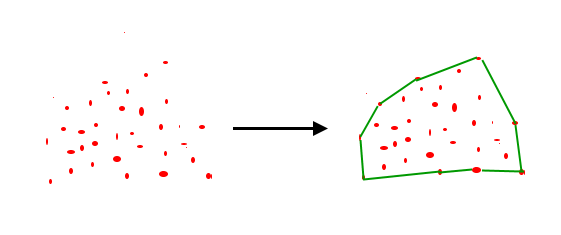
Dado un conjunto de puntos en el plano. la envolvente convexa del conjunto es el polígono convexo más pequeño que contiene todos los puntos del mismo.
CPP
// A C++ program to find convex hull of a set of points. Refer
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/orientation-3-ordered-points/
// for explanation of orientation()
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
// A global point needed for sorting points with reference
// to the first point Used in compare function of qsort()
Point p0;
// A utility function to find next to top in a stack
Point nextToTop(stack<Point> &S)
{
Point p = S.top();
S.pop();
Point res = S.top();
S.push(p);
return res;
}
// A utility function to swap two points
void swap(Point &p1, Point &p2)
{
Point temp = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = temp;
}
// A utility function to return square of distance
// between p1 and p2
int distSq(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return (p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) +
(p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y);
}
// To find orientation of ordered triplet (p, q, r).
// The function returns following values
// 0 --> p, q and r are collinear
// 1 --> Clockwise
// 2 --> Counterclockwise
int orientation(Point p, Point q, Point r)
{
int val = (q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x) -
(q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y);
if (val == 0) return 0; // collinear
return (val > 0)? 1: 2; // clock or counterclock wise
}
// A function used by library function qsort() to sort an array of
// points with respect to the first point
int compare(const void *vp1, const void *vp2)
{
Point *p1 = (Point *)vp1;
Point *p2 = (Point *)vp2;
// Find orientation
int o = orientation(p0, *p1, *p2);
if (o == 0)
return (distSq(p0, *p2) >= distSq(p0, *p1))? -1 : 1;
return (o == 2)? -1: 1;
}
// Prints convex hull of a set of n points.
void convexHull(Point points[], int n)
{
// Find the bottommost point
int ymin = points[0].y, min = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int y = points[i].y;
// Pick the bottom-most or choose the left
// most point in case of tie
if ((y < ymin) || (ymin == y &&
points[i].x < points[min].x))
ymin = points[i].y, min = i;
}
// Place the bottom-most point at first position
swap(points[0], points[min]);
// Sort n-1 points with respect to the first point.
// A point p1 comes before p2 in sorted output if p2
// has larger polar angle (in counterclockwise
// direction) than p1
p0 = points[0];
qsort(&points[1], n-1, sizeof(Point), compare);
// If two or more points make same angle with p0,
// Remove all but the one that is farthest from p0
// Remember that, in above sorting, our criteria was
// to keep the farthest point at the end when more than
// one points have same angle.
int m = 1; // Initialize size of modified array
for (int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
// Keep removing i while angle of i and i+1 is same
// with respect to p0
while (i < n-1 && orientation(p0, points[i],
points[i+1]) == 0)
i++;
points[m] = points[i];
m++; // Update size of modified array
}
// If modified array of points has less than 3 points,
// convex hull is not possible
if (m < 3) return;
// Create an empty stack and push first three points
// to it.
stack<Point> S;
S.push(points[0]);
S.push(points[1]);
S.push(points[2]);
// Process remaining n-3 points
for (int i = 3; i < m; i++)
{
// Keep removing top while the angle formed by
// points next-to-top, top, and points[i] makes
// a non-left turn
while (S.size()>1 && orientation(nextToTop(S), S.top(), points[i]) != 2)
S.pop();
S.push(points[i]);
}
// Now stack has the output points, print contents of stack
while (!S.empty())
{
Point p = S.top();
cout << "(" << p.x << ", " << p.y <<")" << endl;
S.pop();
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
Point points[] = {{0, 3}, {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {4, 4},
{0, 0}, {1, 2}, {3, 1}, {3, 3}};
int n = sizeof(points)/sizeof(points[0]);
convexHull(points, n);
return 0;
}
Python3
# A Python3 program to find convex hull of a set of points. Refer
# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/orientation-3-ordered-points/
# for explanation of orientation()
from functools import cmp_to_key
# A class used to store the x and y coordinates of points
class Point:
def __init__(self, x = None, y = None):
self.x = x
self.y = y
# A global point needed for sorting points with reference
# to the first point
p0 = Point(0, 0)
# A utility function to find next to top in a stack
def nextToTop(S):
return S[-2]
# A utility function to return square of distance
# between p1 and p2
def distSq(p1, p2):
return ((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) +
(p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y))
# To find orientation of ordered triplet (p, q, r).
# The function returns following values
# 0 --> p, q and r are collinear
# 1 --> Clockwise
# 2 --> Counterclockwise
def orientation(p, q, r):
val = ((q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x) -
(q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y))
if val == 0:
return 0 # collinear
elif val > 0:
return 1 # clock wise
else:
return 2 # counterclock wise
# A function used by cmp_to_key function to sort an array of
# points with respect to the first point
def compare(p1, p2):
# Find orientation
o = orientation(p0, p1, p2)
if o == 0:
if distSq(p0, p2) >= distSq(p0, p1):
return -1
else:
return 1
else:
if o == 2:
return -1
else:
return 1
# Prints convex hull of a set of n points.
def convexHull(points, n):
# Find the bottommost point
ymin = points[0].y
min = 0
for i in range(1, n):
y = points[i].y
# Pick the bottom-most or choose the left
# most point in case of tie
if ((y < ymin) or
(ymin == y and points[i].x < points[min].x)):
ymin = points[i].y
min = i
# Place the bottom-most point at first position
points[0], points[min] = points[min], points[0]
# Sort n-1 points with respect to the first point.
# A point p1 comes before p2 in sorted output if p2
# has larger polar angle (in counterclockwise
# direction) than p1
p0 = points[0]
points = sorted(points, key=cmp_to_key(compare))
# If two or more points make same angle with p0,
# Remove all but the one that is farthest from p0
# Remember that, in above sorting, our criteria was
# to keep the farthest point at the end when more than
# one points have same angle.
m = 1 # Initialize size of modified array
for i in range(1, n):
# Keep removing i while angle of i and i+1 is same
# with respect to p0
while ((i < n - 1) and
(orientation(p0, points[i], points[i + 1]) == 0)):
i += 1
points[m] = points[i]
m += 1 # Update size of modified array
# If modified array of points has less than 3 points,
# convex hull is not possible
if m < 3:
return
# Create an empty stack and push first three points
# to it.
S = []
S.append(points[0])
S.append(points[1])
S.append(points[2])
# Process remaining n-3 points
for i in range(3, m):
# Keep removing top while the angle formed by
# points next-to-top, top, and points[i] makes
# a non-left turn
while ((len(S) > 1) and
(orientation(nextToTop(S), S[-1], points[i]) != 2)):
S.pop()
S.append(points[i])
# Now stack has the output points,
# print contents of stack
while S:
p = S[-1]
print("(" + str(p.x) + ", " + str(p.y) + ")")
S.pop()
# Driver Code
input_points = [(0, 3), (1, 1), (2, 2), (4, 4),
(0, 0), (1, 2), (3, 1), (3, 3)]
points = []
for point in input_points:
points.append(Point(point[0], point[1]))
n = len(points)
convexHull(points, n)
# This code is contributed by Kevin Joshi
Javascript
// JavaScript program to find convex hull of a set of
// points. Refer
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/orientation-3-ordered-points/
// for explanation of orientation()
// A class used to store the x and y coordinates of points
class Point {
constructor(x = null, y = null)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
// A global point needed for sorting points with reference
// to the first point
let p0
= new Point(0, 0);
// A utility function to find next to top in a stack
function nextToTop(S) { return S[S.length - 2]; }
// A utility function to return square of distance
// between p1 and p2
function distSq(p1, p2)
{
return ((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x)
+ (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y));
}
// To find orientation of ordered triplet (p, q, r).
// The function returns following values
// 0 --> p, q and r are collinear
// 1 --> Clockwise
// 2 --> Counterclockwise
function orientation(p, q, r)
{
let val = ((q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x)
- (q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y));
if (val == 0)
return 0; // collinear
else if (val > 0)
return 1; // clock wise
else
return 2; // counterclock wise
}
// A function used by cmp_to_key function to sort an array
// of points with respect to the first point
function compare(p1, p2)
{
// Find orientation
let o = orientation(p0, p1, p2);
if (o == 0) {
if (distSq(p0, p2) >= distSq(p0, p1))
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
else {
if (o == 2)
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
}
// Prints convex hull of a set of n points.
function convexHull(points, n)
{
// Find the bottommost point
let ymin = points[0].y;
let min = 0;
for (var i = 1; i < n; i++) {
let y = points[i].y;
// Pick the bottom-most or choose the left
// most point in case of tie
if ((y < ymin)
|| ((ymin == y)
&& (points[i].x < points[min].x))) {
ymin = points[i].y;
min = i;
}
}
// Place the bottom-most point at first position
points[0], points[min] = points[min], points[0];
// Sort n-1 points with respect to the first point.
// A point p1 comes before p2 in sorted output if p2
// has larger polar angle (in counterclockwise
// direction) than p1
let p0 = points[0];
points.sort(compare);
// If two or more points make same angle with p0,
// Remove all but the one that is farthest from p0
// Remember that, in above sorting, our criteria was
// to keep the farthest point at the end when more than
// one points have same angle.
let m = 1; // Initialize size of modified array
for (var i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// Keep removing i while angle of i and i+1 is same
// with respect to p0
while ((i < n - 1)
&& (orientation(p0, points[i], points[i + 1])
== 0))
i += 1;
points[m] = points[i];
m += 1; // Update size of modified array
}
// If modified array of points has less than 3 points,
// convex hull is not possible
if (m < 3)
return;
// Create an empty stack and push first three points
// to it.
let S = [];
S.push(points[0]);
S.push(points[1]);
S.push(points[2]);
// Process remaining n-3 points
for (var i = 3; i < m; i++) {
// Keep removing top while the angle formed by
// points next-to-top, top, and points[i] makes
// a non-left turn
while (true) {
if (S.length < 2)
break;
if (orientation(nextToTop(S), S[S.length - 1],
points[i])
>= 2)
break;
S.pop();
}
S.push(points[i]);
}
// Now stack has the output points,
// print contents of stack
while (S.length > 0) {
let p = S[S.length - 1];
console.log("(" + p.x + ", " + p.y + ")");
S.pop();
}
}
// Driver Code
let points = [
new Point(0, 3), new Point(1, 1), new Point(2, 2),
new Point(4, 4), new Point(0, 0), new Point(1, 2),
new Point(3, 1), new Point(3, 3)
];
let n = points.length;
convexHull(points, n);
// This code is contributed by phasing17
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA