Como hemos visto, podemos crear un hermoso gráfico de barras en Android, pero ¿qué pasa si tenemos que representar datos en forma de grupos en nuestro gráfico de barras? Para que podamos trazar un grupo de datos en nuestro gráfico de barras. Por lo tanto, crearemos un gráfico de barras de grupo en nuestra aplicación de Android en este artículo.
¿Qué vamos a construir en este artículo?
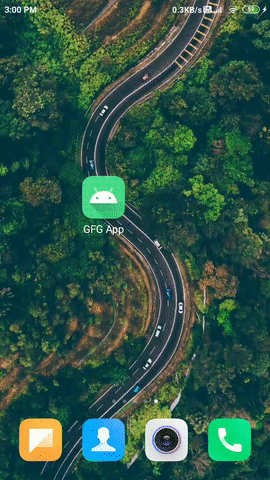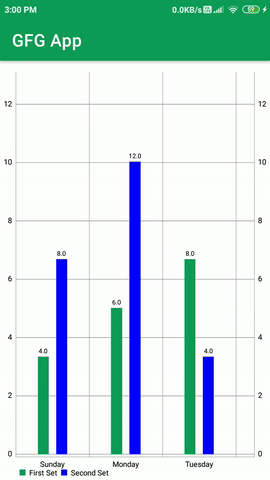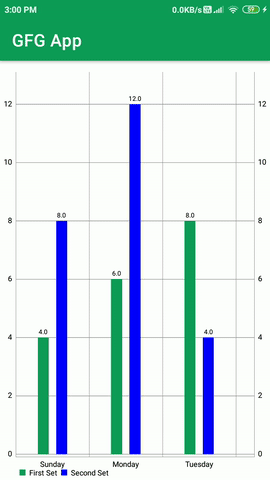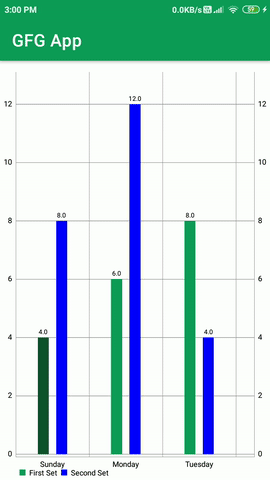
Construiremos una aplicación simple en la que mostraremos un gráfico de barras con múltiples conjuntos de datos en nuestra aplicación de Android. Mostraremos los datos en forma de grupo en nuestro gráfico de barras. qué
Implementación paso a paso
Paso 1: Crear un nuevo proyecto
Para crear un nuevo proyecto en Android Studio, consulte Cómo crear/iniciar un nuevo proyecto en Android Studio . Tenga en cuenta que seleccione Java como lenguaje de programación.
Paso 2: agregue la dependencia y el repositorio de JitPack
Navegue a Gradle Scripts > build.gradle(Module:app) y agregue la siguiente dependencia en la sección de dependencias.
implementación ‘com.github.PhilJay:MPAndroidChart:v3.1.0’
Agregue el repositorio de JitPack a su archivo de compilación. Agréguelo a su root build.gradle al final de los repositorios dentro de la sección allprojects{ }.
todos los proyectos {
repositorios {
…
experto {url «https://jitpack.io»}
}
}
Después de agregar esta dependencia, sincronice su proyecto y ahora avanzaremos hacia su implementación.
Paso 3: trabajar con el archivo activity_main.xml
Vaya a la aplicación > res > diseño > actividad_principal.xml y agregue el siguiente código a ese archivo. A continuación se muestra el código para el archivo activity_main.xml .
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <!--Ui component for our bar chart--> <com.github.mikephil.charting.charts.BarChart android:id="@+id/idBarChart" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </RelativeLayout>
Paso 4: trabajar con el archivo MainActivity.java
Vaya al archivo MainActivity.java y consulte el siguiente código. A continuación se muestra el código del archivo MainActivity.java . Se agregan comentarios dentro del código para comprender el código con más detalle.
Java
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.github.mikephil.charting.charts.BarChart;
import com.github.mikephil.charting.components.XAxis;
import com.github.mikephil.charting.data.BarData;
import com.github.mikephil.charting.data.BarDataSet;
import com.github.mikephil.charting.data.BarEntry;
import com.github.mikephil.charting.formatter.IndexAxisValueFormatter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// variable for our bar chart
BarChart barChart;
// variable for our bar data set.
BarDataSet barDataSet1, barDataSet2;
// array list for storing entries.
ArrayList barEntries;
// creating a string array for displaying days.
String[] days = new String[]{"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// initializing variable for bar chart.
barChart = findViewById(R.id.idBarChart);
// creating a new bar data set.
barDataSet1 = new BarDataSet(getBarEntriesOne(), "First Set");
barDataSet1.setColor(getApplicationContext().getResources().getColor(R.color.purple_200));
barDataSet2 = new BarDataSet(getBarEntriesTwo(), "Second Set");
barDataSet2.setColor(Color.BLUE);
// below line is to add bar data set to our bar data.
BarData data = new BarData(barDataSet1, barDataSet2);
// after adding data to our bar data we
// are setting that data to our bar chart.
barChart.setData(data);
// below line is to remove description
// label of our bar chart.
barChart.getDescription().setEnabled(false);
// below line is to get x axis
// of our bar chart.
XAxis xAxis = barChart.getXAxis();
// below line is to set value formatter to our x-axis and
// we are adding our days to our x axis.
xAxis.setValueFormatter(new IndexAxisValueFormatter(days));
// below line is to set center axis
// labels to our bar chart.
xAxis.setCenterAxisLabels(true);
// below line is to set position
// to our x-axis to bottom.
xAxis.setPosition(XAxis.XAxisPosition.BOTTOM);
// below line is to set granularity
// to our x axis labels.
xAxis.setGranularity(1);
// below line is to enable
// granularity to our x axis.
xAxis.setGranularityEnabled(true);
// below line is to make our
// bar chart as draggable.
barChart.setDragEnabled(true);
// below line is to make visible
// range for our bar chart.
barChart.setVisibleXRangeMaximum(3);
// below line is to add bar
// space to our chart.
float barSpace = 0.1f;
// below line is use to add group
// spacing to our bar chart.
float groupSpace = 0.5f;
// we are setting width of
// bar in below line.
data.setBarWidth(0.15f);
// below line is to set minimum
// axis to our chart.
barChart.getXAxis().setAxisMinimum(0);
// below line is to
// animate our chart.
barChart.animate();
// below line is to group bars
// and add spacing to it.
barChart.groupBars(0, groupSpace, barSpace);
// below line is to invalidate
// our bar chart.
barChart.invalidate();
}
// array list for first set
private ArrayList<BarEntry> getBarEntriesOne() {
// creating a new array list
barEntries = new ArrayList<>();
// adding new entry to our array list with bar
// entry and passing x and y axis value to it.
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(1f, 4));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(2f, 6));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(3f, 8));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(4f, 2));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(5f, 4));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(6f, 1));
return barEntries;
}
// array list for second set.
private ArrayList<BarEntry> getBarEntriesTwo() {
// creating a new array list
barEntries = new ArrayList<>();
// adding new entry to our array list with bar
// entry and passing x and y axis value to it.
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(1f, 8));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(2f, 12));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(3f, 4));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(4f, 1));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(5f, 7));
barEntries.add(new BarEntry(6f, 3));
return barEntries;
}
}
Ahora ejecute su aplicación y vea el resultado de la aplicación.
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por chaitanyamunje y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA