Requisito previo: manejo de archivos a través de clases de C++
En C++ , los archivos se tratan principalmente mediante el uso de tres clases fstream, ifstream, ofstream disponibles en el archivo de encabezado fstream . En esta publicación, discutiremos cómo almacenar datos mediante el manejo de archivos .
La idea es tomar un ejemplo de Book Database e implementarlo de la misma manera en C++. A continuación se muestran las funciones utilizadas:
- Cómo insertar registro de libro
- Cómo ver todos los registros del libro
- Cómo buscar registro de libro
- Cómo borrar registro de libro
- Cómo actualizar el registro de libros
A continuación se muestra la implementación de las operaciones de manejo de archivos:
C++
// C++ program for implementing the above
// mentioned functionalities
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// Book class
class Book {
private:
int bookid;
// Max book title size 20
char title[20];
float price;
public:
// Default Constructor
Book()
{
bookid = 0;
strcpy(title, "no title");
price = 0;
}
// Function for taking book data
void getBookData()
{
cout << "Enter bookid, title, "
<< " price: ";
cin >> bookid;
cin.ignore();
cin.getline(title, 19);
cin >> price;
}
// Function for showing book data
void showBookData()
{
cout << "\n"
<< bookid
<< " " << title << " " << price;
}
int storeBook();
void viewAllBooks();
void searchBook(char*);
void deleteBook(char*);
void updateBook(char*);
};
// Function for update book data
void Book::updateBook(char* t)
{
fstream file;
// Open the file
file.open("myfile3.txt",
ios::in | ios::out | ios::ate | ios::binary);
file.seekg(0);
file.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
// Read the file
while (!file.eof()) {
if (!strcmp(t, title)) {
getBookData();
file.seekp(file.tellp() - sizeof(*this));
file.write((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
}
file.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
}
// Close the file
file.close();
}
// Function for delete book data
void Book::deleteBook(char* t)
{
ifstream fin;
ofstream fout;
fin.open("myfile3.txt",
ios::app | ios::binary);
if (!fin)
cout << "\n File not found";
else {
fout.open("tempfile.txt",
ios::app | ios::binary);
fin.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
// Until end of file is not reached
while (!fin.eof()) {
if (strcmp(title, t))
fout.write((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
fin.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
}
fin.close();
fout.close();
remove("myfile3.txt");
rename("tempfile.txt", "myfile3.txt");
}
}
// Function to search the Book
void Book::searchBook(char* t)
{
int counter = 0;
ifstream fin;
fin.open("myfile3.txt",
ios::in | ios::binary);
// If file is not found
if (!fin)
cout << "File not found";
else {
fin.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
// Until end of file is not reached
while (!fin.eof()) {
if (!strcmp(t, title)) {
showBookData();
counter++;
}
fin.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
}
if (counter == 0)
cout << "No record found";
fin.close();
}
}
// Function to view all the Book
void Book::viewAllBooks()
{
ifstream fin;
// Open function open file named
// myfile.txt
fin.open("myfile3.txt", ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!fin)
cout << "File not found";
else {
fin.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
// Until end of file is
// not reached
while (!fin.eof()) {
showBookData();
// read is object of ifstream
// class which is used for
// read data of file
fin.read((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
}
fin.close();
}
}
// Function to implement the store of
// all the books
int Book::storeBook()
{
if (bookid == 0 && price == 0) {
cout << "book data not"
<< " initialized";
return (0);
}
else {
ofstream fout;
// In the below line open function
// used to open files. If the file
// does not exist then it will
// create the file "myfile.txt"
fout.open("myfile3.txt", ios::app | ios::binary);
// Write function is used for
// data to write in the file
fout.write((char*)this, sizeof(*this));
fout.close();
return (1);
}
}
// Function to display the menu of the
// current menu-driver
int menu()
{
int choice;
cout << "\nBook Management";
cout << "\n1.Insert book record";
cout << "\n2.View all book record";
cout << "\n3.Search book record";
cout << "\n4.Delete book record";
cout << "\n5.Update book record";
cout << "\n6.Exit";
cout << "\n\nEnter your choice : ";
cin >> (choice);
return (choice);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Object of the class Book
Book b1;
char title[20];
while (1) {
system("cls");
switch (menu()) {
case 1:
b1.getBookData();
b1.storeBook();
cout << "\nRecord inserted";
break;
case 2:
b1.viewAllBooks();
break;
case 3:
cout << "\nEnter title of "
<< "book to search : ";
cin.ignore();
cin.getline(title, 19);
b1.searchBook(title);
break;
case 4:
cout << "\nEnter book title "
<< "for delete record : ";
cin.ignore();
cin.getline(title, 19);
b1.deleteBook(title);
break;
case 5:
cout << "\nEnter book title "
<< "to update record : ";
cin.ignore();
cin.getline(title, 19);
b1.updateBook(title);
break;
case 6:
cout << "\n Thanks for using";
cout << "\n Press any key to exit";
getch();
exit(0);
default:
cout << "Invalid input";
}
getch();
}
}
Producción:
- Salida para insertar registro de libro usando la opción 1:

- Salida después de insertar nuevamente el registro del libro usando la opción 1:
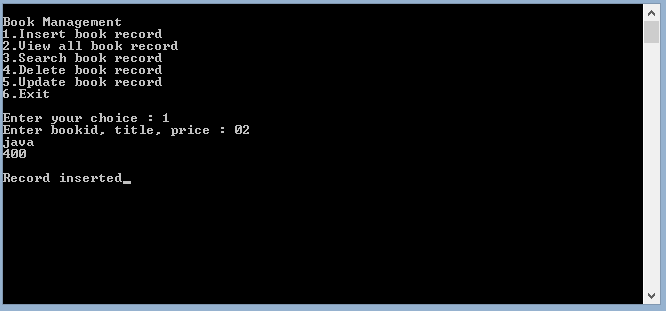
- Salida para insertar el registro 3, 4 y podemos mostrar el registro usando la opción 2. Ver todos los registros del libro. Si se agrega «0» como prefijo de bookid, se ignora como podemos ver en la imagen a continuación:

- Salida para el libro de búsqueda usando su nombre de título usando la opción 3:

- Salida para actualizar los datos previamente insertados como se muestra a continuación:
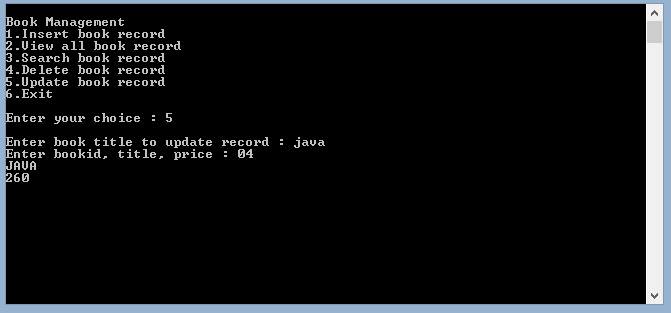
- Ahora, finalmente, se puede ver en la imagen a continuación que «java» se actualiza como «JAVA», así como la identificación del libro como 4 y el precio como «350» . Se pueden ver los datos anteriores del libro java en la 3ra imagen. El registro de C++ se elimina, por eso no se muestra a continuación:

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por urvish_patel y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA