Requisitos previos: ordenación por inserción , ordenación rápida , ordenación por selección
En este artículo, se implementa un algoritmo híbrido con la combinación de ordenación rápida y ordenación por inserción . Como sugiere el nombre, el algoritmo híbrido combina más de un algoritmo.
Por qué Algoritmo híbrido: el algoritmo
Quicksort es eficiente si el tamaño de la entrada es muy grande. Sin embargo, la ordenación por inserción es más eficiente que la ordenación rápida en el caso de arreglos pequeños, ya que la cantidad de comparaciones e intercambios es menor en comparación con la ordenación rápida. Así que combinamos los dos algoritmos para ordenar eficientemente usando ambos enfoques.
Nota: ordenación por selecciónEl algoritmo también se puede usar para combinar con quicksort . Aunque la complejidad de tiempo es de O(N 2 ), estos algoritmos demuestran ser eficientes en este caso porque se usan solo cuando el tamaño de la array es menor que un valor de umbral ( 10 en este artículo).
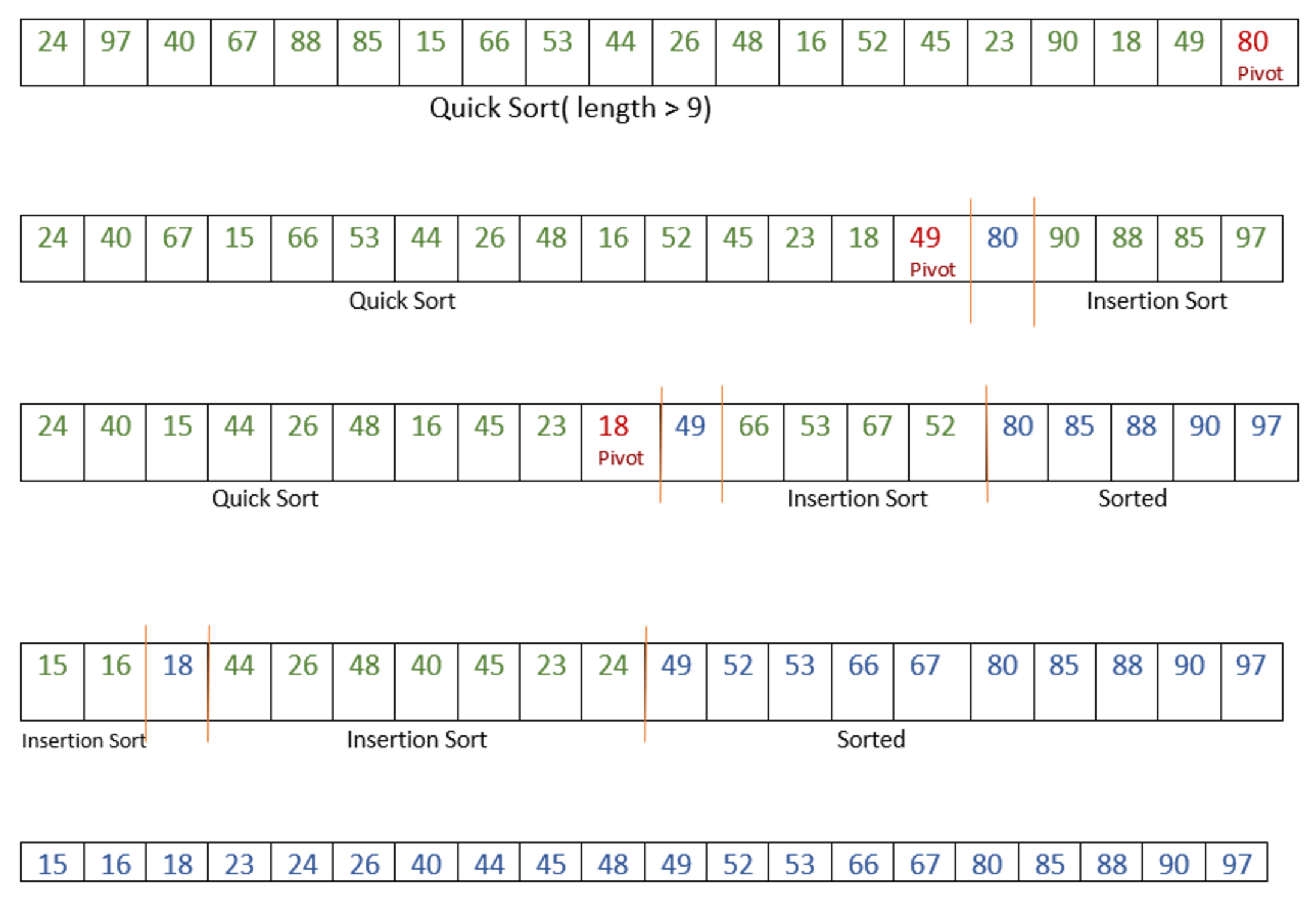
Ejecución en seco del algoritmo:
Sea arr[] = {24, 97, 40, 67, 88, 85, 15, 66, 53, 44, 26, 48, 16, 52, 45, 23, 90, 18, 49, 80}
Enfoque: La idea es usar la recursividad y encontrar continuamente el tamaño de la array. Si el tamaño es mayor que el valor de umbral (10), se llama a la función de clasificación rápida para esa parte de la array. De lo contrario, se llama a la ordenación por inserción.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del algoritmo híbrido:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to perform the insertion sort
void insertion_sort(int arr[], int low, int n)
{
for(int i=low+1;i<n+1;i++)
{
int val = arr[i] ;
int j = i ;
while (j>low && arr[j-1]>val)
{
arr[j]= arr[j-1] ;
j-= 1;
}
arr[j]= val ;
}
}
//The following two functions are used
// to perform quicksort on the array.
// Partition function for quicksort
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high] ;
int i ,j;
i = low;
j = low;
for (int i = low; i < high; i++)
{
if(arr[i]<pivot)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
j += 1;
}
}
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return j;
}
// Function to call the partition function
// and perform quick sort on the array
void quick_sort(int arr[], int low,int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high);
quick_sort(arr, low, pivot-1) ;
quick_sort(arr, pivot + 1, high) ;
}
}
// Hybrid function -> Quick + Insertion sort
void hybrid_quick_sort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
while (low < high)
{
// If the size of the array is less
// than threshold apply insertion sort
// and stop recursion
if (high-low + 1 < 10)
{
insertion_sort(arr, low, high);
break;
}
else
{
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high) ;
// Optimised quicksort which works on
// the smaller arrays first
// If the left side of the pivot
// is less than right, sort left part
// and move to the right part of the array
if (pivot-low<high-pivot)
{
hybrid_quick_sort(arr, low, pivot - 1);
low = pivot + 1;
}
else
{
// If the right side of pivot is less
// than left, sort right side and
// move to the left side
hybrid_quick_sort(arr, pivot + 1, high);
high = pivot-1;
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[21] = { 24, 97, 40, 67, 88, 85, 15,
66, 53, 44, 26, 48, 16, 52,
45, 23, 90, 18, 49, 80, 23 };
hybrid_quick_sort(arr, 0, 20);
for(int i = 0; i < 21; i++)
cout << arr[i] << ", ";
}
// This code is contributed by ishayadav2918
Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
private static void insertionSort(int a[], int low,
int high)
{
for (int i = low + 1; i <= high; i++) {
for (int j = i - 1; j >= low; j--) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
// Swap
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
else
break;
}
}
}
private static int partition(int arr[], int low,
int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low;
int j = low;
while (i <= high) {
if (arr[i] > pivot)
i++;
else {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
i++;
j++;
}
}
return j - 1;
}
public static void hybridQuickSort(int arr[], int low,
int high)
{
while (low < high) {
// Check if array size on which we will be working is less than 10
if (high - low < 10) {
insertionSort(arr, low, high);
break;
}
else {
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high);
// We will do recursion on small size
// subarray So we can check pivot - low and
// pivot - high
if (pivot - low < pivot - high) {
hybridQuickSort(arr, low, pivot - 1);
low = pivot + 1;
}
else {
hybridQuickSort(arr, pivot + 1, high);
high = pivot - 1;
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[]
= { 24, 97, 40, 67, 88, 85, 15, 66, 53, 44, 26,
48, 16, 52, 45, 23, 90, 18, 49, 80, 23 };
hybridQuickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
for (int i : arr)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// This code is contribute by @mahi_07
Python3
# Python implementation of the above approach # Function to perform the insertion sort def insertion_sort(arr, low, n): for i in range(low + 1, n + 1): val = arr[i] j = i while j>low and arr[j-1]>val: arr[j]= arr[j-1] j-= 1 arr[j]= val # The following two functions are used # to perform quicksort on the array. # Partition function for quicksort def partition(arr, low, high): pivot = arr[high] i = j = low for i in range(low, high): if arr[i]<pivot: a[i], a[j]= a[j], a[i] j+= 1 a[j], a[high]= a[high], a[j] return j # Function to call the partition function # and perform quick sort on the array def quick_sort(arr, low, high): if low<high: pivot = partition(arr, low, high) quick_sort(arr, low, pivot-1) quick_sort(arr, pivot + 1, high) return arr # Hybrid function -> Quick + Insertion sort def hybrid_quick_sort(arr, low, high): while low<high: # If the size of the array is less # than threshold apply insertion sort # and stop recursion if high-low + 1<10: insertion_sort(arr, low, high) break else: pivot = partition(arr, low, high) # Optimised quicksort which works on # the smaller arrays first # If the left side of the pivot # is less than right, sort left part # and move to the right part of the array if pivot-low<high-pivot: hybrid_quick_sort(arr, low, pivot-1) low = pivot + 1 else: # If the right side of pivot is less # than left, sort right side and # move to the left side hybrid_quick_sort(arr, pivot + 1, high) high = pivot-1 # Driver code a = [ 24, 97, 40, 67, 88, 85, 15, 66, 53, 44, 26, 48, 16, 52, 45, 23, 90, 18, 49, 80, 23 ] hybrid_quick_sort(a, 0, 20) print(a)
15, 16, 18, 23, 23, 24, 26, 40, 44, 45, 48, 49, 52, 53, 66, 67, 80, 85, 88, 90, 97,
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N^2)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)