Dada una string codificada str que consta de dígitos y * que se puede completar con cualquier dígito del 1 al 9 , la tarea es encontrar el número de formas de decodificar esa string en una secuencia de alfabetos AZ .
Nota: La string de entrada contiene números del 0 al 9 y el carácter ‘*’ únicamente.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: str = “1*”
Salida: 18
Explicación:
Dado que * se puede reemplazar por cualquier valor de (1-9),
la string dada se puede decodificar como A[AI] + [JR] = 9 + 9 formasEntrada: str = “12*3”
Salida: 28
Enfoque ingenuo: una solución simple es resolver el problema usando la recursividad considerando todas las posibles decodificaciones de la string.
A continuación se muestra el árbol de recursión para el problema:
12*3
/ \
12*(3) 12(*3)
/ \ / \
12(*)(3) 1(2*)(3) 1(2)(*3) ""
/ \ \ /
1(2)(*)(3) "" "" ""
/
""
Enfoque Eficiente: La idea es resolver el problema utilizando Programación Dinámica utilizando la subestructura óptima para considerar todos los casos de los dígitos actuales y anteriores de la string y su número de formas de decodificar la string.
Definición del estado DP: en este problema, ![]() denota el número de formas de decodificar la string hasta el
denota el número de formas de decodificar la string hasta el ![]() índice.
índice.
Estados iniciales de DP: Inicialmente, el valor de los estados de DP se define a continuación:
// Number of ways to decode
// an empty string
dp[0] = 1
// Number of ways to decode the
// first character
if (s[0] == '*')
dp[1] = 9 // 9 ways
else
dp[1] = 1
Subestructura óptima: generalmente hay dos formas de decodificar el carácter actual de la string:
- Incluir el carácter actual como un solo dígito para decodificar: si el carácter actual se usa como un solo dígito, generalmente puede haber dos casos para que el carácter sea:
- Caso 1: si el carácter actual es igual a
 , entonces hay 9 formas posibles de tomar cualquier dígito de [1-9] y decodificarlo como cualquier carácter de [AZ].
, entonces hay 9 formas posibles de tomar cualquier dígito de [1-9] y decodificarlo como cualquier carácter de [AZ].
- Caso 1: si el carácter actual es igual a
if (current == "*")
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i-1]
- Caso 2: si el carácter actual es igual a cualquier otro dígito de [0-9], entonces el número de formas posibles de decodificar es igual al número de formas de decodificar la string hasta el
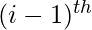 índice.
índice.
if (current != "*")
dp[i] += dp[i-1]
- Incluir el carácter actual como dos dígitos para decodificar: si el carácter actual se va a decodificar como dos dígitos, hay dos casos posibles:
- Caso 1: si el carácter anterior es igual a
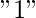 o
o 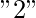 , entonces puede haber dos subcasos más posibles que dependerán del carácter actual:
, entonces puede haber dos subcasos más posibles que dependerán del carácter actual:
- Caso 1.1: si el carácter actual es igual a
 , entonces el total de formas posibles de decodificar es 9 si el carácter anterior es 1, de lo contrario, 6 si el carácter anterior es 2.
, entonces el total de formas posibles de decodificar es 9 si el carácter anterior es 1, de lo contrario, 6 si el carácter anterior es 2. - Caso 1.2: si el carácter actual es menor que igual a 6, entonces el número total de formas posibles de decodificar la string dependerá solo del número de formas de decodificar hasta el carácter anterior. Eso es
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com dp[i-2]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1072191aab574b3d1552e1b2abe0be42_l3.png)
- Caso 1.1: si el carácter actual es igual a
- Caso 2: si el carácter anterior es
 , entonces puede haber dos subcasos más posibles que dependerán del carácter actual:
, entonces puede haber dos subcasos más posibles que dependerán del carácter actual:
- Caso 2.1: si el carácter actual también es
 , entonces el número total de casos será
, entonces el número total de casos será ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com 15 * dp[i-2]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-39ffa567ceabd39bdc2225be417a9679_l3.png) , porque los dígitos individuales de las formas de decodificación del carácter anterior ya deben estar incluidos.
, porque los dígitos individuales de las formas de decodificación del carácter anterior ya deben estar incluidos. - Caso 2.2: Si el carácter actual es menor que 6, entonces el número total de formas será
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com 2*dp[i-2]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d9a9cac31528689a896a580444e406b6_l3.png) , porque entonces el número de formas para elegir los dígitos del primer carácter es 2. Eso es [1, 2].
, porque entonces el número de formas para elegir los dígitos del primer carácter es 2. Eso es [1, 2]. - Caso 2.3: si el carácter actual es cualquier dígito, entonces el número total de formas será el número de formas de decodificar hasta el dígito anterior solamente. eso
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com dp[i-2]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a21eeab3680f17dcca68a13da9231fdb_l3.png) es
es
- Caso 2.1: si el carácter actual también es
- Caso 1: si el carácter anterior es igual a
C++
// C++ implementation to count the
// possible decodings of the given
// digit sequence
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to count the number of
// ways to decode the given digit
// sequence
int waysToDecode2(string s) {
int n = s.size();
// Array to store the dp states
vector<int> dp(n+1,0);
// Case of empty string
dp[0]=1;
// Condition to check if the
// first character of string is 0
if(s[0]=='0')
return 0;
// Base case for single length
// string
dp[1]= ((s[0]=='*')? 9 : 1);
// Bottom-up dp for the string
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
// Previous character
char first= s[i-2];
// Current character
char second= s[i-1];
// Case to include the Current
// digit as a single digit for
// decoding the string
if(second=='*')
{
dp[i]+= 9*dp[i-1];
}
else if(second>'0')
dp[i]+=dp[i-1];
// Case to include the current
// character as two-digit for
// decoding the string
if(first=='1'|| first=='2')
{
// Condition to check if the
// current character is "*"
if(second=='*')
{
if(first=='1')
dp[i]+= 9 * dp[i-2];
else if(first=='2')
dp[i]+= 6 * dp[i-2];
}
// Condition to check if the
// current character is less than
// or equal to 26
else if(((first-'0')* 10 +
(second-'0'))<= 26)
dp[i]+=dp[i-2];
}
// Condition to check if the
// Previous digit is equal to "*"
else if(first=='*')
{
if(second=='*')
{
dp[i]+= 15 * dp[i-2];
}
else if(second<='6')
dp[i]+= 2* dp[i-2];
else
dp [i]+= dp[i-2];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
// Driver Code
int main() {
string str = "12*3";
// Function Call
cout << waysToDecode2(str) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to count the
// possible decodings of the given
// digit sequence
class GFG{
// Function to count the number of
// ways to decode the given digit
// sequence
static int waysToDecode2(char []s)
{
int n = s.length;
// Array to store the dp states
int []dp = new int[n + 1];
// Case of empty String
dp[0] = 1;
// Condition to check if the
// first character of String is 0
if(s[0] == '0')
return 0;
// Base case for single length
// String
dp[1] = ((s[0] == '*') ? 9 : 1);
// Bottom-up dp for the String
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
// Previous character
char first = s[i - 2];
// Current character
char second = s[i - 1];
// Case to include the Current
// digit as a single digit for
// decoding the String
if(second == '*')
{
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 1];
}
else if(second > '0')
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
// Case to include the current
// character as two-digit for
// decoding the String
if(first == '1' || first == '2')
{
// Condition to check if the
// current character is "*"
if(second == '*')
{
if(first == '1')
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 2];
else if(first == '2')
dp[i] += 6 * dp[i - 2];
}
// Condition to check if the
// current character is less than
// or equal to 26
else if(((first - '0') * 10 +
(second - '0')) <= 26)
{
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
// Condition to check if the
// previous digit is equal to "*"
else if(first == '*')
{
if(second == '*')
{
dp[i] += 15 * dp[i - 2];
}
else if(second <= '6')
{
dp[i] += 2 * dp[i - 2];
}
else
{
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "12*3";
// Function Call
System.out.print(waysToDecode2(
str.toCharArray()) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
C#
// C# implementation to count the
// possible decodings of the given
// digit sequence
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to count the number of
// ways to decode the given digit
// sequence
static int waysToDecode2(char []s)
{
int n = s.Length;
// Array to store the dp states
int []dp = new int[n + 1];
// Case of empty String
dp[0] = 1;
// Condition to check if the
// first character of String is 0
if(s[0] == '0')
return 0;
// Base case for single length
// String
dp[1] = ((s[0] == '*') ? 9 : 1);
// Bottom-up dp for the String
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
// Previous character
char first = s[i - 2];
// Current character
char second = s[i - 1];
// Case to include the current
// digit as a single digit for
// decoding the String
if(second == '*')
{
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 1];
}
else if(second > '0')
{
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
}
// Case to include the current
// character as two-digit for
// decoding the String
if(first == '1' || first == '2')
{
// Condition to check if the
// current character is "*"
if(second == '*')
{
if(first == '1')
{
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 2];
}
else if(first == '2')
{
dp[i] += 6 * dp[i - 2];
}
}
// Condition to check if the
// current character is less than
// or equal to 26
else if(((first - '0') * 10 +
(second - '0')) <= 26)
{
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
// Condition to check if the
// previous digit is equal to "*"
else if(first == '*')
{
if(second == '*')
{
dp[i] += 15 * dp[i - 2];
}
else if(second <= '6')
{
dp[i] += 2 * dp[i - 2];
}
else
{
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String str = "12*3";
// Function Call
Console.Write(waysToDecode2(
str.ToCharArray()) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation to count the
// possible decodings of the given
// digit sequence
// Function to count the number of
// ways to decode the given digit
// sequence
function waysToDecode2(s)
{
let n = s.length;
// Array to store the dp states
let dp = Array.from({length: n+1}, (_, i) => 0);
// Case of empty String
dp[0] = 1;
// Condition to check if the
// first character of String is 0
if(s[0] == '0')
return 0;
// Base case for single length
// String
dp[1] = ((s[0] == '*') ? 9 : 1);
// Bottom-up dp for the String
for(let i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
// Previous character
let first = s[i - 2];
// Current character
let second = s[i - 1];
// Case to include the Current
// digit as a single digit for
// decoding the String
if(second == '*')
{
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 1];
}
else if(second > '0')
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
// Case to include the current
// character as two-digit for
// decoding the String
if(first == '1' || first == '2')
{
// Condition to check if the
// current character is "*"
if(second == '*')
{
if(first == '1')
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 2];
else if(first == '2')
dp[i] += 6 * dp[i - 2];
}
// Condition to check if the
// current character is less than
// or equal to 26
else if(((first - '0') * 10 +
(second - '0')) <= 26)
{
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
// Condition to check if the
// previous digit is equal to "*"
else if(first == '*')
{
if(second == '*')
{
dp[i] += 15 * dp[i - 2];
}
else if(second <= '6')
{
dp[i] += 2 * dp[i - 2];
}
else
{
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
// Driver Code
let str = "12*3";
// Function Call
document.write(waysToDecode2(
str.split('')) + "\n");
</script>
Python3
# Python3 implementation to count the
# possible decodings of the given
# digit sequence
# Function to count the number of
# ways to decode the given digit
# sequence
def waysToDecode2(s):
n = len(s)
# Array to store the dp states
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
# Case of empty string
dp[0] = 1
# Condition to check if the
# first character of string is 0
if s[0] == "0":
return 0
# Base case for single length
# string
dp[1] = 9 if (s[0] == "*") else 1
# Bottom-up dp for the string
for i in range(2, n+1):
# Previous character
first = s[i - 2]
# Current character
second = s[i - 1]
# Case to include the Current
# digit as a single digit for
# decoding the string
if second == "*":
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 1]
elif second > "0":
dp[i] += dp[i - 1]
# Case to include the current
# character as two-digit for
# decoding the string
if first == "1" or first == "2":
# Condition to check if the
# current character is "*"
if second == "*":
if first == "1":
dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 2]
elif first == "2":
dp[i] += 6 * dp[i - 2]
# Condition to check if the
# current character is less than
# or equal to 26
elif (ord(first) - ord("0")) * 10 + (ord(second) - ord("0")) <= 26:
dp[i] += dp[i - 2]
# Condition to check if the
# Previous digit is equal to "*"
elif first == "*":
if second == "*":
dp[i] += 15 * dp[i - 2]
elif second <= "6":
dp[i] += 2 * dp[i - 2]
else:
dp[i] += dp[i - 2]
return dp[n]
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
str = "12*3"
# Function Call
print(waysToDecode2(str))
Producción:
28
- Complejidad de tiempo: O(N)
- Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por akhiltomar098 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA