Dado un árbol N-ario con borde ponderado y consultas Q donde cada consulta contiene dos Nodes del árbol. La tarea es encontrar el borde ponderado máximo en el camino simple entre estos dos Nodes.
Ejemplos:
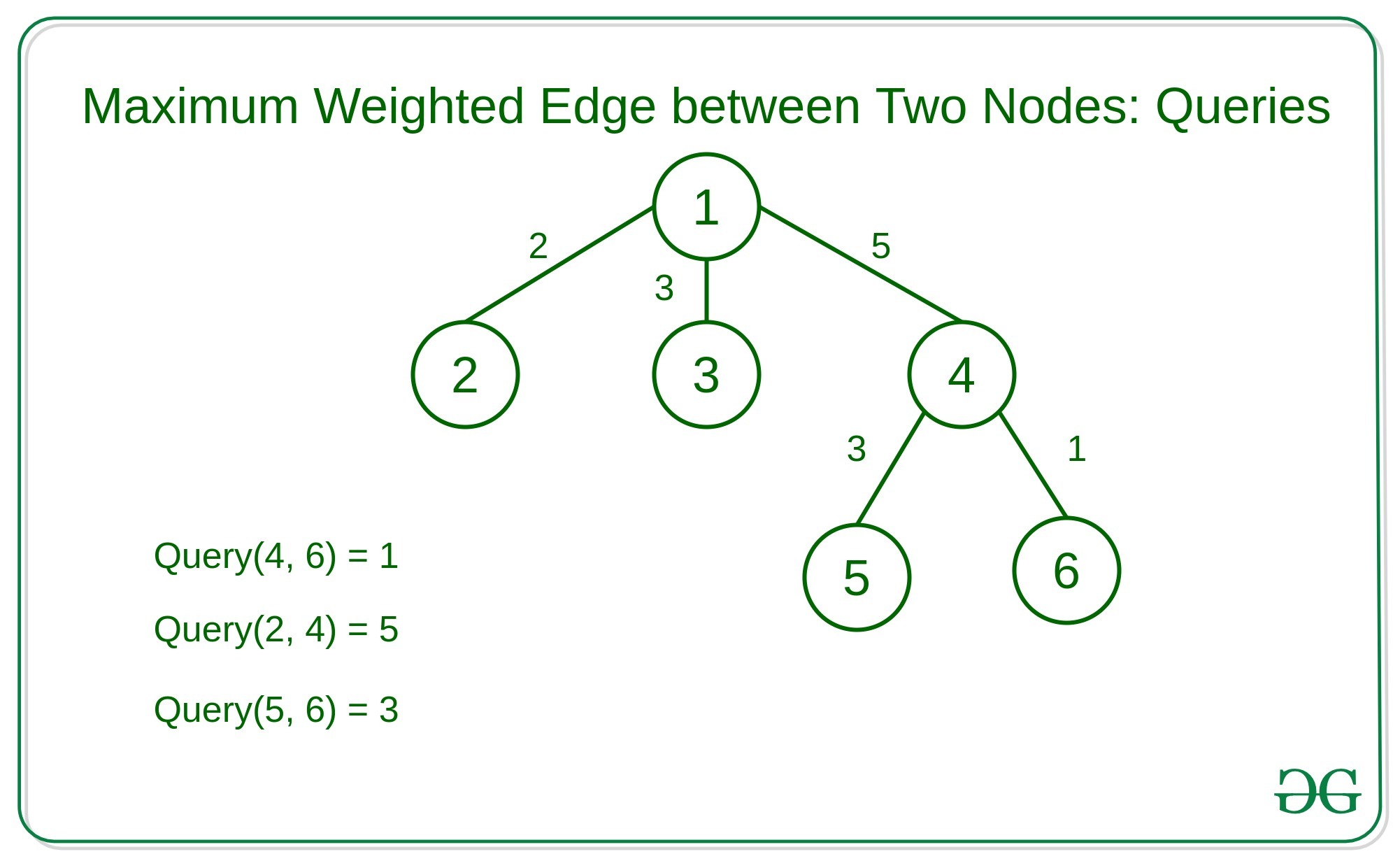
Enfoque ingenuo: una solución simple es recorrer todo el árbol para cada consulta y encontrar la ruta entre los dos Nodes.
Enfoque eficiente: la idea es utilizar la elevación binaria para precalcular el borde ponderado máximo de cada Node a todos los demás Nodes a una distancia de algunos
![]()
. Guardaremos el borde ponderado máximo hasta ![]()
nivel.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6390ef4fd05773ba01d3073094c60d57_l3.png)
y
dónde
- j es el Node y
- yo es la distancia de
![]()
- dp[i][j] almacena el padre de j en
![]()
- distancia si está presente, de lo contrario almacenará 0
- mx[i][j] almacena el borde máximo del Node j al padre de este Node en
![]()
- distancia.
Haremos una búsqueda profunda para encontrar a todos los padres en ![]()
distancia y su peso y luego precalcular los padres y los bordes máximos en cada ![]()
distancia.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// maximum weighted edge in the simple
// path between two nodes in N-ary Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
// Depths of Nodes
vector<int> level(N);
const int LG = 20;
// Parent at every 2^i level
vector<vector<int> > dp(LG, vector<int>(N));
// Maximum node at every 2^i level
vector<vector<int> > mx(LG, vector<int>(N));
// Graph that stores destinations
// and its weight
vector<vector<pair<int, int> > > v(N);
int n;
// Function to traverse the nodes
// using the Depth-First Search Traversal
void dfs_lca(int a, int par, int lev)
{
dp[0][a] = par;
level[a] = lev;
for (auto i : v[a]) {
// Condition to check if its
// equal to its parent then skip
if (i.first == par)
continue;
mx[0][i.first] = i.second;
// DFS Recursive Call
dfs_lca(i.first, a, lev + 1);
}
}
// Function to find the ancestor
void find_ancestor()
{
// Loop to set every 2^i distance
for (int i = 1; i < LG; i++) {
// Loop to calculate for
// each node in the N-ary tree
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[i][j]
= dp[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]];
// Storing maximum edge
mx[i][j]
= max(mx[i - 1][j],
mx[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]);
}
}
}
int getMax(int a, int b)
{
// Swaping if node a is at more depth
// than node b because we will
// always take at more depth
if (level[b] < level[a])
swap(a, b);
int ans = 0;
// Difference between the depth of
// the two given nodes
int diff = level[b] - level[a];
while (diff > 0) {
int log = log2(diff);
ans = max(ans, mx[log][b]);
// Changing Node B to its
// parent at 2 ^ i distance
b = dp[log][b];
// Subtracting distance by 2^i
diff -= (1 << log);
}
// Take both a, b to its
// lca and find maximum
while (a != b) {
int i = log2(level[a]);
// Loop to find the 2^ith
// parent that is different
// for both a and b i.e below the lca
while (i > 0
&& dp[i][a] == dp[i][b])
i--;
// Updating ans
ans = max(ans, mx[i][a]);
ans = max(ans, mx[i][b]);
// Changing value to its parent
a = dp[i][a];
b = dp[i][b];
}
return ans;
}
// Function to compute the Least
// common Ancestor
void compute_lca()
{
dfs_lca(1, 0, 0);
find_ancestor();
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Undirected tree
n = 5;
v[1].push_back(make_pair(2, 2));
v[2].push_back(make_pair(1, 2));
v[1].push_back(make_pair(3, 5));
v[3].push_back(make_pair(1, 5));
v[3].push_back(make_pair(4, 3));
v[4].push_back(make_pair(3, 4));
v[3].push_back(make_pair(5, 1));
v[5].push_back(make_pair(3, 1));
// Computing LCA
compute_lca();
int queries[][2]
= { { 3, 5 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 } };
int q = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int max_edge = getMax(queries[i][0],
queries[i][1]);
cout << max_edge << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find the
// maximum weighted edge in the simple
// path between two nodes in N-ary Tree
import java.util.*;
import java.awt.Point;
public class Main
{
static int N = 100005;
// Depths of Nodes
static int[] level = new int[N];
static int LG = 20;
// Parent at every 2^i level
static int[][] dp = new int[LG][N];
// Maximum node at every 2^i level
static int[][] mx = new int[LG][N];
// Graph that stores destinations
// and its weight
static Vector<Vector<Point>> v = new Vector<Vector<Point>>();
static int n = 0;
// Function to traverse the
// nodes using the Depth-First
// Search Traversal
static void dfs_lca(int a, int par, int lev)
{
dp[0][a] = par;
level[a] = lev;
for(int i = 0; i < v.get(a).size(); i++)
{
// Condition to check
// if its equal to its
// parent then skip
if (v.get(a).get(i).x == par)
continue;
mx[0][v.get(a).get(i).x] = v.get(a).get(i).y;
// DFS Recursive Call
dfs_lca(v.get(a).get(i).x, a, lev + 1);
}
}
// Function to find the ancestor
static void find_ancestor()
{
// Loop to set every 2^i distance
for(int i = 1; i < 16; i++)
{
// Loop to calculate for
// each node in the N-ary tree
for(int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]];
// Storing maximum edge
mx[i][j] = Math.max(mx[i - 1][j], mx[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]);
}
}
}
static int getMax(int a, int b)
{
// Swaping if node a is at more depth
// than node b because we will
// always take at more depth
if (level[b] < level[a])
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int ans = 0;
// Difference between the
// depth of the two given
// nodes
int diff = level[b] - level[a];
while (diff > 0)
{
int log = (int)(Math.log(diff) / Math.log(2));
ans = Math.max(ans, mx[log][b]);
// Changing Node B to its
// parent at 2 ^ i distance
b = dp[log][b];
// Subtracting distance by 2^i
diff -= (1 << log);
}
// Take both a, b to its
// lca and find maximum
while (a != b)
{
int i = (int)(Math.log(level[a]) / Math.log(2));
// Loop to find the maximum 2^ith
// parent the is different
// for both a and b
while (i > 0 && dp[i][a] == dp[i][b])
{
i-=1;
}
// Updating ans
ans = Math.max(ans, mx[i][a]);
ans = Math.max(ans, mx[i][b]);
// Changing value to
// its parent
a = dp[i][a];
b = dp[i][b];
}
return ans;
}
// Function to compute the Least
// common Ancestor
static void compute_lca()
{
dfs_lca(1, 0, 0);
find_ancestor();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < LG; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = 0;
mx[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
v.add(new Vector<Point>());
}
// Undirected tree
v.get(1).add(new Point(2, 2));
v.get(2).add(new Point(1, 2));
v.get(1).add(new Point(3, 5));
v.get(3).add(new Point(1, 5));
v.get(3).add(new Point(4, 3));
v.get(4).add(new Point(3, 4));
v.get(3).add(new Point(5, 1));
v.get(5).add(new Point(3, 1));
// Computing LCA
compute_lca();
int[][] queries
= { { 3, 5 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 } };
int q = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int max_edge = getMax(queries[i][0],
queries[i][1]);
System.out.println(max_edge);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
Python3
# Python3 implementation to # find the maximum weighted # edge in the simple path # between two nodes in N-ary Tree import math N = 100005; # Depths of Nodes level = [0 for i in range(N)] LG = 20; # Parent at every 2^i level dp = [[0 for j in range(N)] for i in range(LG)] # Maximum node at every 2^i level mx = [[0 for j in range(N)] for i in range(LG)] # Graph that stores destinations # and its weight v = [[] for i in range(N)] n = 0 # Function to traverse the # nodes using the Depth-First # Search Traversal def dfs_lca(a, par, lev): dp[0][a] = par; level[a] = lev; for i in v[a]: # Condition to check # if its equal to its # parent then skip if (i[0] == par): continue; mx[0][i[0]] = i[1]; # DFS Recursive Call dfs_lca(i[0], a, lev + 1); # Function to find the ancestor def find_ancestor(): # Loop to set every 2^i distance for i in range(1, 16): # Loop to calculate for # each node in the N-ary tree for j in range(1, n + 1): dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]; # Storing maximum edge mx[i][j] = max(mx[i - 1][j], mx[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]); def getMax(a, b): # Swaping if node a is at more depth # than node b because we will # always take at more depth if (level[b] < level[a]): a, b = b, a ans = 0; # Difference between the # depth of the two given # nodes diff = level[b] - level[a]; while (diff > 0): log = int(math.log2(diff)); ans = max(ans, mx[log][b]); # Changing Node B to its # parent at 2 ^ i distance b = dp[log][b]; # Subtracting distance by 2^i diff -= (1 << log); # Take both a, b to its # lca and find maximum while (a != b): i = int(math.log2(level[a])); # Loop to find the maximum 2^ith # parent the is different # for both a and b while (i > 0 and dp[i][a] == dp[i][b]): i-=1 # Updating ans ans = max(ans, mx[i][a]); ans = max(ans, mx[i][b]); # Changing value to # its parent a = dp[i][a]; b = dp[i][b]; return ans; # Function to compute the Least # common Ancestor def compute_lca(): dfs_lca(1, 0, 0); find_ancestor(); # Driver code if __name__=="__main__": # Undirected tree n = 5; v[1].append([2, 2]); v[2].append([1, 2]); v[1].append([3, 5]); v[3].append([1, 5]); v[3].append([4, 3]); v[4].append([3, 4]); v[3].append([5, 1]); v[5].append([3, 1]); # Computing LCA compute_lca(); queries= [[3, 5], [2, 3], [2,4]] q = 3; for i in range(q): max_edge = getMax(queries[i][0], queries[i][1]); print(max_edge) # This code is contributed by Rutvik_56
C#
// C# implementation to find the
// maximum weighted edge in the simple
// path between two nodes in N-ary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int N = 100005;
// Depths of Nodes
static int[] level = new int[N];
static int LG = 20;
// Parent at every 2^i level
static int[,] dp = new int[LG, N];
// Maximum node at every 2^i level
static int[,] mx = new int[LG, N];
// Graph that stores destinations
// and its weight
static List<List<Tuple<int,int>>> v = new List<List<Tuple<int,int>>>();
static int n = 0;
// Function to traverse the
// nodes using the Depth-First
// Search Traversal
static void dfs_lca(int a, int par, int lev)
{
dp[0,a] = par;
level[a] = lev;
for(int i = 0; i < v[a].Count; i++)
{
// Condition to check
// if its equal to its
// parent then skip
if (v[a][i].Item1 == par)
continue;
mx[0,v[a][i].Item1] = v[a][i].Item2;
// DFS Recursive Call
dfs_lca(v[a][i].Item1, a, lev + 1);
}
}
// Function to find the ancestor
static void find_ancestor()
{
// Loop to set every 2^i distance
for(int i = 1; i < 16; i++)
{
// Loop to calculate for
// each node in the N-ary tree
for(int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++)
{
dp[i,j] = dp[i - 1,dp[i - 1,j]];
// Storing maximum edge
mx[i,j] = Math.Max(mx[i - 1,j], mx[i - 1,dp[i - 1,j]]);
}
}
}
static int getMax(int a, int b)
{
// Swaping if node a is at more depth
// than node b because we will
// always take at more depth
if (level[b] < level[a])
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int ans = 0;
// Difference between the
// depth of the two given
// nodes
int diff = level[b] - level[a];
while (diff > 0)
{
int log = (int)(Math.Log(diff) / Math.Log(2));
ans = Math.Max(ans, mx[log,b]);
// Changing Node B to its
// parent at 2 ^ i distance
b = dp[log,b];
// Subtracting distance by 2^i
diff -= (1 << log);
}
// Take both a, b to its
// lca and find maximum
while (a != b)
{
int i = (int)(Math.Log(level[a]) / Math.Log(2));
// Loop to find the maximum 2^ith
// parent the is different
// for both a and b
while (i > 0 && dp[i,a] == dp[i,b])
{
i-=1;
}
// Updating ans
ans = Math.Max(ans, mx[i,a]);
ans = Math.Max(ans, mx[i,b]);
// Changing value to
// its parent
a = dp[i,a];
b = dp[i,b];
}
return ans;
}
// Function to compute the Least
// common Ancestor
static void compute_lca()
{
dfs_lca(1, 0, 0);
find_ancestor();
}
static void Main() {
for(int i = 0; i < LG; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
dp[i,j] = 0;
mx[i,j] = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
v.Add(new List<Tuple<int,int>>());
}
// Undirected tree
v[1].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(2, 2));
v[2].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(1, 2));
v[1].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(3, 5));
v[3].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(1, 5));
v[3].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(4, 3));
v[4].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(3, 4));
v[3].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(5, 1));
v[5].Add(new Tuple<int,int>(3, 1));
// Computing LCA
compute_lca();
int[,] queries
= { { 3, 5 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 } };
int q = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int max_edge = getMax(queries[i,0],
queries[i,1]);
Console.WriteLine(max_edge);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to find the
// maximum weighted edge in the simple
// path between two nodes in N-ary Tree
let N = 100005;
// Depths of Nodes
let level = new Array(N);
level.fill(0);
let LG = 20;
// Parent at every 2^i level
let dp = new Array(LG);
for(let i = 0; i < LG; i++)
{
dp[i] = new Array(N);
for(let j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Maximum node at every 2^i level
let mx = new Array(LG);
for(let i = 0; i < LG; i++)
{
mx[i] = new Array(N);
for(let j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
mx[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Graph that stores destinations
// and its weight
let v = [];
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
v.push([]);
}
let n = 0;
// Function to traverse the
// nodes using the Depth-First
// Search Traversal
function dfs_lca(a, par, lev)
{
dp[0][a] = par;
level[a] = lev;
for(let i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
// Condition to check
// if its equal to its
// parent then skip
if (v[a][0] == par)
continue;
mx[0][v[a][0]] = v[a][1];
// DFS Recursive Call
dfs_lca(v[a][0], a, lev + 1);
}
}
// Function to find the ancestor
function find_ancestor()
{
// Loop to set every 2^i distance
for(let i = 1; i < 16; i++)
{
// Loop to calculate for
// each node in the N-ary tree
for(let j = 1; j < n + 1; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]];
// Storing maximum edge
mx[i][j] = Math.max(mx[i - 1][j], mx[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]);
}
}
}
function getMax(a, b)
{
// Swaping if node a is at more depth
// than node b because we will
// always take at more depth
if (level[b] < level[a])
{
let temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
let ans = 0;
// Difference between the
// depth of the two given
// nodes
let diff = level[b] - level[a];
while (diff > 0)
{
let log = parseInt(Math.log(diff) / Math.log(2), 10);
ans = Math.max(ans, mx[log][b]);
// Changing Node B to its
// parent at 2 ^ i distance
b = dp[log][b];
// Subtracting distance by 2^i
diff -= (1 << log);
}
// Take both a, b to its
// lca and find maximum
while (a == b)
{
i = parseInt(Math.log(level[a]) / Math.log(2), 10);
// Loop to find the maximum 2^ith
// parent the is different
// for both a and b
while (i > 0 && dp[i][a] == dp[i][b])
{
i-=1;
}
// Updating ans
ans = Math.max(ans, mx[i][a]);
ans = Math.max(ans, mx[i][b]);
// Changing value to
// its parent
a = dp[i][a];
b = dp[i][b];
}
return ans*2 + 1;
}
// Function to compute the Least
// common Ansector
function compute_lca()
{
dfs_lca(1, 0, 0);
find_ancestor();
}
// Undirected tree
n = 5;
v[1].push(2);
v[1].push(2);
v[2].push(1);
v[2].push(2);
v[1].push(3);
v[1].push(5);
v[3].push(1);
v[3].push(5);
v[3].push(4);
v[3].push(3);
v[4].push(3);
v[4].push(4);
v[3].push(5);
v[3].push(1);
v[5].push(3);
v[5].push(1);
// Computing LCA
compute_lca();
let queries= [[3, 5], [2, 3], [2,4]];
let q = 3;
for(let i = 0; i <q; i++)
{
let max_edge = getMax(queries[i][0],
queries[i][1]);
document.write(max_edge + "</br>");
}
// This code is contributed by suresh07.
</script>
1 5 5
Complejidad temporal: O(N*logN).
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N*logN).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por insiderpants y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA