Dado un número entero N , la tarea es encontrar el número de cuadrados perfectos de longitud N.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 1
Salida: 3
Explicación: Los cuadrados perfectos de un dígito son 1, 4 y 9.
Entrada: N = 2
Salida: 6
Explicación: Los cuadrados perfectos de dos dígitos son 16, 25, 36, 49, 64 y 81 .
Enfoque ingenuo: para resolver este problema, podemos verificar todos los números entre 10 (N – 1) y 10 N – 1 e incrementar el contador cada vez que encontramos un cuadrado perfecto.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to count perfect
// squares of given length
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to check if a
// number is perfect square
bool isPerfectSquare(long double x)
{
// Find floating point value of
// square root of x.
long double sr = sqrt(x);
// If square root is an integer
return ((sr - floor(sr)) == 0);
}
// Function to return the count of
// n digit perfect squares
int countSquares(int n)
{
// Initialize result
int cnt = 0;
// Traverse through all numbers
// of n digits
for (int i = pow(10, (n - 1));
i < pow(10, n); i++) {
// Check if current number
// 'i' is perfect square
if (i != 0 && isPerfectSquare(i))
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 3;
cout << countSquares(n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to count perfect
// squares of given length
class GFG{
// Function to check if a
// number is perfect square
static boolean isPerfectSquare(double x)
{
// Find floating point value of
// square root of x.
double sr = Math.sqrt(x);
// If square root is an integer
return ((sr - Math.floor(sr)) == 0);
}
// Function to return the count of
// n digit perfect squares
static int countSquares(int n)
{
// Initialize result
int cnt = 0;
// Traverse through all numbers
// of n digits
for(int i = (int) Math.pow(10, (n - 1));
i < Math.pow(10, n); i++)
{
// Check if current number
// 'i' is perfect square
if (i != 0 && isPerfectSquare(i))
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 3;
System.out.print(countSquares(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 Program to count perfect # squares of given length import math; # Function to check if a # number is perfect square def isPerfectSquare(x): # Find floating point value of # square root of x. sr = math.sqrt(x); # If square root is an integer return ((sr - math.floor(sr)) == 0); # Function to return the count of # n digit perfect squares def countSquares(n): # Initialize result cnt = 0; # Traverse through all numbers # of n digits for i in range(int(math.pow(10, (n - 1))), int(math.pow(10, n))): # Check if current number # 'i' is perfect square if (i != 0 and isPerfectSquare(i)): cnt += 1; return cnt; # Driver code n = 3; print(countSquares(n)); # This code is contributed by Akanksha_Rai
C#
// C# program to count perfect
// squares of given length
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to check if a
// number is perfect square
static bool isPerfectSquare(double x)
{
// Find floating point value of
// square root of x.
double sr = Math.Sqrt(x);
// If square root is an integer
return ((sr - Math.Floor(sr)) == 0);
}
// Function to return the count of
// n digit perfect squares
static int countSquares(int n)
{
// Initialize result
int cnt = 0;
// Traverse through all numbers
// of n digits
for(int i = (int) Math.Pow(10, (n - 1));
i < Math.Pow(10, n); i++)
{
// Check if current number
// 'i' is perfect square
if (i != 0 && isPerfectSquare(i))
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 3;
Console.Write(countSquares(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript Program to count perfect
// squares of given length
// Function to check if a
// number is perfect square
function isPerfectSquare(x)
{
// Find floating point value of
// square root of x.
let sr = Math.sqrt(x);
// If square root is an integer
return ((sr - Math.floor(sr)) == 0);
}
// Function to return the count of
// n digit perfect squares
function countSquares(n)
{
// Initialize result
let cnt = 0;
// Traverse through all numbers
// of n digits
for (let i = Math.pow(10, (n - 1));
i < Math.pow(10, n); i++) {
// Check if current number
// 'i' is perfect square
if (i != 0 && isPerfectSquare(i))
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// Driver code
let n = 3;
document.write(countSquares(n));
// This code is contributed by subhammahato348.
</script>
22
Enfoque eficiente: para resolver este problema, simplemente podemos encontrar el número de cuadrados perfectos de longitud N usando una fórmula:
- Un número n tiene d dígitos si
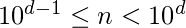
- Por lo tanto, un cuadrado perfecto n 2 tiene d dígitos si
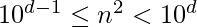 o
o 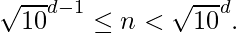
- Por lo tanto, la respuesta requerida para el conteo de cuadrados perfectos de N dígitos es
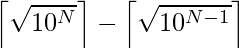
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to count
// perfect squares of given length
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to return the count of
// n digit perfect squares
int countSquares(int n)
{
int r = ceil(sqrt(pow(10, n)));
int l = ceil(sqrt(pow(10, n - 1)));
return r - l;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 3;
cout << countSquares(n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to count perfect
// squares of given length
class GFG{
// Function to return the count
// of n digit perfect squares
static int countSquares(int n)
{
int r = (int) Math.ceil(Math.sqrt
(Math.pow(10, n)));
int l = (int) Math.ceil(Math.sqrt
(Math.pow(10, n - 1)));
return r - l;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 3;
System.out.print(countSquares(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rohit_ranjan
Python3
# Python3 program to count perfect # squares of given length import math # Function to return the count # of n digit perfect squares def countSquares(n): r = math.ceil(math.sqrt (math.pow(10, n))); l = math.ceil(math.sqrt (math.pow(10, n - 1))); return r - l; # Driver code n = 3; print(countSquares(n)); # This code is contributed by grand_master
C#
// C# Program to count perfect
// squares of given length
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to return the count
// of n digit perfect squares
static int countSquares(int n)
{
int r = (int) Math.Ceiling(Math.Sqrt
(Math.Pow(10, n)));
int l = (int) Math.Ceiling(Math.Sqrt
(Math.Pow(10, n - 1)));
return r - l;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 3;
Console.Write(countSquares(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Nidhi_Biet
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to count
// perfect squares of given length
// Function to return the count of
// n digit perfect squares
function countSquares(n)
{
let r = Math.ceil(Math.sqrt(Math.pow(10, n)));
let l = Math.ceil(Math.sqrt(Math.pow(10, n - 1)));
return r - l;
}
// Driver code
let n = 3;
document.write(countSquares(n));
</script>
22
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)