Dada una array binaria de dimensiones N * M , la tarea es encontrar los índices de la array tales que el recorrido de la array dada desde la celda (0, 0) conduce al exterior de la array según las siguientes condiciones:
- Si el valor de arr[i][j] es 0 , entonces muévase en la misma dirección y verifique el siguiente valor.
- Si el valor de arr[i][j] es 1 , actualice arr[i][j] a 0 y cambie la dirección actual de arriba , derecha , abajo o izquierda a las direcciones derecha , abajo , izquierda y arriba respectivamente.
Ejemplos:
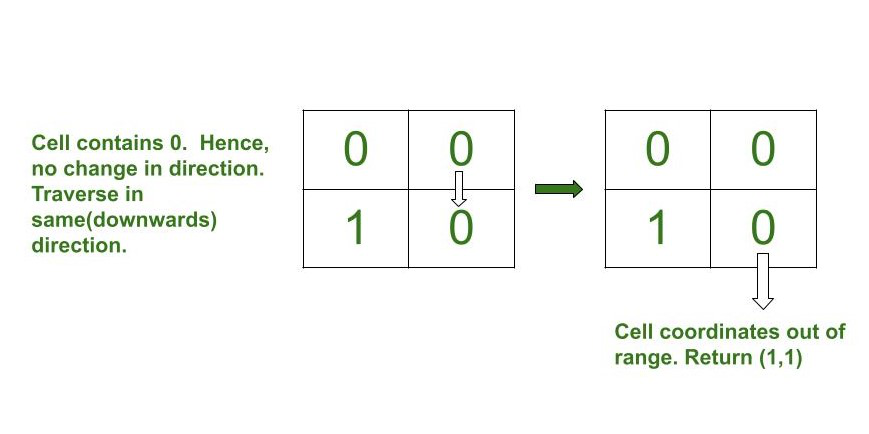
Entrada: arr[] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}}
Salida: (1, 1)
Explicación:
A continuación se muestra la imagen para ilustrar la simulación:Entrada: arr[] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 0, 0}}
Salida: (2, 0)
Enfoque: siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
-
- Inicializa dos variables, digamos current_i y current_j , ambas como 0 .
- Atraviese la array desde el índice (0, 0) y establezca la dirección actual a la derecha como R .
- Si el valor de current_i o current_j es N o M respectivamente, realice las siguientes operaciones:
- Si el valor de arr[i][j] es 0 , entonces muévase en la misma dirección y verifique el siguiente valor.
- De lo contrario, actualice arr[i][j] a 0 y elija una dirección que esté a la derecha de la dirección actual. Si la dirección que es derecha a la dirección actual es:
- L: Mueve la fila actual hacia atrás, es decir, j – 1 .
- R: Mueve la fila actual hacia adelante, es decir, j + 1 .
- U: Mover la columna actual hacia arriba, es decir, i – 1 .
- D: Mover la columna actual hacia abajo, es decir, i + 1 .
- Si las nuevas coordenadas no están dentro del rango, imprima las coordenadas actuales como las coordenadas resultantes y salga del ciclo .
C++
// CPP program for the above approach
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to check if the indices (i, j)
// are valid indices in a Matrix or not
bool issafe(int m, int n, int i, int j)
{
// Cases for invalid cells
if (i < 0)
return false;
if (j < 0)
return false;
if (i >= m)
return false;
if (j >= n)
return false;
// Return true if valid
return true;
}
// Function to find indices of cells
// of a matrix from which traversal
// leads to out of the matrix
pair<int,int> endpoints(vector<vector<int>> arr, int m, int n){
// Starting from cell (0, 0),
// traverse in right direction
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int current_i = 0;
int current_j = 0;
char current_d = 'r';
// Stores direction changes
map<char,char> rcd = {{'l', 'u'},{'u', 'r'},
{'r', 'd'},
{'d', 'l'}};
// Iterate until the current cell
// exceeds beyond the matrix
while (issafe(m, n, i, j)){
// Current index
current_i = i;
current_j = j;
// If the current cell is 1
if (arr[i][j] == 1){
char move_in = rcd[current_d];
// Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i][j] = 0;
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (move_in == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(move_in == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'r')
j += 1;
current_d = move_in;
}
// Otherwise
else{
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (current_d == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(current_d == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'r')
j += 1;
}
}
// The exit coordinates
return {current_i, current_j};
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of rows
int M = 3;
// Number of columns
int N = 5;
// Given matrix arr[][]
vector<vector<int>> arr{{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0}};
pair<int,int> p = endpoints(arr, M, N);
cout << "(" << p.first << ", " << p.second << ")" << endl;
}
// This code is contributed by ipg2016107.
Java
// JAVA program for the above approach
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class GFG
{
// Function to check if the indices (i, j)
// are valid indices in a Matrix or not
static boolean issafe(int m, int n, int i, int j)
{
// Cases for invalid cells
if (i < 0)
return false;
if (j < 0)
return false;
if (i >= m)
return false;
if (j >= n)
return false;
// Return true if valid
return true;
}
// Function to find indices of cells
// of a matrix from which traversal
// leads to out of the matrix
static int [] endpoints(int [][]arr, int m, int n){
// Starting from cell (0, 0),
// traverse in right direction
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int current_i = 0;
int current_j = 0;
char current_d = 'r';
// Stores direction changes
Map<Character,Character> rcd = new HashMap<>();
rcd.put('l', 'u');
rcd.put('u', 'r');
rcd.put('r', 'd');
rcd.put('d', 'l');
// Iterate until the current cell
// exceeds beyond the matrix
while (issafe(m, n, i, j)){
// Current index
current_i = i;
current_j = j;
// If the current cell is 1
if (arr[i][j] == 1){
char move_in = rcd.get(current_d);
// Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i][j] = 0;
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (move_in == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(move_in == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'r')
j += 1;
current_d = move_in;
}
// Otherwise
else{
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (current_d == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(current_d == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'r')
j += 1;
}
}
// The exit coordinates
return new int[]{current_i, current_j};
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of rows
int M = 3;
// Number of columns
int N = 5;
// Given matrix arr[][]
int [][]arr = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0}};
int []p = endpoints(arr, M, N);
System.out.print("(" + p[0]+ ", " + p[1]+ ")" +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Python3
# Python program for the above approach
# Function to check if the indices (i, j)
# are valid indices in a Matrix or not
def issafe(m, n, i, j):
# Cases for invalid cells
if i < 0:
return False
if j < 0:
return False
if i >= m:
return False
if j >= n:
return False
# Return true if valid
return True
# Function to find indices of cells
# of a matrix from which traversal
# leads to out of the matrix
def endpoints(arr, m, n):
# Starting from cell (0, 0),
# traverse in right direction
i = 0
j = 0
current_d = 'r'
# Stores direction changes
rcd = {'l': 'u',
'u': 'r',
'r': 'd',
'd': 'l'}
# Iterate until the current cell
# exceeds beyond the matrix
while issafe(m, n, i, j):
# Current index
current_i = i
current_j = j
# If the current cell is 1
if arr[i][j] == 1:
move_in = rcd[current_d]
# Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i][j] = 0
# Update indices according
# to the direction
if move_in == 'u':
i -= 1
elif move_in == 'd':
i += 1
elif move_in == 'l':
j -= 1
elif move_in == 'r':
j += 1
current_d = move_in
# Otherwise
else:
# Update indices according
# to the direction
if current_d == 'u':
i -= 1
elif current_d == 'd':
i += 1
elif current_d == 'l':
j -= 1
elif current_d == 'r':
j += 1
# The exit coordinates
return (current_i, current_j)
# Driver Code
# Number of rows
M = 3
# Number of columns
N = 5
# Given matrix arr[][]
arr = [[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
]
print(endpoints(arr, M, N))
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Function to check if the indices (i, j)
// are valid indices in a Matrix or not
static bool issafe(int m, int n, int i, int j)
{
// Cases for invalid cells
if (i < 0)
return false;
if (j < 0)
return false;
if (i >= m)
return false;
if (j >= n)
return false;
// Return true if valid
return true;
}
// Function to find indices of cells
// of a matrix from which traversal
// leads to out of the matrix
static int[] endpoints(int[, ] arr, int m, int n)
{
// Starting from cell (0, 0),
// traverse in right direction
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int current_i = 0;
int current_j = 0;
char current_d = 'r';
// Stores direction changes
Dictionary<char, char> rcd
= new Dictionary<char, char>();
rcd['l'] = 'u';
rcd['u'] = 'r';
rcd['r'] = 'd';
rcd['d'] = 'l';
// Iterate until the current cell
// exceeds beyond the matrix
while (issafe(m, n, i, j)) {
// Current index
current_i = i;
current_j = j;
// If the current cell is 1
if (arr[i, j] == 1) {
char move_in = rcd[current_d];
// Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i, j] = 0;
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (move_in == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if (move_in == 'd')
i += 1;
else if (move_in == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if (move_in == 'r')
j += 1;
current_d = move_in;
}
// Otherwise
else {
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (current_d == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if (current_d == 'd')
i += 1;
else if (current_d == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if (current_d == 'r')
j += 1;
}
}
// The exit coordinates
return new int[] { current_i, current_j };
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Number of rows
int M = 3;
// Number of columns
int N = 5;
// Given matrix arr[][]
int[, ] arr = { { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 } };
int[] p = endpoints(arr, M, N);
Console.WriteLine("(" + p[0] + ", " + p[1] + ")"
+ "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Function to check if the indices (i, j)
// are valid indices in a Matrix or not
function issafe(m,n,i,j)
{
// Cases for invalid cells
if (i < 0)
return false;
if (j < 0)
return false;
if (i >= m)
return false;
if (j >= n)
return false;
// Return true if valid
return true;
}
// Function to find indices of cells
// of a matrix from which traversal
// leads to out of the matrix
function endpoints(arr,m,n)
{
// Starting from cell (0, 0),
// traverse in right direction
let i = 0;
let j = 0;
let current_i = 0;
let current_j = 0;
let current_d = 'r';
// Stores direction changes
let rcd = new Map();
rcd.set('l', 'u');
rcd.set('u', 'r');
rcd.set('r', 'd');
rcd.set('d', 'l');
// Iterate until the current cell
// exceeds beyond the matrix
while (issafe(m, n, i, j)){
// Current index
current_i = i;
current_j = j;
// If the current cell is 1
if (arr[i][j] == 1){
let move_in = rcd.get(current_d);
// Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i][j] = 0;
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (move_in == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(move_in == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'r')
j += 1;
current_d = move_in;
}
// Otherwise
else{
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (current_d == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(current_d == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'r')
j += 1;
}
}
// The exit coordinates
return [current_i, current_j];
}
// Driver Code
// Number of rows
let M = 3;
// Number of columns
let N = 5;
// Given matrix arr[][]
let arr = [[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0]];
let p = endpoints(arr, M, N);
document.write("(" + p[0]+ ", " + p[1]+ ")" +"\n");
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
Producción
(2, 0)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sailees14032000 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA