Un árbol ordenado es un árbol orientado en el que los hijos de un Node están ordenados de alguna manera. Es un árbol enraizado en el que se especifica un ordenamiento para los hijos de cada vértice. Esto se llama un «árbol plano» porque el orden de los hijos es equivalente a una incrustación del árbol en el plano, con la raíz en la parte superior y los hijos de cada vértice por debajo de ese vértice.
Los árboles ordenados se pueden especificar más como árboles ordenados etiquetados y árboles ordenados no etiquetados.
Prerrequisito: Números Catalanes | Coeficiente binomial .
Árboles ordenados etiquetados: un árbol etiquetado es un árbol en el que a cada vértice se le asigna un número único del 1 al n.

Si T1 y T2 son árboles ordenados. Entonces, T1 != T2 sino T1 = T2.
Árboles ordenados sin etiqueta: un árbol sin etiqueta es un árbol en el que todos los vértices no están etiquetados. A continuación se muestran los posibles árboles ordenados sin etiqueta que tienen 3 vértices.

El número total de árboles ordenados sin etiquetar que tienen n Nodes es igual al (n – 1)-ésimo número catalán .
A continuación se muestran los posibles árboles ordenados sin etiqueta que tienen 4 Nodes. Este diagrama funcionará como un ejemplo de referencia para los próximos resultados.
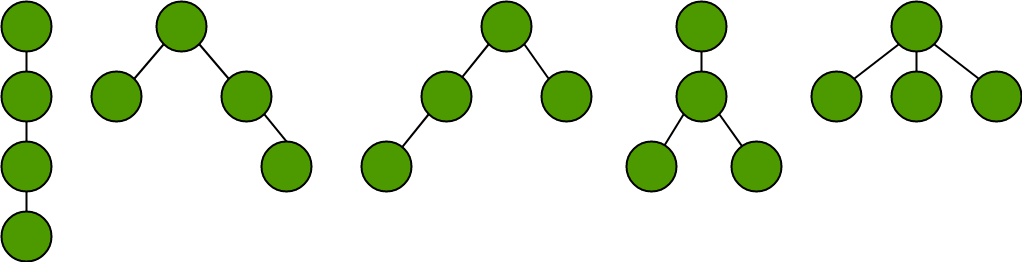
1. Número de árboles con exactamente k hojas.
Consideremos que tenemos aristas ‘n’. Entonces, la solución para el total de árboles ordenados posibles que tienen ‘k’ hojas está dada por:

2. Número total de Nodes de grado d en estos árboles.
Consideremos que tenemos aristas ‘n’. Entonces, la solución para el número total de Nodes que tienen un grado ‘d’ está dada por:

3. Número de árboles en los que la raíz tiene grado r.
Consideremos que tenemos aristas ‘n’. Entonces, la solución para el total de árboles ordenados posibles cuya raíz tiene grado ‘r’ está dada por:

A continuación se muestra la implementación de las funciones combinatorias anteriores utilizando el coeficiente binomial:
C++
// C++ code to find the number of ordered trees
// with given number of edges and leaves
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function returns value of
// Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int C[n + 1][k + 1] = { 0 };
int i, j;
// Calculate value of Binomial
// Coefficient in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= min(i, k); j++) {
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i][j] = 1;
// Calculate value using
// previously stored values
else
C[i][j] = C[i - 1][j - 1] + C[i - 1][j];
}
}
return C[n][k];
}
// Function to calculate the number
// of trees with exactly k leaves.
int k_Leaves(int n, int k)
{
int ans = (binomialCoeff(n, k) * binomialCoeff(n, k - 1)) / n;
cout << "Number of trees having 4 edges"
<< " and exactly 2 leaves : " << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate total number of
// nodes of degree d in these trees.
int numberOfNodes(int n, int d)
{
int ans = binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - d, n - 1);
cout << "Number of nodes of degree 1 in"
<< " a tree having 4 edges : " << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// trees in which the root has degree r.
int rootDegreeR(int n, int r)
{
int ans = r * binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - r, n - 1);
ans = ans / n;
cout << "Number of trees having 4 edges"
<< " where root has degree 2 : " << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Number of trees having 3
// edges and exactly 2 leaves
k_Leaves(3, 2);
// Number of nodes of degree
// 3 in a tree having 4 edges
numberOfNodes(3, 1);
// Number of trees having 3
// edges where root has degree 2
rootDegreeR(3, 2);
return 0;
}
Java
// java code to find the number of ordered
// trees with given number of edges and
// leaves
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Function returns value of
// Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
static int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int [][]C = new int[n+1][k+1];
int i, j;
// Calculate value of Binomial
// Coefficient in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= Math.min(i, k); j++)
{
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i][j] = 1;
// Calculate value using
// previously stored values
else
C[i][j] = C[i - 1][j - 1]
+ C[i - 1][j];
}
}
return C[n][k];
}
// Function to calculate the number
// of trees with exactly k leaves.
static int k_Leaves(int n, int k)
{
int ans = (binomialCoeff(n, k) *
binomialCoeff(n, k - 1)) / n;
System.out.println( "Number of trees "
+ "having 4 edges and exactly 2 "
+ "leaves : " + ans) ;
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate total number of
// nodes of degree d in these trees.
static int numberOfNodes(int n, int d)
{
int ans = binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - d,
n - 1);
System.out.println("Number of nodes "
+"of degree 1 in a tree having 4 "
+ "edges : " + ans);
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// trees in which the root has degree r.
static int rootDegreeR(int n, int r)
{
int ans = r * binomialCoeff(2 * n
- 1 - r, n - 1);
ans = ans / n;
System.out.println("Number of trees "
+ "having 4 edges where root has"
+ " degree 2 : " + ans);
return 0;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Number of trees having 3
// edges and exactly 2 leaves
k_Leaves(3, 2);
// Number of nodes of degree
// 3 in a tree having 4 edges
numberOfNodes(3, 1);
// Number of trees having 3
// edges where root has degree 2
rootDegreeR(3, 2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
Python3
# Python3 code to find the number of ordered
# trees with given number of edges and
# leaves
# Function returns value of
# Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
def binomialCoeff(n, k):
C = [[0 for i in range(k + 1)]
for j in range(n + 1)]
# Calculate value of Binomial
# Coefficient in bottom up manner
for i in range(n + 1):
for j in range(min(i, k) + 1):
# Base Cases
if (j == 0 or j == i):
C[i][j] = 1
# Calculate value using
# previously stored values
else:
C[i][j] = (C[i - 1][j - 1] +
C[i - 1][j])
return C[n][k]
# Function to calculate the number
# of trees with exactly k leaves.
def k_Leaves(n, k):
ans = ((binomialCoeff(n, k) *
binomialCoeff(n, k - 1)) // n)
print("Number of trees ",
"having 4 edges and exactly 2 ",
"leaves : ", ans)
# Function to calculate total number of
# Nodes of degree d in these trees.
def numberOfNodes(n, d):
ans = binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - d, n - 1)
print("Number of Nodes ",
"of degree 1 in a tree having 4 ",
"edges : ", ans)
# Function to calculate the number of
# trees in which the root has degree r.
def rootDegreeR(n, r):
ans = r * binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - r, n - 1)
ans = ans // n
print("Number of trees ",
"having 4 edges where root has ",
"degree 2 : ", ans)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Number of trees having 3
# edges and exactly 2 leaves
k_Leaves(3, 2)
# Number of Nodes of degree
# 3 in a tree having 4 edges
numberOfNodes(3, 1)
# Number of trees having 3
# edges where root has degree 2
rootDegreeR(3, 2)
# This code is contributed by aashish1995
C#
// C# code to find the number of ordered
// trees with given number of edges and
// leaves
using System;
class GFG {
// Function returns value of
// Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
static int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int [,]C = new int[n+1,k+1];
int i, j;
// Calculate value of Binomial
// Coefficient in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= Math.Min(i, k); j++)
{
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i,j] = 1;
// Calculate value using
// previously stored values
else
C[i,j] = C[i - 1,j - 1]
+ C[i - 1,j];
}
}
return C[n,k];
}
// Function to calculate the number
// of trees with exactly k leaves.
static int k_Leaves(int n, int k)
{
int ans = (binomialCoeff(n, k) *
binomialCoeff(n, k - 1)) / n;
Console.WriteLine( "Number of trees "
+ "having 4 edges and exactly 2 "
+ "leaves : " + ans) ;
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate total number of
// nodes of degree d in these trees.
static int numberOfNodes(int n, int d)
{
int ans = binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - d,
n - 1);
Console.WriteLine("Number of nodes "
+"of degree 1 in a tree having 4 "
+ "edges : " + ans);
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// trees in which the root has degree r.
static int rootDegreeR(int n, int r)
{
int ans = r * binomialCoeff(2 * n
- 1 - r, n - 1);
ans = ans / n;
Console.WriteLine("Number of trees "
+ "having 4 edges where root has"
+ " degree 2 : " + ans);
return 0;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main ()
{
// Number of trees having 3
// edges and exactly 2 leaves
k_Leaves(3, 2);
// Number of nodes of degree
// 3 in a tree having 4 edges
numberOfNodes(3, 1);
// Number of trees having 3
// edges where root has degree 2
rootDegreeR(3, 2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
PHP
<?php
// PHP code to find the number of ordered
// trees with given number of edges and
// leaves
// Function returns value of Binomial
// Coefficient C(n, k)
function binomialCoeff($n, $k)
{
$C = array(array());
$i; $j;
// Calculate value of Binomial
// Coefficient in bottom up manner
for ($i = 0; $i <= $n; $i++) {
for ($j = 0; $j <= min($i, $k); $j++)
{
// Base Cases
if ($j == 0 or $j == $i)
$C[$i][$j] = 1;
// Calculate value using
// previously stored values
else
$C[$i][$j] = $C[$i - 1][$j - 1]
+ $C[$i - 1][$j];
}
}
return $C[$n][$k];
}
// Function to calculate the number
// of trees with exactly k leaves.
function k_Leaves( $n, $k)
{
$ans = (binomialCoeff($n, $k) *
binomialCoeff($n, $k - 1)) / $n;
echo "Number of trees having 4 edges and ",
"exactly 2 leaves : " , $ans ,"\n";
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate total number of
// nodes of degree d in these trees.
function numberOfNodes( $n, $d)
{
$ans = binomialCoeff(2 * $n - 1 - $d, $n - 1);
echo "Number of nodes of degree 1 in"
, " a tree having 4 edges : " , $ans,"\n" ;
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// trees in which the root has degree r.
function rootDegreeR( $n, $r)
{
$ans = $r * binomialCoeff(2 * $n - 1 - $r,
$n - 1);
$ans = $ans / $n;
echo "Number of trees having 4 edges"
, " where root has degree 2 : " , $ans ;
return 0;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
// Number of trees having 3
// edges and exactly 2 leaves
k_Leaves(3, 2);
// Number of nodes of degree
// 3 in a tree having 4 edges
numberOfNodes(3, 1);
// Number of trees having 3
// edges where root has degree 2
rootDegreeR(3, 2);
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
Javascript
<script>
// javascript code to find the number of ordered
// trees with given number of edges and leaves
// Function returns value of
// Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
function binomialCoeff(n, k)
{
let C = new Array(n+1);
let i, j;
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
C[i] = new Array(k + 1);
for (j = 0; j <= k; j++)
{
C[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Calculate value of Binomial
// Coefficient in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= Math.min(i, k); j++)
{
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i][j] = 1;
// Calculate value using
// previously stored values
else
C[i][j] = C[i - 1][j - 1]
+ C[i - 1][j];
}
}
return C[n][k];
}
// Function to calculate the number
// of trees with exactly k leaves.
function k_Leaves(n, k)
{
let ans = parseInt((binomialCoeff(n, k) * binomialCoeff(n, k - 1)) / n, 10);
document.write( "Number of trees "
+ "having 4 edges and exactly 2 "
+ "leaves : " + ans + "</br>");
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate total number of
// nodes of degree d in these trees.
function numberOfNodes(n, d)
{
let ans = binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - d,
n - 1);
document.write("Number of nodes "
+"of degree 1 in a tree having 4 "
+ "edges : " + ans + "</br>");
return 0;
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// trees in which the root has degree r.
function rootDegreeR(n, r)
{
let ans = r * binomialCoeff(2 * n - 1 - r, n - 1);
ans = parseInt(ans / n, 10);
document.write("Number of trees "
+ "having 4 edges where root has"
+ " degree 2 : " + ans + "</br>");
return 0;
}
// Number of trees having 3
// edges and exactly 2 leaves
k_Leaves(3, 2);
// Number of nodes of degree
// 3 in a tree having 4 edges
numberOfNodes(3, 1);
// Number of trees having 3
// edges where root has degree 2
rootDegreeR(3, 2);
</script>
Number of trees having 4 edges and exactly 2 leaves : 3 Number of nodes of degree 1 in a tree having 4 edges : 6 Number of trees having 4 edges where root has degree 2 : 2
Complejidad temporal: O(n*k).
Espacio Auxiliar : O(n*k).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sumit.chauhan y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA