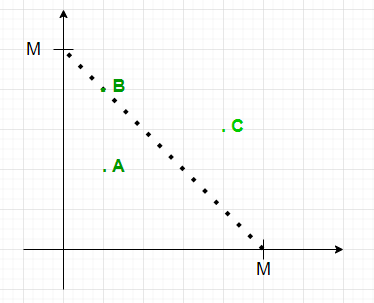
Dada una array arr[][] de dimensión N * 2 que representa las coordenadas de N puntos y una array Q[] que consta de M enteros, la tarea para cada elemento en Q[i] es encontrar el número de puntos acostado dentro o sobre el triángulo isósceles de ángulo recto formado en el eje de coordenadas positivas con dos lados iguales de longitud Q[i] en cada consulta.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N =4, arr[][] = { {2.1, 3.0}, {3.7, 1.2}, {1.5, 6.5}, {1.2, 0.0} }, Q[] = { 2, 8, 5}, M = 3
Salida: 1 4 2
Explicación:
- Primera consulta: El punto (1.2, 0.0) se encuentra dentro del triángulo.
- Segunda consulta: Los puntos { (2.1, 3.0), (3.7, 1.2), (1.2, 0.0) } se encuentran dentro del triángulo y el punto (1.5, 6.5) se encuentra en el triángulo.
- Tercera consulta: Los puntos {(3.7, 1.2), (1.2, 0.0)} se encuentran dentro del triángulo.
Entrada: N =3, arr[][] = { {0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 1} }, Q[] = {1, 2, 3}, M = 3 Salida
: 1 2 3
Explicación:
- Primera consulta: El punto (0, 0) se encuentra dentro del triángulo.
- Segunda consulta: Los puntos { (0, 0), (1, 1) } se encuentran dentro del triángulo.
- Tercera consulta: Todos los puntos están dentro del triángulo.
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque más simple es en cada consulta atravesar la array de puntos y verificar si se encuentra dentro del triángulo rectángulo formado. Después de completar los pasos anteriores, imprima el conteo.
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(N * M)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Enfoque eficiente: el enfoque anterior se puede optimizar en función de las siguientes observaciones:
- Un punto (x, y) se encuentra dentro del triángulo rectángulo isósceles formado en el eje de coordenadas cuyos dos lados iguales son X si:
- x ≥ 0 && y ≥ 0 && x + y ≤ X
- Prealmacenando el conteo de puntos con coordenadas suma ≤ X , la consulta puede ser respondida en tiempo constante.
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice una array , digamos pre[] de tamaño máximo , para almacenar el recuento de puntos cuya suma de coordenadas es menor o igual que el índice de la array.
- Recorra la array arr[][] e incremente el recuento de ceil(arr[i][0] + arr[i][1]) en 1.
- Calcule la array de suma de prefijos de la array pre[].
- Recorra la array Q[] e imprima el pre[Q[i]] .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int const MAX = 1e6 + 5;
// Function to find answer of each query
int query(vector<vector<float> > arr,
vector<int> Q)
{
// Stores the count of points with sum
// less than or equal to their indices
int pre[MAX] = { 0 };
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
// If both x and y-coordinate < 0
if (arr[i][0] < 0 || arr[i][1] < 0)
continue;
// Stores the sum of co-ordinates
int sum = ceil((arr[i][0] + arr[i][1]));
// Increment count of sum by 1
pre[sum]++;
}
// Prefix array
for (int i = 1; i < MAX; i++)
pre[i] += pre[i - 1];
// Perform queries
for (int i = 0; i < Q.size(); i++) {
cout << pre[Q[i]] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Drivers Code
int main()
{
vector<vector<float> > arr = { { 2.1, 3.0 },
{ 3.7, 1.2 },
{ 1.5, 6.5 },
{ 1.2, 0.0 } };
vector<int> Q = { 2, 8, 5 };
int N = arr.size();
int M = Q.size();
query(arr, Q);
}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = (int) (1e6 + 5);
// Function to find answer of each query
static void query(double [][]arr,
int []Q)
{
// Stores the count of points with sum
// less than or equal to their indices
int pre[] = new int[MAX];
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
// If both x and y-coordinate < 0
if (arr[i][0] < 0 || arr[i][1] < 0)
continue;
// Stores the sum of co-ordinates
int sum = (int) Math.ceil((arr[i][0] + arr[i][1]));
// Increment count of sum by 1
pre[sum]++;
}
// Prefix array
for (int i = 1; i < MAX; i++)
pre[i] += pre[i - 1];
// Perform queries
for (int i = 0; i < Q.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(pre[Q[i]]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Drivers Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[][] arr = { { 2.1, 3.0 },
{ 3.7, 1.2 },
{ 1.5, 6.5 },
{ 1.2, 0.0 } };
int []Q = { 2, 8, 5 };
int N = arr.length;
int M = Q.length;
query(arr, Q);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach MAX = 10**6 + 5 from math import ceil # Function to find answer of each query def query(arr, Q): # Stores the count of points with sum # less than or equal to their indices pre = [0]*(MAX) # Traverse the array for i in range(len(arr)): #` If both x and y-coordinate < 0 if (arr[i][0] < 0 or arr[i][1] < 0): continue # Stores the sum of co-ordinates sum = ceil((arr[i][0] + arr[i][1])); # Increment count of sum by 1 pre[sum] += 1 # Prefix array for i in range(1, MAX): pre[i] += pre[i - 1] # Perform queries for i in range(len(Q)): print(pre[Q[i]], end = " ") # Drivers Code if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [[ 2.1, 3.0], [ 3.7, 1.2], [ 1.5, 6.5], [ 1.2, 0.0]] Q = [2, 8, 5] N = len(arr) M = len(Q) query(arr, Q) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.
C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System;
public class GFG
{
static int MAX = (int) (1e6 + 5);
// Function to find answer of each query
static void query(double [,]arr,
int []Q)
{
// Stores the count of points with sum
// less than or equal to their indices
int []pre = new int[MAX];
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++)
{
// If both x and y-coordinate < 0
if (arr[i,0] < 0 || arr[i,1] < 0)
continue;
// Stores the sum of co-ordinates
int sum = (int) Math.Ceiling((arr[i,0] + arr[i,1]));
// Increment count of sum by 1
pre[sum]++;
}
// Prefix array
for (int i = 1; i < MAX; i++)
pre[i] += pre[i - 1];
// Perform queries
for (int i = 0; i < Q.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(pre[Q[i]]+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Drivers Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
double[,] arr = { { 2.1, 3.0 },
{ 3.7, 1.2 },
{ 1.5, 6.5 },
{ 1.2, 0.0 } };
int []Q = { 2, 8, 5 };
int N = arr.GetLength(0);
int M = Q.Length;
query(arr, Q);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of above approach
let MAX = (1e6 + 5)
// Function to find answer of each query
function query(arr,Q)
{
// Stores the count of points with sum
// less than or equal to their indices
let pre = new Array(MAX);
for(let i=0;i<MAX;i++)
pre[i]=0;
// Traverse the array
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
// If both x and y-coordinate < 0
if (arr[i][0] < 0 || arr[i][1] < 0)
continue;
// Stores the sum of co-ordinates
let sum = Math.ceil((arr[i][0] + arr[i][1]));
// Increment count of sum by 1
pre[sum]++;
}
// Prefix array
for (let i = 1; i < MAX; i++)
pre[i] += pre[i - 1];
// Perform queries
for (let i = 0; i < Q.length; i++)
{
document.write(pre[Q[i]]+ " ");
}
document.write("<br>");
}
// Drivers Code
let arr=[[ 2.1, 3.0 ],
[ 3.7, 1.2 ],
[ 1.5, 6.5 ],
[ 1.2, 0.0 ] ];
let Q=[2, 8, 5];
let N = arr.length;
let M = Q.length;
query(arr, Q);
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
1 4 2
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ashutoshrathi y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA