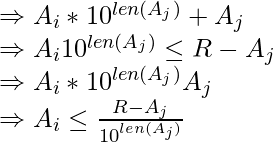Dada una array arr[] de tamaño N y los números enteros L y R que definen el rango dado, la tarea es encontrar la cantidad de elementos en el rango dado que se pueden generar concatenando dos elementos cualesquiera de la array.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 2, L = 10, R = 52, arr = {2, 5}
Salida: 3
Explicación: Todos los pares disponibles
(2, 2) => 22 (10 ≤ 22 ≤ 52)
(2, 5) = > 25 (10 ≤ 25 ≤ 52)
(5, 2) => 52 (10 ≤ 52 ≤ 52)
(5, 5) => 55 (10 ≤ 55 > 52) no válido
Por lo tanto, la salida es 3.Entrada: N = 3, L = 100, R = 1000, arr = {28, 5, 100}
Salida: 2
Explicación: Los únicos pares válidos disponibles
(28, 5) => 285 (100 ≤ 285 ≤ 1000)
(5 , 28) => 528 (100 ≤ 528 ≤ 1000)
Resto otros pares se quedan cortos o más altos que el rango dado
Por lo tanto, la salida es 2.
Planteamiento: La idea para resolver el problema se basa en la siguiente observación:
Observaciones:
- La longitud del par válido es crucial ya que puede ayudarnos a distinguir los pares correctos.
- Si se permite la longitud, debemos verificar si cada elemento está en el límite o no.
- Similarmente

Siga los pasos a continuación para implementar el enfoque anterior:
- Primero ordene la array dada.
- Encuentre la longitud del primer elemento del par.
- Para cualquier par {x, y} , x * 10 len(y) + y da el valor de “xy” cuando se concatenan.
- Luego, simplemente itera j de 1 a N :
- Use la condición anterior para encontrar el rango donde se encontrará el otro valor (por ejemplo, x ).
- Use la búsqueda binaria para encontrar cuántos elementos de array posibles hay en el rango que puede asumir el valor x .
- Incremente el conteo en esa cantidad.
- El conteo final es la respuesta requerida.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find valid pairs in given range
int ValidPair(int a[], int n, int l, int r)
{
// Sort the array in the increasing order
sort(a, a + n);
// Precompute the powers
// to avoid later calculations
vector<int> pow10(17, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= 16; i++) {
pow10[i] = pow10[i - 1] * 10;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Determining the length of a[j]
int len = 0;
int cur = a[j];
while (cur) {
cur /= 10;
len++;
}
// Finding out the range
int right = (r - a[j]) / pow10[len];
int left = (l - a[j] + pow10[len] - 1) / pow10[len];
// Applying the binary search to find number of
// elements
if (left <= right)
ans += (upper_bound(a, a + n, right)
- lower_bound(a, a + n, left));
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 2;
int L = 10, R = 52;
int arr[2] = { 2, 5 };
cout << ValidPair(arr, N, L, R) << endl;
return 0;
}
Python3
# Python3 code for the above approach def upper_bound(arr, X) : low = 0 high = len(arr) while low < high : mid = low + int((high - low) / 2) if (X >= arr[mid]) : low = mid + 1 else : high = mid; if low < N and arr[low] <= X : low+=1 return low def lower_bound(a, val) : lo = 0 hi = len(a) - 1 while (lo < hi) : mid = (lo + int((hi - lo) / 2)) if (a[mid] < val) : lo = mid + 1 else : hi = mid return lo # Function to find valid pairs in given range def ValidPair(a, n, l, r) : # Sort the array in the increasing order a.sort() # Precompute the powers # to avoid later calculations #vector<int> pow10(17, 1); pow10 = [1]*17 for i in range(1,17) : pow10[i] = pow10[i - 1] * 10 ans = 0; for j in range(0,n) : # Determining the length of a[j] len = 0 cur = a[j]; while (cur>0) : cur = int(cur/10) len+=1 # Finding out the range right = int((r - a[j]) / pow10[len]) left = int((l - a[j] + pow10[len] - 1) / pow10[len]) # Applying the binary search to find number of # elements if left <= right : ans += (upper_bound(a, right) - lower_bound(a, left)) return ans # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__" : N = 2 L = 10 R = 52 arr = [ 2, 5 ] # Function call print(ValidPair(arr, N, L, R)) # This code is contributed by adityapatil12
C#
using System;
public class GFG{
// Function to implement lower_bound
public static int lower_bound(int[] arr, int N, int X)
{
int mid;
// Initialise starting index and
// ending index
int low = 0;
int high = N;
// Till low is less than high
while (low < high) {
mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If X is less than or equal
// to arr[mid], then find in
// left subarray
if (X <= arr[mid]) {
high = mid;
}
// If X is greater arr[mid]
// then find in right subarray
else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
// if X is greater than arr[n-1]
if(low < N && arr[low] < X) {
low++;
}
// Return the lower_bound index
return low;
}
// Function to implement upper_bound
public static int upper_bound(int[] arr, int N, int X)
{
int mid;
// Initialise starting index and
// ending index
int low = 0;
int high = N;
// Till low is less than high
while (low < high) {
// Find the middle index
mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If X is greater than or equal
// to arr[mid] then find
// in right subarray
if (X >= arr[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
}
// If X is less than arr[mid]
// then find in left subarray
else {
high = mid;
}
}
// if X is greater than arr[n-1]
if(low < N && arr[low] <= X) {
low++;
}
// Return the upper_bound index
return low;
}
// Function to find valid pairs in given range
public static int ValidPair(int[] a, int n, int l, int r)
{
// Sort the array in the increasing order
Array.Sort(a);
// Precompute the powers
// to avoid later calculations
int[] pow10 = new int[17];
for(int i=0;i<17;i++)
{
pow10[i]=1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 16; i++) {
pow10[i] = pow10[i - 1] * 10;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Determining the length of a[j]
int len = 0;
int cur = a[j];
while (cur>0) {
cur /= 10;
len++;
}
// Finding out the range
int right = (r - a[j]) / pow10[len];
int left = (l - a[j] + pow10[len] - 1) / pow10[len];
// Applying the binary search to find number of
// elements
if (left <= right)
ans += (upper_bound(a,a.Length, right)
- lower_bound(a, a.Length, left));
}
return ans;
}
static public void Main (){
int N = 2;
int L = 10;
int R = 52;
int[] arr = { 2, 5 };
Console.WriteLine( ValidPair(arr, N, L, R));
}
}
// This code is contributed by akashish__
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code for the above approach
function upper_bound(arr, N, X) {
let mid;
let low = 0;
let high = arr.length;
while (low < high) {
mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (X >= arr[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
}
else {
high = mid;
}
}
if (low < N && arr[low] <= X) {
low++;
}
return low;
}
function lower_bound(a, val) {
let lo = 0, hi = a.length - 1;
while (lo < hi) {
let mid = Math.floor(lo + (hi - lo) / 2);
if (a[mid] < val)
lo = mid + 1;
else
hi = mid;
}
return lo;
}
function ValidPair(a, n, l, r)
{
a.sort(function (a, b) { return a - b })
let pow10 = new Array(17).fill(1);
for (let i = 1; i <= 16; i++) {
pow10[i] = pow10[i - 1] * 10;
}
let ans = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
let len = 0;
let cur = a[j];
while (cur) {
cur = Math.floor(cur / 10);
len++;
}
let right = (r - a[j]) / pow10[len];
let left = (l - a[j] + pow10[len] - 1) / pow10[len];
if (left <= right)
ans += (upper_bound(a, a + n, right)
- lower_bound(a, a + n, left));
}
return ans;
}
let N = 2;
let L = 10, R = 52;
let arr = [2, 5];
document.write(ValidPair(arr, N, L, R) + '<br>');
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh
</script>
3
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N * logN)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por hemantrathore2705 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA