. */
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
dist[i][j] = graph[i][j];
/* Add all vertices one by one
to the set of intermediate
vertices.
---> Before start of an iteration,
we have shortest
distances between all pairs
of vertices such that
the shortest distances consider
only the vertices in
set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as
intermediate vertices.
----> After the end of an iteration,
vertex no. k is added
to the set of intermediate
vertices and the set
becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination for the
// above picked source
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j])
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
// Print the shortest distance matrix
printSolution(dist);
}
void printSolution(int dist[][])
{
System.out.println("The following matrix shows the shortest "+
"distances between every pair of vertices");
for (int i=0; i<V; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<V; ++j)
{
if (dist[i][j]==INF)
System.out.print("INF ");
else
System.out.print(dist[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void main (String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3 */
int graph[][] = { {0, 5, INF, 10},
{INF, 0, 3, INF},
{INF, INF, 0, 1},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
AllPairShortestPath a = new AllPairShortestPath();
// Print the solution
a.floydWarshall(graph);
}
}
// Contributed by Aakash Hasija
Python3
# Python Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm
# Number of vertices in the graph
V = 4
# Define infinity as the large
# enough value. This value will be
# used for vertices not connected to each other
INF = 99999
# Solves all pair shortest path
# via Floyd Warshall Algorithm
def floydWarshall(graph):
""" dist[][] will be the output
matrix that will finally
have the shortest distances
between every pair of vertices """
""" initializing the solution matrix
same as input graph matrix
OR we can say that the initial
values of shortest distances
are based on shortest paths considering no
intermediate vertices """
dist = list(map(lambda i: list(map(lambda j: j, i)), graph))
""" Add all vertices one by one
to the set of intermediate
vertices.
---> Before start of an iteration,
we have shortest distances
between all pairs of vertices
such that the shortest
distances consider only the
vertices in the set
{0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as intermediate vertices.
----> After the end of a
iteration, vertex no. k is
added to the set of intermediate
vertices and the
set becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k}
"""
for k in range(V):
# pick all vertices as source one by one
for i in range(V):
# Pick all vertices as destination for the
# above picked source
for j in range(V):
# If vertex k is on the shortest path from
# i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j]
dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j],
dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]
)
printSolution(dist)
# A utility function to print the solution
def printSolution(dist):
print ("Following matrix shows the shortest distances\
between every pair of vertices")
for i in range(V):
for j in range(V):
if(dist[i][j] == INF):
print ("%7s" % ("INF"),end=" ")
else:
print ("%7d\t" % (dist[i][j]),end=' ')
if j == V-1:
print ()
# Driver program to test the above program
# Let us create the following weighted graph
"""
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3 """
graph = [[0, 5, INF, 10],
[INF, 0, 3, INF],
[INF, INF, 0, 1],
[INF, INF, INF, 0]
]
# Print the solution
floydWarshall(graph)
# This code is contributed by Mythri J L
C#
// A C# program for Floyd Warshall All
// Pairs Shortest Path algorithm.
using System;
public class AllPairShortestPath
{
readonly static int INF = 99999, V = 4;
void floydWarshall(int[,] graph)
{
int[,] dist = new int[V, V];
int i, j, k;
// Initialize the solution matrix
// same as input graph matrix
// Or we can say the initial
// values of shortest distances
// are based on shortest paths
// considering no intermediate
// vertex
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < V; j++) {
dist[i, j] = graph[i, j];
}
}
/* Add all vertices one by one to
the set of intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of a iteration,
we have shortest distances
between all pairs of vertices
such that the shortest distances
consider only the vertices in
set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as
intermediate vertices.
---> After the end of a iteration,
vertex no. k is added
to the set of intermediate
vertices and the set
becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source
// one by one
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination
// for the above picked source
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest
// path from i to j, then update
// the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i, k] + dist[k, j] < dist[i, j])
{
dist[i, j] = dist[i, k] + dist[k, j];
}
}
}
}
// Print the shortest distance matrix
printSolution(dist);
}
void printSolution(int[,] dist)
{
Console.WriteLine("Following matrix shows the shortest "+
"distances between every pair of vertices");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; ++j)
{
if (dist[i, j] == INF) {
Console.Write("INF ");
} else {
Console.Write(dist[i, j] + " ");
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* Let us create the following
weighted graph
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3 */
int[,] graph = { {0, 5, INF, 10},
{INF, 0, 3, INF},
{INF, INF, 0, 1},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
AllPairShortestPath a = new AllPairShortestPath();
// Print the solution
a.floydWarshall(graph);
}
}
// This article is contributed by
// Abdul Mateen Mohammed
PHP
<?php
// PHP Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm
// Solves the all-pairs shortest path problem
// using Floyd Warshall algorithm
function floydWarshall ($graph, $V, $INF)
{
/* dist[][] will be the output matrix
that will finally have the shortest
distances between every pair of vertices */
$dist = array(array(0,0,0,0),
array(0,0,0,0),
array(0,0,0,0),
array(0,0,0,0));
/* Initialize the solution matrix same
as input graph matrix. Or we can say the
initial values of shortest distances are
based on shortest paths considering no
intermediate vertex. */
for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++)
for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++)
$dist[$i][$j] = $graph[$i][$j];
/* Add all vertices one by one to the set
of intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of an iteration, we have
shortest distances between all pairs of
vertices such that the shortest distances
consider only the vertices in set
{0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as intermediate vertices.
----> After the end of an iteration, vertex
no. k is added to the set of intermediate
vertices and the set becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for ($k = 0; $k < $V; $k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination
// for the above picked source
for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j]
if ($dist[$i][$k] + $dist[$k][$j] <
$dist[$i][$j])
$dist[$i][$j] = $dist[$i][$k] +
$dist[$k][$j];
}
}
}
// Print the shortest distance matrix
printSolution($dist, $V, $INF);
}
/* A utility function to print solution */
function printSolution($dist, $V, $INF)
{
echo "The following matrix shows the " .
"shortest distances between " .
"every pair of vertices \n";
for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++)
{
for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++)
{
if ($dist[$i][$j] == $INF)
echo "INF " ;
else
echo $dist[$i][$j], " ";
}
echo "\n";
}
}
// Driver Code
// Number of vertices in the graph
$V = 4 ;
/* Define Infinite as a large enough
value. This value will be used for
vertices not connected to each other */
$INF = 99999 ;
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3 */
$graph = array(array(0, 5, $INF, 10),
array($INF, 0, 3, $INF),
array($INF, $INF, 0, 1),
array($INF, $INF, $INF, 0));
// Print the solution
floydWarshall($graph, $V, $INF);
// This code is contributed by Ryuga
?>
Javascript
<script>
// A JavaScript program for Floyd Warshall All
// Pairs Shortest Path algorithm.
var INF = 99999;
class AllPairShortestPath {
constructor() {
this.V = 4;
}
floydWarshall(graph) {
var dist = Array.from(Array(this.V), () => new Array(this.V).fill(0));
var i, j, k;
// Initialize the solution matrix
// same as input graph matrix
// Or we can say the initial
// values of shortest distances
// are based on shortest paths
// considering no intermediate
// vertex
for (i = 0; i < this.V; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < this.V; j++) {
dist[i][j] = graph[i][j];
}
}
/* Add all vertices one by one to
the set of intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of a iteration,
we have shortest distances
between all pairs of vertices
such that the shortest distances
consider only the vertices in
set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as
intermediate vertices.
---> After the end of a iteration,
vertex no. k is added
to the set of intermediate
vertices and the set
becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (k = 0; k < this.V; k++) {
// Pick all vertices as source
// one by one
for (i = 0; i < this.V; i++) {
// Pick all vertices as destination
// for the above picked source
for (j = 0; j < this.V; j++) {
// If vertex k is on the shortest
// path from i to j, then update
// the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) {
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
}
// Print the shortest distance matrix
this.printSolution(dist);
}
printSolution(dist) {
document.write(
"Following matrix shows the shortest " +
"distances between every pair of vertices<br>"
);
for (var i = 0; i < this.V; ++i) {
for (var j = 0; j < this.V; ++j) {
if (dist[i][j] == INF) {
document.write(" INF ");
} else {
document.write(" " + dist[i][j] + " ");
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
/* Let us create the following
weighted graph
10
(0)------->(3)
| /|\
5 | |
| | 1
\|/ |
(1)------->(2)
3 */
var graph = [
[0, 5, INF, 10],
[INF, 0, 3, INF],
[INF, INF, 0, 1],
[INF, INF, INF, 0],
];
var a = new AllPairShortestPath();
// Print the solution
a.floydWarshall(graph);
// This code is contributed by rdtaank.
</script>
Producción:
Following matrix shows the shortest distances between every pair of vertices
0 5 8 9
INF 0 3 4
INF INF 0 1
INF INF INF 0
Complejidad del Tiempo: O(V 3 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V 2 )
El programa anterior solo imprime las distancias más cortas. Podemos modificar la solución para imprimir las rutas más cortas también almacenando la información del predecesor en una array 2D separada.
Además, el valor de INF se puede tomar como INT_MAX de los límites.h para asegurarnos de que manejamos el valor máximo posible. Cuando tomamos INF como INT_MAX, necesitamos cambiar la condición if en el programa anterior para evitar el desbordamiento aritmético.
#include
#define INF INT_MAX
..........................
if ( dist[i][k] != INF &&
dist[k][j] != INF &&
dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]
)
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
...........................
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA