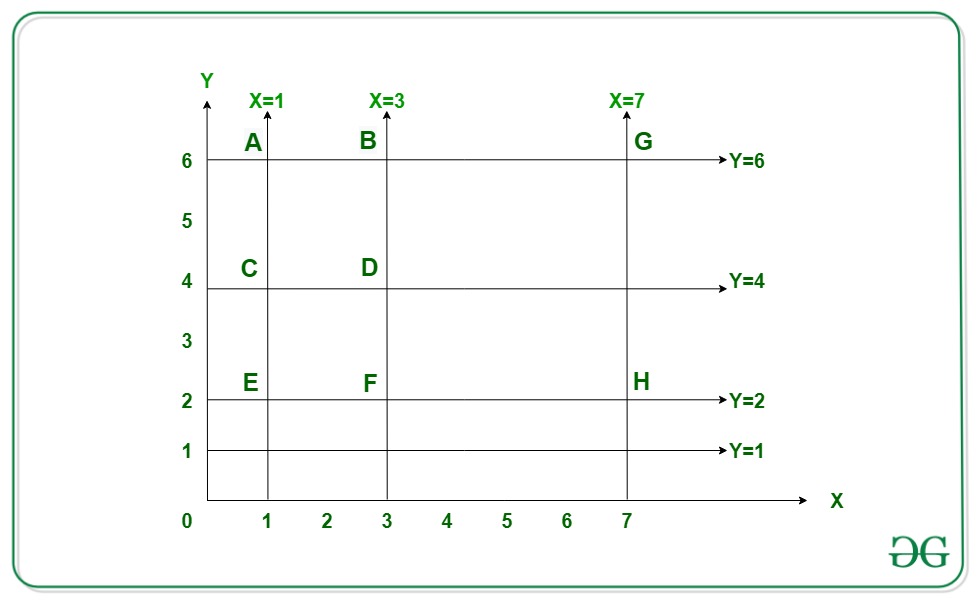
Dados dos arreglos X[] e Y[] que consisten en N y M enteros tales que hay N líneas paralelas al eje y y M líneas paralelas al eje x . La tarea es encontrar el número total de cuadrados formados por estas líneas en un plano de coordenadas.
Cada número entero (por ejemplo , a ) en la array X[] denota líneas que tienen la ecuación x = a , paralelas al eje y .
Cada número entero (digamos b ) en la array Y[] denota líneas que tienen la ecuación y = b , paralelas al eje x .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 3, M = 4, X[] = {1, 3, 7}, Y[] = {2, 4, 6, 1}
Salida: 3
Explicación:
3 líneas son paralelas al eje y para x = 1, x = 3 y x = 7.
4 líneas son paralelas al eje x para y = 2, y = 4, y = 6 e y = 1.
A partir de la imagen de arriba, a continuación se forman tres cuadrados posibles:
1) cuadrado CDEF (x = 1, x = 3, y = 2, y = 4), lado = 2 unidades.
2) cuadrado ABDC (x = 1, x = 3, y = 4, y = 6), lado = 2 unidades.
3) cuadrado BGHF (x = 3, x = 7, y = 2, y = 6), lado = 4 unidades.Entrada: N = 5, M = 4, X[] = {1, 9, 2, 3, 7}, Y[] = {1, 2, 4, 6}
Salida: 8
Enfoque: siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Encuentre la distancia entre todos los pares en la array X[] y almacene el conteo en un Mapa , digamos M1 .
- Encuentre la distancia entre todos los pares en la array Y[] y almacene el conteo en un Map M2 .
- Si la distancia de los pares de M1 está presente en M2 , entonces se puede hacer un cuadrado usando ambos pares.
- Por lo tanto, el recuento total de cuadrados se puede calcular sumando todos los recuentos de distancias almacenados en M1 y en M2 .
- Imprima el recuento total de cuadrados después de completar los pasos anteriores.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to count all the possible
// squares with given lines parallel
// to both the X and Y axis
int numberOfSquares(int X[], int Y[],
int N, int M)
{
// Stores the count of all possible
// distances in X[] & Y[] respectively
unordered_map<int, int> m1, m2;
int i, j, ans = 0;
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array X[]
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
int dist = abs(X[i] - X[j]);
// Add the count to m1
m1[dist]++;
}
}
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array Y[]
for (i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < M; j++) {
int dist = abs(Y[i] - Y[j]);
// Add the count to m2
m2[dist]++;
}
}
// Find sum of m1[i] * m2[i]
// for same distance
for (auto i = m1.begin();
i != m1.end(); i++) {
// Find current count in m2
if (m2.find(i->first)
!= m2.end()) {
// Add to the total count
ans += (i->second
* m2[i->first]);
}
}
// Return the final count
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given lines
int X[] = { 1, 3, 7 };
int Y[] = { 2, 4, 6, 1 };
int N = sizeof(X) / sizeof(X[0]);
int M = sizeof(Y) / sizeof(Y[0]);
// Function Call
cout << numberOfSquares(X, Y, N, M);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to count all the possible
// squares with given lines parallel
// to both the X and Y axis
static int numberOfSquares(int[] X, int[] Y, int N,
int M)
{
// Stores the count of all possible
// distances in X[] & Y[] respectively
HashMap<Integer,
Integer> m1 = new HashMap<Integer,
Integer>();
HashMap<Integer,
Integer> m2 = new HashMap<Integer,
Integer>();
int i, j, ans = 0;
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array X[]
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for(j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
int dist = Math.abs(X[i] - X[j]);
// Add the count to m1
m1.put(dist, m1.getOrDefault(dist, 0) + 1);
}
}
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array Y[]
for(i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for(j = i + 1; j < M; j++)
{
int dist = Math.abs(Y[i] - Y[j]);
// Add the count to m2
m2.put(dist, m2.getOrDefault(dist, 0) + 1);
}
}
// Find sum of m1[i] * m2[i]
// for same distance
for(Map.Entry<Integer,
Integer> entry : m1.entrySet())
{
// Find current count in m2
if (m2.containsKey(entry.getKey()))
{
// Add to the total count
ans += (entry.getValue() *
m2.get(entry.getKey()));
}
}
// Return the final count
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given lines
int X[] = { 1, 3, 7 };
int Y[] = { 2, 4, 6, 1 };
int N = X.length;
int M = Y.length;
// Function call
System.out.println(numberOfSquares(X, Y, N, M));
}
}
// This code is contributed by akhilsaini
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to count all the possible
# squares with given lines parallel
# to both the X and Y axis
def numberOfSquares(X, Y, N, M):
# Stores the count of all possible
# distances in X[] & Y[] respectively
m1 = {}
m2 = {}
ans = 0
# Find distance between all
# pairs in the array X[]
for i in range(0, N):
for j in range(i + 1, N):
dist = abs(X[i] - X[j])
# Add the count to m1
if dist in m1:
m1[dist] = m1[dist] + 1
else:
m1[dist] = 1
# Find distance between all
# pairs in the array Y[]
for i in range(0, M):
for j in range(i + 1, M):
dist = abs(Y[i] - Y[j])
# Add the count to m2
if dist in m2:
m2[dist] = m2[dist] + 1
else:
m2[dist] = 1
# Find sum of m1[i] * m2[i]
# for same distance
for key in m1:
# Find current count in m2
if key in m2:
# Add to the total count
ans = ans + (m1[key] * m2[key])
# Return the final count
return ans
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Given lines
X = [ 1, 3, 7 ]
Y = [ 2, 4, 6, 1 ]
N = len(X)
M = len(Y)
# Function call
print(numberOfSquares(X, Y, N, M))
# This code is contributed by akhilsaini
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to count all the possible
// squares with given lines parallel
// to both the X and Y axis
static int numberOfSquares(int[] X, int[] Y, int N,
int M)
{
// Stores the count of all possible
// distances in X[] & Y[] respectively
Dictionary<int,
int> m1 = new Dictionary<int,
int>();
Dictionary<int,
int> m2 = new Dictionary<int,
int>();
int i, j, ans = 0;
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array X[]
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for(j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
int dist = Math.Abs(X[i] - X[j]);
// Add the count to m1
if (m1.ContainsKey(dist))
m1[dist]++;
else
m1.Add(dist, 1);
}
}
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array Y[]
for(i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for(j = i + 1; j < M; j++)
{
int dist = Math.Abs(Y[i] - Y[j]);
// Add the count to m2
if (m2.ContainsKey(dist))
m2[dist]++;
else
m2.Add(dist, 1);
}
}
// Find sum of m1[i] * m2[i]
// for same distance
foreach(KeyValuePair<int, int> entry in m1)
{
// Find current count in m2
if (m2.ContainsKey(entry.Key))
{
// Add to the total count
ans += (entry.Value *
m2[entry.Key]);
}
}
// Return the final count
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given lines
int[] X = { 1, 3, 7 };
int[] Y = { 2, 4, 6, 1 };
int N = X.Length;
int M = Y.Length;
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(numberOfSquares(X, Y, N, M));
}
}
// This code is contributed by akhilsaini
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Function to count all the possible
// squares with given lines parallel
// to both the X and Y axis
function numberOfSquares(X, Y, N, M)
{
// Stores the count of all possible
// distances in X[] & Y[] respectively
var m1 = new Map(), m2 = new Map();
var i, j, ans = 0;
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array X[]
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
var dist = Math.abs(X[i] - X[j]);
// Add the count to m1
if(m1.has(dist))
m1.set(dist, m1.get(dist)+1)
else
m1.set(dist, 1);
}
}
// Find distance between all
// pairs in the array Y[]
for (i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < M; j++) {
var dist = Math.abs(Y[i] - Y[j]);
// Add the count to m2
if(m2.has(dist))
m2.set(dist, m2.get(dist)+1)
else
m2.set(dist, 1);
}
}
// Find sum of m1[i] * m2[i]
// for same distance
m1.forEach((value, key) => {
// Find current count in m2
if (m2.has(key)) {
// Add to the total count
ans += (value
* m2.get(key));
}
});
// Return the final count
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
// Given lines
var X = [1, 3, 7];
var Y = [2, 4, 6, 1];
var N = X.length;
var M = Y.length;
// Function Call
document.write( numberOfSquares(X, Y, N, M));
// This code is contributed by rrrtnx.
</script>
3
Tiempo Complejidad: O(N 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)