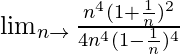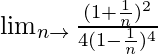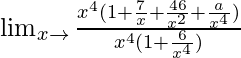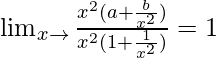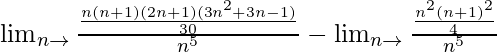Pregunta 14. Lim n→∞ {1 2 + 2 2 + ……………. + n 2 }/(n 3 )
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lim n→∞ {1 2 + 2 2 + ……………. + n 2 }/(n 3 )
= Lím n→∞ [n(n+1)(2n+1)]/6n 3
= Lím n→∞ [(n+1)(2n+1)]/6n 2
=
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n) → 0
= 2/6
= 1/3
Pregunta 15. Lim n→∞ {1 + 2 + 3 + 4 +………………. + n – 1}/n 2
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lim n→∞ {1 + 2 + 3 + 4 +………………. + n – 1}/n 2
= Lím n→∞ [n(n – 1)/2n 2 ]
= Lím n→∞ [n 2 – n/2n 2 ]
= Lím n→∞ (1/2 – 1/2n)
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n) → 0
= 1/2
Pregunta 16. Lim n→∞ {1 3 + 2 3 + ……………. + n 3 }/(n 4 )
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lim n→∞ {1 3 + 2 3 + ……………. + n 3 }/(n 4 )
= Lim n→∞ [n 2 (n + 1) 2 ]/(4n 4 ) [puesto que (1 3 + 2 3 + …………. + n 3 ) = n 2 (n + 1) 2 /4]
= Lim n→∞ [(n + 1) 2 ]/(4n 2 )
= Lim n→∞ [(1 + 1/n) 2 × (1/4)]
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n) → 0
= 1/4
Pregunta 17. Lim n→∞ {1 3 + 2 3 + ……………. + n 3 }/(n – 1) 4
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lim n→∞ {1 3 + 2 3 + ……………. + n 3 }/(n – 1) 4
= Lim n→∞ [n 2 (n + 1) 2 ]/[4(n – 1) 4 ] [ya que (1 3 + 2 3 + …………. + n 3 ) = n 2 (n + 1 ) 2 /4]
=
=
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n) → 0
= 1/4
Pregunta 18. Lim x→∞ [√x{√(x + 1) – √x}]
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lim x→∞ [√x{√(x + 1) – √x}]
Al racionalizar el numerador, obtenemos
= Lim x→∞ [(√x){(x + 1) – x}]/{√(x + 1) + √x}
= Lim x→∞ (√x}/{√(x + 1) + √x}
=
Cuando x → ∞, (1/x) → 0.
= 1/(√1 + 1)
= 1/2
Pregunta 19. Lim x→∞ [1/3 + 1/3 2 + 1/3 3 + ……………… + 1/3 n ]
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lim x→∞ [1/3 + 1/3 2 + 1/3 3 + ……………… + 1/3 n ]
Esta es la serie GP de relación común 1/3.
Entonces, la suma de n términos de GP S n = [a(1 – r n )]/(1 – r) (i)
a = 1/3, r = 1/3
Al poner el valor de a & r en la ecuación (i), obtenemos
Sn = (1/2)(1 – 1 / 3n )
= Lim x→∞ [(1/2)(1 – 1/3 n )]
= (1/2)Lím x→∞ (1 – 1/3 n )
= (1/2)(1 – 0)
= 1/2
Pregunta 20. Lim x→∞ {(x 4 + 7x 3 + 46x + a)}/{(x 4 + 6)}.
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lim x→∞ {(x 4 + 7x 3 + 46x + a)}/{(x 4 + 6)}
=
Cuando x → ∞, (1/x), (1/x 2 ), (1/x 3 ), (1/x 4 ) → 0
= 1/1
= 1
Pregunta 21. f(x) = (ax 2 + b)/(x 2 + 1), Lim x→0 f(x) = 1, Lim x→∞ f(x) = 1, luego prueba que f(- 2) = f(2) = 1
Solución:
Tenemos,
f(x) = (ax 2 + b)/(x 2 + 1)
= Lim x→0 [(ax 2 + b)/(x 2 + 1)]
b/1 = 1
segundo = 1
= Lim x→∞ [(ax 2 + b)/(x 2 + 1)]
=
Cuando x → ∞, (1/x 2 ) → 0.
(a + 0)/(1 + 0) = 1
un = 1
Por lo tanto, a = 1, b = 1
f(x) = (x2 + 1)/(x2 + 1)
f(x) = 1
f(-2) = 1
f(2) = 1 (Ya que f(x) es independiente de x)
f(-2) = f(2) = 1
Por lo tanto probado
Pregunta 22. Demuestra que Lim x→∞ [√(x 2 + x + 1) – x] ≠ Lim x→∞ [√(x 2 + 1) – x]
Solución:
Tenemos,
LHS,
= Lim x→∞ [√(x 2 + x + 1) – x]
Al racionalizar el numerador, obtenemos
= Límite x→∞ [(x 2 + x + 1) – x 2 ]/[√(x 2 + x + 1) + x]
= Lim x→∞ (x + 1)/[√(x 2 + x + 1) + x]
= Lim x→∞ [x(1 + 1/x)/[x{√(1 + 1/x + 1/x 2 ) + 1}]
= Lim x→∞ [(1 + 1/x)/[{√(1 + 1/x + 1/x 2 ) + 1}]
Cuando x → ∞, (1/x), (1/x 2 ) → 0.
= 1/(√1 + 1)
= 1/2
Ahora resolvemos RHS,
= Lim x→∞ [√(x 2 + 1) – x]
Al racionalizar el numerador, obtenemos
= Límite x→∞ [(x 2 + 1) – x 2 ]/[√(x 2 + 1) + x]
= Lim x→∞ (1)/[√(x 2 + 1) + x]
= 1/[√(∞ + 1) + ∞]
= 1/∞
= 0
IZQ ≠ DERECHO
Por lo tanto, Lim x→∞ [√(x 2 + x + 1) – x] ≠ Lim x→∞ [√(x 2 + 1) – x]
Pregunta 23. Lim x→-∞ [√(4x 2 – 7x) + 2x]
Solución:
Tenemos,
Límite x→-∞ [√(4x 2 – 7x) + 2x]
Sea x = -n cuando x → -∞, entonces n → ∞.
= Lím n→∞ [√(4n 2 + 7n) – 2n]
Al racionalizar el numerador, obtenemos
= Lim n→∞ [(4n 2 + 7n) – 4n 2 ]/[√(4n 2 + 7n) + 2n]
= Lim n→∞ [(7n)/[√(4n 2 + 7n) + 2n]
= Lim n→∞ (7n)/[n{√(4 + 7/n) + 2}]
= Lim n→∞ (7)/{√(4 + 7/n) + 2}
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n) → 0
= 7/(√4 + 2)
= 7/(2 + 2)
= 7/4
Pregunta 24. Lim x→-∞ [√(x 2 – 8x) + x]
Solución:
Tenemos,
Límite x→-∞ [√(x 2 – 8x) + x]
Sea x = -n cuando x → -∞, entonces n → ∞.
= Lim n→∞ [√(n 2 + 8n) – n]
Al racionalizar el numerador, obtenemos
= Lim n→∞ [(n 2 + 8n) – n 2 ]/[√(n 2 + 8n) + n]
= Lim n→∞ [(8n)/[√(n 2 + 8n) + n]
= Lim n→∞ (8n)/[n{√(1 + 8/n) + 1}]
= Lim n→∞ (8)/{√(1 + 8/n) + 1}
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n) → 0
= 8/(√1 + 1)
= 8/2
= 4
Pregunta 25. Lim n→∞ (1 4 + 2 4 + ……….+ n 4 )/n 5 – Lim n→∞ (1 3 + 2 3 + ………. + n 3 )/n 5
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lím n→∞ (1 4 + 2 4 + ……….+ n 4 )/n 5 – Lím n→∞ (1 3 + 2 3 + ………. + n 3 )/n 5
=
=
=
=
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n), (1/n 2 ), (1/n 3 ) → 0
= 1/3 × 1 × 2 × 3 – 1/4 × 0
= 6/30
= 1/5
Pregunta 26. Lim n→∞ {(1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 + ……….+ n (n + 1)}/n 3
Solución:
Tenemos,
Lím n→∞ {(1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 + ……….+ n (n + 1)}/n 3
=
=
=
=
=
=
Cuando n → ∞, (1/n) → 0
= (1 × 2)/6
= 2/6
= 1/3
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por vivekray59 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA