¿Qué es el determinante de una array?
El determinante de una Array es un número especial que se define solo para arrays cuadradas (arrays que tienen el mismo número de filas y columnas). Un determinante se usa en muchos lugares en cálculo y otras arrays relacionadas con el álgebra, en realidad representa la array en términos de un número real que se puede usar para resolver un sistema de ecuación lineal y encontrar la inversa de una array.
¿Como calcular?
El valor del determinante de una array se puede calcular mediante el siguiente procedimiento:
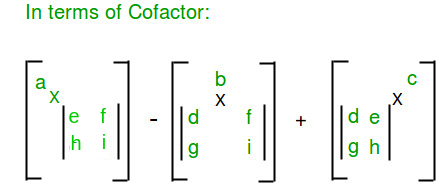
para cada elemento de la primera fila o primera columna, obtenga el cofactor de esos elementos y luego multiplique el elemento con el determinante del cofactor correspondiente, y finalmente súmelos con signos alternos. Como caso base, el valor del determinante de una array 1*1 es el valor único en sí mismo.
El cofactor de un elemento es una array que podemos obtener eliminando la fila y la columna de ese elemento de esa array.
Determinante de la array 2 x 2:


Determinante de la array 3 x 3: 
C++
// C++ program to find Determinant of a matrix
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Dimension of input square matrix
#define N 4
// Function to get cofactor of mat[p][q] in temp[][]. n is
// current dimension of mat[][]
void getCofactor(int mat[N][N], int temp[N][N], int p,
int q, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
// Looping for each element of the matrix
for (int row = 0; row < n; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
// Copying into temporary matrix only those
// element which are not in given row and
// column
if (row != p && col != q)
{
temp[i][j++] = mat[row][col];
// Row is filled, so increase row index and
// reset col index
if (j == n - 1)
{
j = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
}
}
/* Recursive function for finding determinant of matrix.
n is current dimension of mat[][]. */
int determinantOfMatrix(int mat[N][N], int n)
{
int D = 0; // Initialize result
// Base case : if matrix contains single element
if (n == 1)
return mat[0][0];
int temp[N][N]; // To store cofactors
int sign = 1; // To store sign multiplier
// Iterate for each element of first row
for (int f = 0; f < n; f++)
{
// Getting Cofactor of mat[0][f]
getCofactor(mat, temp, 0, f, n);
D += sign * mat[0][f]
* determinantOfMatrix(temp, n - 1);
// terms are to be added with alternate sign
sign = -sign;
}
return D;
}
/* function for displaying the matrix */
void display(int mat[N][N], int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
cout <<" " << mat[i][j];
cout <<"n";
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/* int mat[N][N] = {{6, 1, 1},
{4, -2, 5},
{2, 8, 7}}; */
int mat[N][N] = { { 1, 0, 2, -1 },
{ 3, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 2, 1, 4, -3 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0 } };
// Function call
cout <<"Determinant of the matrix is : " << determinantOfMatrix(mat, N);
return 0;
}
// this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C
// C program to find Determinant of a matrix
#include <stdio.h>
// Dimension of input square matrix
#define N 4
// Function to get cofactor of mat[p][q] in temp[][]. n is
// current dimension of mat[][]
void getCofactor(int mat[N][N], int temp[N][N], int p,
int q, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
// Looping for each element of the matrix
for (int row = 0; row < n; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
// Copying into temporary matrix only those
// element which are not in given row and
// column
if (row != p && col != q)
{
temp[i][j++] = mat[row][col];
// Row is filled, so increase row index and
// reset col index
if (j == n - 1)
{
j = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
}
}
/* Recursive function for finding determinant of matrix.
n is current dimension of mat[][]. */
int determinantOfMatrix(int mat[N][N], int n)
{
int D = 0; // Initialize result
// Base case : if matrix contains single element
if (n == 1)
return mat[0][0];
int temp[N][N]; // To store cofactors
int sign = 1; // To store sign multiplier
// Iterate for each element of first row
for (int f = 0; f < n; f++)
{
// Getting Cofactor of mat[0][f]
getCofactor(mat, temp, 0, f, n);
D += sign * mat[0][f]
* determinantOfMatrix(temp, n - 1);
// terms are to be added with alternate sign
sign = -sign;
}
return D;
}
/* function for displaying the matrix */
void display(int mat[N][N], int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
printf(" %d", mat[i][j]);
printf("n");
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/* int mat[N][N] = {{6, 1, 1},
{4, -2, 5},
{2, 8, 7}}; */
int mat[N][N] = { { 1, 0, 2, -1 },
{ 3, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 2, 1, 4, -3 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0 } };
// Function call
printf("Determinant of the matrix is : %d",
determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find Determinant of
// a matrix
class GFG {
// Dimension of input square matrix
static final int N = 4;
// Function to get cofactor of
// mat[p][q] in temp[][]. n is
// current dimension of mat[][]
static void getCofactor(int mat[][], int temp[][],
int p, int q, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
// Looping for each element of
// the matrix
for (int row = 0; row < n; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
// Copying into temporary matrix
// only those element which are
// not in given row and column
if (row != p && col != q)
{
temp[i][j++] = mat[row][col];
// Row is filled, so increase
// row index and reset col
// index
if (j == n - 1)
{
j = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
}
}
/* Recursive function for finding determinant
of matrix. n is current dimension of mat[][]. */
static int determinantOfMatrix(int mat[][], int n)
{
int D = 0; // Initialize result
// Base case : if matrix contains single
// element
if (n == 1)
return mat[0][0];
// To store cofactors
int temp[][] = new int[N][N];
// To store sign multiplier
int sign = 1;
// Iterate for each element of first row
for (int f = 0; f < n; f++)
{
// Getting Cofactor of mat[0][f]
getCofactor(mat, temp, 0, f, n);
D += sign * mat[0][f]
* determinantOfMatrix(temp, n - 1);
// terms are to be added with
// alternate sign
sign = -sign;
}
return D;
}
/* function for displaying the matrix */
static void display(int mat[][], int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
System.out.print(mat[i][j]);
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int mat[][] = { { 1, 0, 2, -1 },
{ 3, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 2, 1, 4, -3 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0 } };
System.out.print("Determinant "
+ "of the matrix is : "
+ determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.
Python3
# python program to find
# determinant of matrix.
# defining a function to get the
# minor matrix after excluding
# i-th row and j-th column.
def getcofactor(m, i, j):
return [row[: j] + row[j+1:] for row in (m[: i] + m[i+1:])]
# defining the function to
# calculate determinant value
# of given matrix a.
def determinantOfMatrix(mat):
# if given matrix is of order
# 2*2 then simply return det
# value by cross multiplying
# elements of matrix.
if(len(mat) == 2):
value = mat[0][0] * mat[1][1] - mat[1][0] * mat[0][1]
return value
# initialize Sum to zero
Sum = 0
# loop to traverse each column
# of matrix a.
for current_column in range(len(mat)):
# calculating the sign corresponding
# to co-factor of that sub matrix.
sign = (-1) ** (current_column)
# calling the function recursily to
# get determinant value of
# sub matrix obtained.
sub_det = determinantOfMatrix(getcofactor(mat, 0, current_column))
# adding the calculated determinant
# value of particular column
# matrix to total Sum.
Sum += (sign * mat[0][current_column] * sub_det)
# returning the final Sum
return Sum
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# declaring the matrix.
mat = [[1, 0, 2, -1],
[3, 0, 0, 5],
[2, 1, 4, -3],
[1, 0, 5, 0]]
# printing determinant value
# by function call
print('Determinant of the matrix is :', determinantOfMatrix(mat))
# This code is contributed by Amit Mangal.
C#
// C# program to find Determinant of
// a matrix
using System;
class GFG {
// Dimension of input square matrix
static int N = 4;
// Function to get cofactor of
// mat[p][q] in temp[][]. n is
// current dimension of mat[][]
static void getCofactor(int[, ] mat, int[, ] temp,
int p, int q, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
// Looping for each element of
// the matrix
for (int row = 0; row < n; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
// Copying into temporary matrix
// only those element which are
// not in given row and column
if (row != p && col != q) {
temp[i, j++] = mat[row, col];
// Row is filled, so increase
// row index and reset col
// index
if (j == n - 1) {
j = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
}
}
/* Recursive function for
finding determinant
of matrix. n is current
dimension of mat[][]. */
static int determinantOfMatrix(int[, ] mat, int n)
{
int D = 0; // Initialize result
// Base case : if matrix
// contains single
// element
if (n == 1)
return mat[0, 0];
// To store cofactors
int[, ] temp = new int[N, N];
// To store sign multiplier
int sign = 1;
// Iterate for each element
// of first row
for (int f = 0; f < n; f++)
{
// Getting Cofactor of mat[0][f]
getCofactor(mat, temp, 0, f, n);
D += sign * mat[0, f]
* determinantOfMatrix(temp, n - 1);
// terms are to be added with
// alternate sign
sign = -sign;
}
return D;
}
/* function for displaying
the matrix */
static void display(int[, ] mat, int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
Console.Write(mat[i, j]);
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[, ] mat = { { 1, 0, 2, -1 },
{ 3, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 2, 1, 4, -3 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0 } };
Console.Write("Determinant "
+ "of the matrix is : "
+ determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find Determinant of
// a matrix
// Dimension of input square matrix
let N = 4;
// Function to get cofactor of
// mat[p][q] in temp[][]. n is
// current dimension of mat[][]
function getCofactor(mat,temp,p,q,n)
{
let i = 0, j = 0;
// Looping for each element of
// the matrix
for (let row = 0; row < n; row++)
{
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
// Copying into temporary matrix
// only those element which are
// not in given row and column
if (row != p && col != q)
{
temp[i][j++] = mat[row][col];
// Row is filled, so increase
// row index and reset col
// index
if (j == n - 1)
{
j = 0;
i++;
}
}
}
}
}
/* Recursive function for finding determinant
of matrix. n is current dimension of mat[][]. */
function determinantOfMatrix(mat,n)
{
let D = 0; // Initialize result
// Base case : if matrix contains single
// element
if (n == 1)
return mat[0][0];
// To store cofactors
let temp = new Array(N);
for(let i=0;i<N;i++)
{
temp[i]=new Array(N);
}
// To store sign multiplier
let sign = 1;
// Iterate for each element of first row
for (let f = 0; f < n; f++)
{
// Getting Cofactor of mat[0][f]
getCofactor(mat, temp, 0, f, n);
D += sign * mat[0][f]
* determinantOfMatrix(temp, n - 1);
// terms are to be added with
// alternate sign
sign = -sign;
}
return D;
}
/* function for displaying the matrix */
function display(mat,row,col)
{
for (let i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (let j = 0; j < col; j++)
document.write(mat[i][j]);
document.write("<br>");
}
}
// Driver code
let mat=[[ 1, 0, 2, -1 ],
[ 3, 0, 0, 5 ],
[ 2, 1, 4, -3 ],
[ 1, 0, 5, 0 ]];
document.write("Determinant "
+ "of the matrix is : "
+ determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
// This code is contributed by rag2127
</script>
Determinant of the matrix is : 30
Adjunto e Inverso de una Array
Hay varias propiedades del Determinante que pueden ser útiles para resolver problemas relacionados con arrays.
Este artículo es una contribución de Utkarsh Trivedi. Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
En el método anterior se discute el enfoque recursivo. Cuando el tamaño de la array es grande, consume más tamaño de pila
. En este método, estamos usando las propiedades de Determinante. En este enfoque, estamos convirtiendo la array dada en una array triangular superior utilizando propiedades determinantes. El determinante de la array triangular superior es el producto de todos los elementos diagonales. Para conocer las propiedades del determinante, visite este sitio web https://cran.r-project.org/web /paquetes/matlib/viñetas/det-ex1.html
En este enfoque, estamos iterando cada elemento diagonal y haciendo que todos los elementos de la diagonal sean cero usando propiedades determinantes
Si el elemento diagonal es cero, buscaremos el siguiente elemento distinto de cero en la misma columna
Existen dos casos
Caso 1:
Si no hay ningún elemento distinto de cero. En este caso, el determinante de la array es cero
. Caso 2:
si existe un elemento distinto de cero, existen dos casos
. Caso a:
si el índice tiene el elemento de fila diagonal respectivo. Usando las propiedades determinantes, hacemos que todos los elementos de la columna sean cero
. Caso b:
aquí necesitamos intercambiar la fila con la columna respectiva del elemento diagonal y continuar con el caso ‘a; operación
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to find Determinant of a matrix
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Dimension of input square matrix
#define N 4
// Function to get determinant of matrix
int determinantOfMatrix(int mat[N][N], int n)
{
int num1, num2, det = 1, index,
total = 1; // Initialize result
// temporary array for storing row
int temp[n + 1];
// loop for traversing the diagonal elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
index = i; // initialize the index
// finding the index which has non zero value
while (index < n && mat[index][i] == 0)
{
index++;
}
if (index == n) // if there is non zero element
{
// the determinant of matrix as zero
continue;
}
if (index != i)
{
// loop for swapping the diagonal element row and
// index row
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
swap(mat[index][j], mat[i][j]);
}
// determinant sign changes when we shift rows
// go through determinant properties
det = det * pow(-1, index - i);
}
// storing the values of diagonal row elements
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
temp[j] = mat[i][j];
}
// traversing every row below the diagonal element
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
num1 = temp[i]; // value of diagonal element
num2 = mat[j][i]; // value of next row element
// traversing every column of row
// and multiplying to every row
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
// multiplying to make the diagonal
// element and next row element equal
mat[j][k]
= (num1 * mat[j][k]) - (num2 * temp[k]);
}
total = total * num1; // Det(kA)=kDet(A);
}
}
// multiplying the diagonal elements to get determinant
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
det = det * mat[i][i];
}
return (det / total); // Det(kA)/k=Det(A);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
/*int mat[N][N] = {{6, 1, 1},
{4, -2, 5},
{2, 8, 7}}; */
int mat[N][N] = { { 1, 0, 2, -1 },
{ 3, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 2, 1, 4, -3 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0 } };
// Function call
printf("Determinant of the matrix is : %d",
determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find Determinant of a matrix
class GFG
{
// Dimension of input square matrix
static final int N = 4;
// Function to get determinant of matrix
static int determinantOfMatrix(int mat[][], int n)
{
int num1, num2, det = 1, index,
total = 1; // Initialize result
// temporary array for storing row
int[] temp = new int[n + 1];
// loop for traversing the diagonal elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
index = i; // initialize the index
// finding the index which has non zero value
while (index < n && mat[index][i] == 0)
{
index++;
}
if (index == n) // if there is non zero element
{
// the determinant of matrix as zero
continue;
}
if (index != i)
{
// loop for swapping the diagonal element row
// and index row
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
swap(mat, index, j, i, j);
}
// determinant sign changes when we shift
// rows go through determinant properties
det = (int)(det * Math.pow(-1, index - i));
}
// storing the values of diagonal row elements
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
temp[j] = mat[i][j];
}
// traversing every row below the diagonal
// element
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
num1 = temp[i]; // value of diagonal element
num2 = mat[j]
[i]; // value of next row element
// traversing every column of row
// and multiplying to every row
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
// multiplying to make the diagonal
// element and next row element equal
mat[j][k] = (num1 * mat[j][k])
- (num2 * temp[k]);
}
total = total * num1; // Det(kA)=kDet(A);
}
}
// multiplying the diagonal elements to get
// determinant
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
det = det * mat[i][i];
}
return (det / total); // Det(kA)/k=Det(A);
}
static int[][] swap(int[][] arr, int i1, int j1, int i2,
int j2)
{
int temp = arr[i1][j1];
arr[i1][j1] = arr[i2][j2];
arr[i2][j2] = temp;
return arr;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*int mat[N][N] = {{6, 1, 1},
{4, -2, 5},
{2, 8, 7}}; */
int mat[][] = { { 1, 0, 2, -1 },
{ 3, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 2, 1, 4, -3 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0 } };
// Function call
System.out.printf(
"Determinant of the matrix is : %d",
determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python program to find Determinant of a matrix
def determinantOfMatrix(mat, n):
temp = [0]*n # temporary array for storing row
total = 1
det = 1 # initialize result
# loop for traversing the diagonal elements
for i in range(0, n):
index = i # initialize the index
# finding the index which has non zero value
while(index < n and mat[index][i] == 0):
index += 1
if(index == n): # if there is non zero element
# the determinant of matrix as zero
continue
if(index != i):
# loop for swapping the diagonal element row and index row
for j in range(0, n):
mat[index][j], mat[i][j] = mat[i][j], mat[index][j]
# determinant sign changes when we shift rows
# go through determinant properties
det = det*int(pow(-1, index-i))
# storing the values of diagonal row elements
for j in range(0, n):
temp[j] = mat[i][j]
# traversing every row below the diagonal element
for j in range(i+1, n):
num1 = temp[i] # value of diagonal element
num2 = mat[j][i] # value of next row element
# traversing every column of row
# and multiplying to every row
for k in range(0, n):
# multiplying to make the diagonal
# element and next row element equal
mat[j][k] = (num1*mat[j][k]) - (num2*temp[k])
total = total * num1 # Det(kA)=kDet(A);
# multiplying the diagonal elements to get determinant
for i in range(0, n):
det = det*mat[i][i]
return int(det/total) # Det(kA)/k=Det(A);
# Drivers code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# mat=[[6 1 1][4 -2 5][2 8 7]]
mat = [[1, 0, 2, -1], [3, 0, 0, 5], [2, 1, 4, -3], [1, 0, 5, 0]]
N = len(mat)
# Function call
print("Determinant of the matrix is : ", determinantOfMatrix(mat, N))
C#
// C# program to find Determinant of a matrix
using System;
class GFG {
// Dimension of input square matrix
static readonly int N = 4;
// Function to get determinant of matrix
static int determinantOfMatrix(int[, ] mat, int n)
{
int num1, num2, det = 1, index,
total = 1; // Initialize result
// temporary array for storing row
int[] temp = new int[n + 1];
// loop for traversing the diagonal elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
index = i; // initialize the index
// finding the index which has non zero value
while(index < n && mat[index, i] == 0)
{
index++;
}
if (index == n) // if there is non zero element
{
// the determinant of matrix as zero
continue;
}
if (index != i)
{
// loop for swapping the diagonal element row
// and index row
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
swap(mat, index, j, i, j);
}
// determinant sign changes when we shift
// rows go through determinant properties
det = (int)(det * Math.Pow(-1, index - i));
}
// storing the values of diagonal row elements
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
temp[j] = mat[i, j];
}
// traversing every row below the diagonal
// element
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
num1 = temp[i]; // value of diagonal element
num2 = mat[j,
i]; // value of next row element
// traversing every column of row
// and multiplying to every row
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
// multiplying to make the diagonal
// element and next row element equal
mat[j, k] = (num1 * mat[j, k])
- (num2 * temp[k]);
}
total = total * num1; // Det(kA)=kDet(A);
}
}
// multiplying the diagonal elements to get
// determinant
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
det = det * mat[i, i];
}
return (det / total); // Det(kA)/k=Det(A);
}
static int[, ] swap(int[, ] arr, int i1, int j1, int i2,
int j2)
{
int temp = arr[i1, j1];
arr[i1, j1] = arr[i2, j2];
arr[i2, j2] = temp;
return arr;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/*int mat[N,N] = {{6, 1, 1},
{4, -2, 5},
{2, 8, 7}}; */
int[, ] mat = { { 1, 0, 2, -1 },
{ 3, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 2, 1, 4, -3 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0 } };
// Function call
Console.Write("Determinant of the matrix is : {0}",
determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
Javascript<script>
// javascript program to find Determinant of a matrix
// Dimension of input square matrix
var N = 4;
// Function to get determinant of matrix
function determinantOfMatrix(mat , n)
{
var num1, num2, det = 1, index,
total = 1; // Initialize result
// temporary array for storing row
var temp = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
// loop for traversing the diagonal elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
index = i; // initialize the index
// finding the index which has non zero value
while (index < n && mat[index][i] == 0)
{
index++;
}
if (index == n) // if there is non zero element
{
// the determinant of matrix as zero
continue;
}
if (index != i)
{
// loop for swapping the diagonal element row
// and index row
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
swap(mat, index, j, i, j);
}
// determinant sign changes when we shift
// rows go through determinant properties
det = parseInt((det * Math.pow(-1, index - i)));
}
// storing the values of diagonal row elements
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
temp[j] = mat[i][j];
}
// traversing every row below the diagonal
// element
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
num1 = temp[i]; // value of diagonal element
num2 = mat[j]
[i]; // value of next row element
// traversing every column of row
// and multiplying to every row
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
// multiplying to make the diagonal
// element and next row element equal
mat[j][k] = (num1 * mat[j][k])
- (num2 * temp[k]);
}
total = total * num1; // Det(kA)=kDet(A);
}
}
// multiplying the diagonal elements to get
// determinant
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
det = det * mat[i][i];
}
return (det / total); // Det(kA)/k=Det(A);
}
function swap(arr , i1 , j1 , i2,
j2)
{
var temp = arr[i1][j1];
arr[i1][j1] = arr[i2][j2];
arr[i2][j2] = temp;
return arr;
}
// Driver code
/*var mat[N][N] = [{6, 1, 1],
{4, -2, 5],
{2, 8, 7}]; */
var mat = [ [ 1, 0, 2, -1 ],
[ 3, 0, 0, 5 ],
[ 2, 1, 4, -3 ],
[ 1, 0, 5, 0 ] ];
// Function call
document.write(
"Determinant of the matrix is : ",
determinantOfMatrix(mat, N));
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
Determinant of the matrix is : 30
Complejidad temporal: O(n 3 )
Espacio auxiliar: O(n)
Método 3: usar el paquete numpy en python
Hay una función o método incorporado en el módulo linalg del paquete numpy en python. Se puede llamar como numpy.linalg.det(mat) que devuelve el valor determinante de la array mat pasada en el argumento.
Python3
# importing the numpy package
# as np
import numpy as np
def determinant(mat):
# calling the det() method
det = np.linalg.det(mat)
return round(det)
# Driver Code
# declaring the matrix
mat = [[1, 0, 2, -1],
[3, 0, 0, 5],
[2, 1, 4, -3],
[1, 0, 5, 0]]
# Function call
print('Determinant of the matrix is:',
determinant(mat))
# This code is contributed by Amit Mangal.
Producción:
Determinant of the matrix is: 30
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA