Dado un rango [L, R] , la tarea es contar los números que tienen un número par de dígitos impares y un número impar de dígitos pares. Por ejemplo,
- 8 tiene 1 dígito par y 0 dígitos impares: cumple la condición ya que 1 es impar y 0 es par.
- 545 tiene 1 dígito par y 2 dígitos impares: cumple la condición ya que 1 es impar y 2 es par.
- 4834 tiene 3 dígitos pares y 1 dígito impar: no cumple la condición ya que hay números impares (es decir, 1) de dígitos impares.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: L = 1, R = 9
Salida: 4
2, 4, 6 y 8 son los únicos números enteros del
rango dado que satisfacen las condiciones dadas.Entrada: L = 1, R = 19
Salida: 4Entrada: L = 123, R = 984
Salida: 431
Acercarse:
- Caso 1
Hay un patrón en el que estos números aparecen entre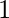 y
y 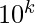 (donde 1<=k<=18).
(donde 1<=k<=18).
Número de ocurrencias de- 1 – 10 y 1 – 100 son 4
- 1 – 1000 y 1 – 10000 son 454
- 1 – 10000 y 1 – 100000 son 45454
- Caso 2
- Si el número de dígitos en un número es par, entonces no puede satisfacer la condición dada porque necesitamos un número impar (de dígitos) y un número par (de dígitos) para satisfacer nuestra condición y número impar + número par siempre es impar
- Entonces, si el número de dígitos para un número dado (digamos n) es par, entonces su número de ocurrencias desde 1 es igual al número de ocurrencias desde
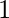 el más grande
el más grande 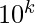 (1<=k<=18) que es menor que n
(1<=k<=18) que es menor que n
Ejemplo:
Sea n = 19, el número de dígitos en 19 es 2
Por lo tanto, el número de ocurrencias de 1 a 19 = número de ocurrencias de 1 a 10 (ya que 10 es el más grandemenor que 19)
- Caso 3
Si el número de dígitos para un número dado (por ejemplo, n) es impar, entonces el número de ocurrencias entre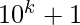 y n es igual a
y n es igual a
donde ![]() es el mayor
es el mayor ![]() menor que n.
menor que n.
Implementación: ahora sabemos cómo calcular el número de ocurrencias de 1 a n dado. Por lo tanto,
Número de ocurrencias de L a R = Número de ocurrencias hasta (R) – Número de ocurrencias hasta (L – 1) donde L no es igual a 1.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++14
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
// Pattern table from Case 1
map<ll, ll> values{{1, 0},
{10, 4},
{100, 4},
{1000, 454},
{10000, 454},
{100000, 45454},
{1000000, 45454},
{10000000, 4545454},
{100000000, 4545454},
{1000000000, 454545454},
{10000000000, 454545454},
{100000000000, 45454545454},
{1000000000000, 45454545454},
{10000000000000, 4545454545454},
{100000000000000, 4545454545454},
{1000000000000000, 454545454545454},
{10000000000000000, 454545454545454},
{100000000000000000, 45454545454545454},
{1000000000000000000, 45454545454545454}};
// Function that returns the number of
// even and odd digits in val
pair<ll, ll> count_even_odd(ll val)
{
ll even = 0, odd = 0;
while (val)
{
ll num = val % 10;
if (num % 2 == 0)
even++;
else
odd++;
val /= 10;
}
return make_pair(even, odd);
}
// Function that returns True if num
// satisfies the given condition
bool satisfies_condition(ll num)
{
pair<ll, ll> answer = count_even_odd(num);
ll even = answer.first;
ll odd = answer.second;
if (even % 2 == 1 and
odd % 2 == 0) return true;
return false;
}
// Function to return the count of
// numbers from 1 to val that
// satisfies the given condition
ll count_upto(ll val)
{
// If the value is already present
// in the values dict
if (values.find(val) != values.end())
return values[val];
ll index = 1;
for (int i = 0;
i < to_string(val).length() - 1;
i++)
index *= 10;
// If the value is even
// Case 2
if (to_string(val).length() % 2 == 0)
return values[index];
ll val_len = to_string(val).length();
ll cnt = values[index];
// Now the problem is to count the desired
// numbers from 10**(val_len-1) + 1 to val
ll left_end = index + 1;
// Case 3
// Eliminating all the even numbers
cnt += (val - left_end) / 2;
if (satisfies_condition(val) or
satisfies_condition(left_end))
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input l and r
ll l = 123, r = 984;
ll right = count_upto(r);
ll left = 0;
if (l == '1')
left = 0;
else
left = count_upto(l - 1);
cout << right - left << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Pattern table from Case 1
static HashMap<Long, Long> values = new HashMap<>();
public static void intitializeMap()
{
values = new HashMap<>();
values.put(1L, 0L);
values.put(10L, 4L);
values.put(100L, 4L);
values.put(1000L, 454L);
values.put(10000L, 454L);
values.put(100000L, 45454L);
values.put(1000000L, 45454L);
values.put(10000000L, 4545454L);
values.put(100000000L, 4545454L);
values.put(1000000000L, 454545454L);
values.put(10000000000L, 454545454L);
values.put(100000000000L, 45454545454L);
values.put(1000000000000L, 45454545454L);
values.put(10000000000000L, 4545454545454L);
values.put(100000000000000L, 4545454545454L);
values.put(1000000000000000L, 454545454545454L);
values.put(10000000000000000L, 454545454545454L);
values.put(100000000000000000L, 45454545454545454L);
values.put(1000000000000000000L, 45454545454545454L);
}
// Function that returns the number of
// even and odd digits in val
static long[] count_even_odd(long val)
{
long even = 0, odd = 0;
while (val > 0)
{
long num = val % 10;
if (num % 2 == 0)
even++;
else
odd++;
val /= 10;
}
return (new long[] { even, odd });
}
// Function that returns True if num
// satisfies the given condition
static boolean satisfies_condition(long num)
{
long[] answer = count_even_odd(num);
long even = answer[0];
long odd = answer[1];
if (even % 2 == 1 && odd % 2 == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Function to return the count of
// numbers from 1 to val that
// satisfies the given condition
static long count_upto(long val)
{
// If the value is already present
// in the values dict
if (values.containsKey(val))
return values.get(val);
long index = 1;
for(int i = 0;
i < Long.toString(val).length() - 1;
i++)
index *= 10;
// If the value is even
// Case 2
if (Long.toString(val).length() % 2 == 0)
return values.get(index);
long val_len = Long.toString(val).length();
long cnt = values.get(index);
// Now the problem is to count the desired
// numbers from 10**(val_len-1) + 1 to val
long left_end = index + 1;
// Case 3
// Eliminating all the even numbers
cnt += (val - left_end) / 2;
if (satisfies_condition(val) ||
satisfies_condition(left_end))
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input l and r
long l = 123, r = 984;
// Function to initialize the Map
intitializeMap();
long right = count_upto(r);
long left = 0;
if (l == '1')
left = 0;
else
left = count_upto(l - 1);
System.out.println(right - left);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Pattern table from Case 1
values = {
1: 0,
10: 4,
100: 4,
1000: 454,
10000: 454,
100000: 45454,
1000000: 45454,
10000000: 4545454,
100000000: 4545454,
1000000000: 454545454,
10000000000: 454545454,
100000000000: 45454545454,
1000000000000: 45454545454,
10000000000000: 4545454545454,
100000000000000: 4545454545454,
1000000000000000: 454545454545454,
10000000000000000: 454545454545454,
100000000000000000: 45454545454545454,
1000000000000000000: 45454545454545454,
}
# Function that returns the number of
# even and odd digits in val
def count_even_odd(val):
even = odd = 0
while val > 0:
num = val % 10
if num % 2 == 0:
even += 1
else:
odd += 1
val //= 10
return even, odd
# Function that returns True if num
# satisfies the given condition
def satisfies_condition(num):
even, odd = count_even_odd(num)
if even % 2 == 1 and odd % 2 == 0:
return True
return False
# Function to return the count of numbers
# from 1 to val that satisfies the given condition
def count_upto(val):
# If the value is already present in the
# values dict
if int(val) in values:
return values[int(val)]
# If the value is even
# Case 2
if len(val) % 2 == 0:
return values[int('1' + '0' * (len(val) - 1))]
val_len = len(val)
count = values[int('1' + '0' * (val_len - 1))]
# Now the problem is to count the desired
# numbers from 10**(val_len-1) + 1 to val
left_end = int('1' + '0' * (val_len - 1)) + 1
# Case 3
# Eliminating all the even numbers
count += (int(val) - left_end) // 2
if satisfies_condition(int(val)) or satisfies_condition(left_end):
count += 1
return count
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Input L and R ( as a string )
l, r = '123', '984'
right = count_upto(r)
left = 0
if(l == '1'):
left = 0
else:
left = count_upto(str(int(l)-1))
print(right - left)
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Pattern table from Case 1
static Dictionary<long,
long> values = new Dictionary<long,
long>();
public static void intitializeMap()
{
values = new Dictionary<long, long>();
values.Add(1L, 0L);
values.Add(10L, 4L);
values.Add(100L, 4L);
values.Add(1000L, 454L);
values.Add(10000L, 454L);
values.Add(100000L, 45454L);
values.Add(1000000L, 45454L);
values.Add(10000000L, 4545454L);
values.Add(100000000L, 4545454L);
values.Add(1000000000L, 454545454L);
values.Add(10000000000L, 454545454L);
values.Add(100000000000L, 45454545454L);
values.Add(1000000000000L, 45454545454L);
values.Add(10000000000000L, 4545454545454L);
values.Add(100000000000000L, 4545454545454L);
values.Add(1000000000000000L, 454545454545454L);
values.Add(10000000000000000L, 454545454545454L);
values.Add(100000000000000000L, 45454545454545454L);
values.Add(1000000000000000000L, 45454545454545454L);
}
// Function that returns the number of
// even and odd digits in val
static long[] count_even_odd(long val)
{
long even = 0, odd = 0;
while (val > 0)
{
long num = val % 10;
if (num % 2 == 0)
even++;
else
odd++;
val /= 10;
}
return (new long[]{ even, odd });
}
// Function that returns True if num
// satisfies the given condition
static bool satisfies_condition(long num)
{
long[] answer = count_even_odd(num);
long even = answer[0];
long odd = answer[1];
if (even % 2 == 1 && odd % 2 == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Function to return the count of
// numbers from 1 to val that
// satisfies the given condition
static long count_upto(long val)
{
// If the value is already present
// in the values dict
if (values.ContainsKey(val))
return values[val];
long index = 1;
for(int i = 0;
i < val.ToString().Length - 1;
i++)
index *= 10;
// If the value is even
// Case 2
if (val.ToString().Length % 2 == 0)
return values[index];
long val_len = val.ToString().Length;
long cnt = values[index];
// Now the problem is to count the desired
// numbers from 10**(val_len-1) + 1 to val
long left_end = index + 1;
// Case 3
// Eliminating all the even numbers
cnt += (val - left_end) / 2;
if (satisfies_condition(val) ||
satisfies_condition(left_end))
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input l and r
long l = 123, r = 984;
// Function to initialize the Map
intitializeMap();
long right = count_upto(r);
long left = 0;
if (l == '1')
left = 0;
else
left = count_upto(l - 1);
Console.WriteLine(right - left);
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation of the approach
// Pattern table from Case 1
let values = new Map();
values.set(1, 0)
values.set(10, 4)
values.set(100, 4)
values.set(1000, 454)
values.set(10000, 454)
values.set(100000, 45454)
values.set(1000000, 45454)
values.set(10000000, 4545454)
values.set(100000000, 4545454)
values.set(1000000000, 454545454)
values.set(10000000000, 454545454)
values.set(100000000000, 45454545454)
values.set(1000000000000, 45454545454)
values.set(10000000000000, 4545454545454)
values.set(100000000000000, 4545454545454)
values.set(1000000000000000, 454545454545454)
values.set(10000000000000000, 454545454545454)
values.set(100000000000000000, 45454545454545454)
values.set(1000000000000000000, 45454545454545454)
// Function that returns the number of
// even and odd digits in val
function count_even_odd(val)
{
let even = 0, odd = 0;
while (val)
{
let num = val % 10;
if (num % 2 == 0)
even++;
else
odd++;
val = Math.floor(val/10);
}
return [even, odd];
}
// Function that returns True if num
// satisfies the given condition
function satisfies_condition(num)
{
let answer = count_even_odd(num);
let even = answer[0];
let odd = answer[1];
if (even % 2 == 1 &&
odd % 2 == 0) return true;
return false;
}
// Function to return the count of
// numbers from 1 to val that
// satisfies the given condition
function count_upto(val)
{
// If the value is already present
// in the values dict
if (values.has(val) == true)
return values.get(val);
let index = 1;
for (let i = 0;i < val.toString().length - 1;i++)
index *= 10;
// If the value is even
// Case 2
if (val.toString().length % 2 == 0)
return values.get(index);
let val_len = Number.toString(val).length;
let cnt = values.get(index);
// Now the problem is to count the desired
// numbers from 10**(val_len-1) + 1 to val
let left_end = index + 1;
// Case 3
// Eliminating all the even numbers
cnt += Math.floor((val - left_end) / 2);
if (satisfies_condition(val) ||
satisfies_condition(left_end))
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
// Driver Code
// Input l and r
let l = 123, r = 984;
let right = count_upto(r);
let left = 0;
if (l == '1')
left = 0;
else
left = count_upto(l - 1);
document.write(right - left);
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
431
Complejidad de tiempo: O(logn)
Espacio auxiliar: O(19*2)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ManoharGanta y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA