Dados tres enteros positivos, L , R , K y un arreglo arr[] que consta de N enteros positivos, la tarea es contar el número de formas de seleccionar al menos K elementos del arreglo que tengan valores en el rango [L, R] .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {12, 4, 6, 13, 5, 10}, K = 3, L = 4, R = 10
Salida: 5
Explicación:
formas posibles de seleccionar al menos K(= 3) elementos de array que tengan los valores en el rango [4, 10] son: { (arr[1], arr[2], arr[4]), (arr[1], arr[2], arr[5]), (arr[1 ], salida[4], salida[5]), (salida[2], salida[4], salida[5]), (salida[1], salida[2], salida[4], salida[5] ) }
Por lo tanto, la salida requerida es 5.Entrada: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, K = 4, L = 1, R = 5
Salida: 6
Enfoque: siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice una variable, digamos cntWays , para almacenar el recuento de formas de seleccionar al menos K elementos de array que tengan valores en el rango [L, R] .
- Inicialice una variable, diga cntNum para almacenar el recuento de números en la array dada cuyos valores se encuentran en el rango rango dado.
- Finalmente, imprima la suma de todos los valores posibles de
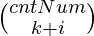 tal que (K + i) sea menor o igual que cntNum .
tal que (K + i) sea menor o igual que cntNum .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate factorial
// of all the numbers up to N
vector<int> calculateFactorial(int N)
{
vector<int> fact(N + 1);
// Factorial of 0 is 1
fact[0] = 1;
// Calculate factorial of
// all the numbers upto N
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
// Calculate factorial of i
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
}
return fact;
}
// Function to find the count of ways to select
// at least K elements whose values in range [L, R]
int cntWaysSelection(int arr[], int N, int K,
int L, int R)
{
// Stores count of ways to select at least
// K elements whose values in range [L, R]
int cntWays = 0;
// Stores count of numbers having
// value lies in the range [L, R]
int cntNum = 0;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Checks if the array elements
// lie in the given range
if (arr[i] >= L && arr[i] <= R) {
// Update cntNum
cntNum++;
}
}
// Stores factorial of numbers upto N
vector<int> fact
= calculateFactorial(cntNum);
// Calculate total ways to select at least
// K elements whose values lies in [L, R]
for (int i = K; i <= cntNum; i++) {
// Update cntWays
cntWays += fact[cntNum] / (fact[i]
* fact[cntNum - i]);
}
return cntWays;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 4, 6, 13, 5, 10 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int K = 3;
int L = 4;
int R = 10;
cout << cntWaysSelection(arr, N, K, L, R);
}
Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
class GFG{
// Function to calculate factorial
// of all the numbers up to N
static int[] calculateFactorial(int N)
{
int []fact = new int[N + 1];
// Factorial of 0 is 1
fact[0] = 1;
// Calculate factorial of
// all the numbers upto N
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
// Calculate factorial of i
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
}
return fact;
}
// Function to find the count of ways to select
// at least K elements whose values in range [L, R]
static int cntWaysSelection(int arr[], int N, int K,
int L, int R)
{
// Stores count of ways to select at least
// K elements whose values in range [L, R]
int cntWays = 0;
// Stores count of numbers having
// value lies in the range [L, R]
int cntNum = 0;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Checks if the array elements
// lie in the given range
if (arr[i] >= L && arr[i] <= R) {
// Update cntNum
cntNum++;
}
}
// Stores factorial of numbers upto N
int []fact
= calculateFactorial(cntNum);
// Calculate total ways to select at least
// K elements whose values lies in [L, R]
for (int i = K; i <= cntNum; i++) {
// Update cntWays
cntWays += fact[cntNum] / (fact[i]
* fact[cntNum - i]);
}
return cntWays;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 12, 4, 6, 13, 5, 10 };
int N = arr.length;
int K = 3;
int L = 4;
int R = 10;
System.out.print(cntWaysSelection(arr, N, K, L, R));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Python3
# Python3 program to implement the # above approach # Function to calculate factorial # of all the numbers up to N def calculateFactorial(N): fact = [0] * (N + 1) # Factorial of 0 is 1 fact[0] = 1 # Calculate factorial of all # the numbers upto N for i in range(1, N + 1): # Calculate factorial of i fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i return fact # Function to find count of ways to select # at least K elements whose values in range[L,R] def cntWaysSelection(arr, N, K, L, R): # Stores count of ways to select at leas # K elements whose values in range[L,R] cntWays = 0 # Stores count of numbers having # Value lies in the range[L,R] cntNum = 0 # Traverse the array for i in range(0, N): # Check if the array elements # Lie in the given range if (arr[i] >= L and arr[i] <= R): # Update cntNum cntNum += 1 # Stores factorial of numbers upto N fact = list(calculateFactorial(cntNum)) # Calculate total ways to select at least # K elements whose values Lies in [L,R] for i in range(K, cntNum + 1): # Update cntWays cntWays += fact[cntNum] // (fact[i] * fact[cntNum - i]) return cntWays # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [ 12, 4, 6, 13, 5, 10 ] N = len(arr) K = 3 L = 4 R = 10 print(cntWaysSelection(arr, N, K, L, R)) # This code is contributed by Virusbuddah
C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate factorial
// of all the numbers up to N
static int[] calculateFactorial(int N)
{
int[] fact = new int[(N + 1)];
// Factorial of 0 is 1
fact[0] = 1;
// Calculate factorial of
// all the numbers upto N
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
// Calculate factorial of i
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
}
return fact;
}
// Function to find the count of ways to select
// at least K elements whose values in range [L, R]
static int cntWaysSelection(int[] arr, int N, int K,
int L, int R)
{
// Stores count of ways to select at least
// K elements whose values in range [L, R]
int cntWays = 0;
// Stores count of numbers having
// value lies in the range [L, R]
int cntNum = 0;
// Traverse the array
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Checks if the array elements
// lie in the given range
if (arr[i] >= L && arr[i] <= R)
{
// Update cntNum
cntNum++;
}
}
// Stores factorial of numbers upto N
int[] fact = calculateFactorial(cntNum);
// Calculate total ways to select at least
// K elements whose values lies in [L, R]
for(int i = K; i <= cntNum; i++)
{
// Update cntWays
cntWays += fact[cntNum] / (fact[i] *
fact[cntNum - i]);
}
return cntWays;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 12, 4, 6, 13, 5, 10 };
int N = arr.Length;
int K = 3;
int L = 4;
int R = 10;
Console.WriteLine(cntWaysSelection(
arr, N, K, L, R));
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_hunt
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to implement
// the above approach
// Function to calculate factorial
// of all the numbers up to N
function calculateFactorial(N)
{
var fact = Array(N + 1);
// Factorial of 0 is 1
fact[0] = 1;
// Calculate factorial of
// all the numbers upto N
for (var i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
// Calculate factorial of i
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
}
return fact;
}
// Function to find the count of ways to select
// at least K elements whose values in range [L, R]
function cntWaysSelection(arr, N, K, L, R)
{
// Stores count of ways to select at least
// K elements whose values in range [L, R]
var cntWays = 0;
// Stores count of numbers having
// value lies in the range [L, R]
var cntNum = 0;
// Traverse the array
for (var i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Checks if the array elements
// lie in the given range
if (arr[i] >= L && arr[i] <= R) {
// Update cntNum
cntNum++;
}
}
// Stores factorial of numbers upto N
var fact = calculateFactorial(cntNum);
// Calculate total ways to select at least
// K elements whose values lies in [L, R]
for (var i = K; i <= cntNum; i++) {
// Update cntWays
cntWays += fact[cntNum] / (fact[i]
* fact[cntNum - i]);
}
return cntWays;
}
// Driver Code
var arr = [ 12, 4, 6, 13, 5, 10 ];
var N = arr.length;
var K = 3;
var L = 4;
var R = 10;
document.write( cntWaysSelection(arr, N, K, L, R));
</script>
5
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)