Declaración del problema: diseñe un autómata finito definido para aceptar la permutación de tres a y tres b sobre la entrada {a, b}
Entrada : S = “aaabbb”
Salida : Aceptada
Explicación :
La entrada tiene tres a y tres b.Entrada : S = “abababa”
Salida : Aceptada
Explicación :
La entrada tiene tres a y tres b.
Para diseñar un DFA necesitamos verificar la entrada carácter por carácter. Estos son algunos pasos que deben tenerse en cuenta al diseñar un DFA.
- Piense en la mayoría de las posibles entradas que se pueden aceptar (como, en este ejemplo, aaabbb, bbbaaa, ababab, abaabb…etc).
- Crear un estado de transición inicial.
- Haga la transición en cada alfabeto de entrada a otros estados de transición.
- Llegar a un estado final tal que en cada paso se aceptara el lenguaje utilizado (como, en este ejemplo, un número igual de a y b).
Pasos de diseño:
Paso 1 : Cree un estado inicial «A» que se indica mediante —>.
Paso 2 : Piense en la posible string que puede aaabbb o bbbaaa que puede ocurrir por transición como,
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «A» al estado «B»
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «B» al estado «C»
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «C» al estado «D»
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «D» al estado muerto «Q2»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «D» al estado «E»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «E» al estado «F»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «F» al estado «G»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «G» al estado muerto «Q2»

Paso 3 : Ahora trabaje en una posibilidad como que b viene después de dos a, por ejemplo aababb, aabbab.
- La transición de ‘b’ del estado «C» al estado «J»
- La transición de ‘a’ del estado «J» al estado «E»
- La transición de ‘b’ del estado «J» al estado «M»
- La transición de ‘a’ del estado «M» al estado «F»
- La transición de ‘b’ del estado «M» al estado «P»
La transición se muestra en el diagrama.

Paso 4: Ahora pensando en la posibilidad de que comience con ‘aba’ y luego cumpla la condición del idioma dado. Para esto, se deben realizar las siguientes transiciones:
- La transición de ‘b’ del estado «B» al estado «I»
- La transición de ‘a’ del estado «I» al estado «J»
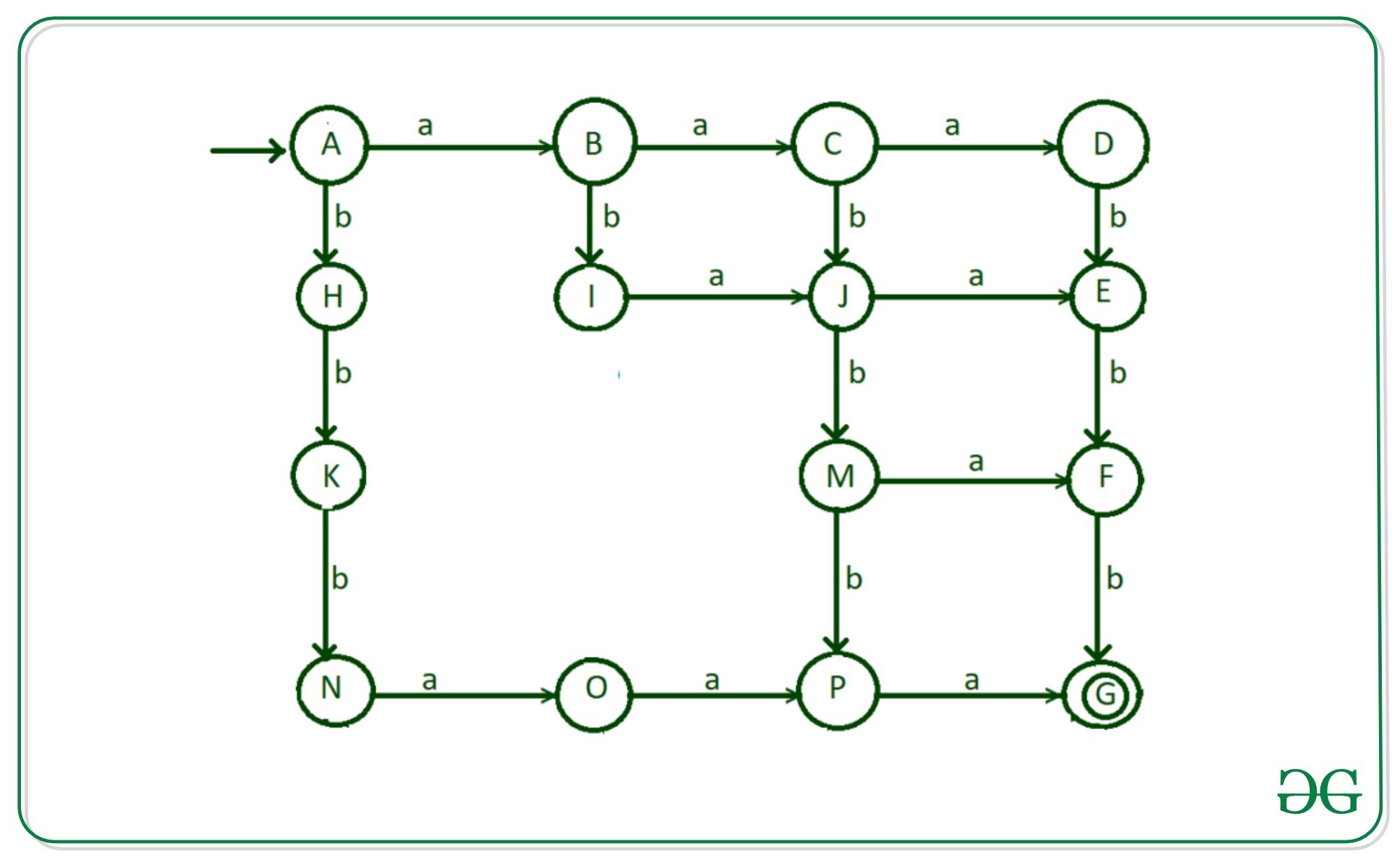
Paso 5: Ahora pensando en la posibilidad de que comience con ‘abb’ y luego cumpla la condición del idioma dado. Para esto, se deben realizar las siguientes transiciones:
- La transición de ‘b’ del estado «I» al estado «L»
- La transición de ‘a’ del estado «L» al estado «M»

Paso 6: Ahora existe la posibilidad de que después de leer una ‘a’, lea las 3 b y luego finalice la ejecución leyendo las 2 a restantes. Para la transición de ‘b’ del estado «L» a «O».

Paso 7: existe la posibilidad de que lea ‘a’ después de leer una ‘b’ y luego lea cualquier combinación de ‘a’ y ‘b’ para que la string contenga 3 a y 3 b. Para esta transición de ‘a ‘ se realiza desde el estado «H» al estado «I».

Paso 8: Ahora, piense en las strings que comienzan con dos b y busque cualquier combinación de strings para obtener el resultado deseado. Para esto, hacemos una transición de ‘a’ de la mirada «K» al estado «L».
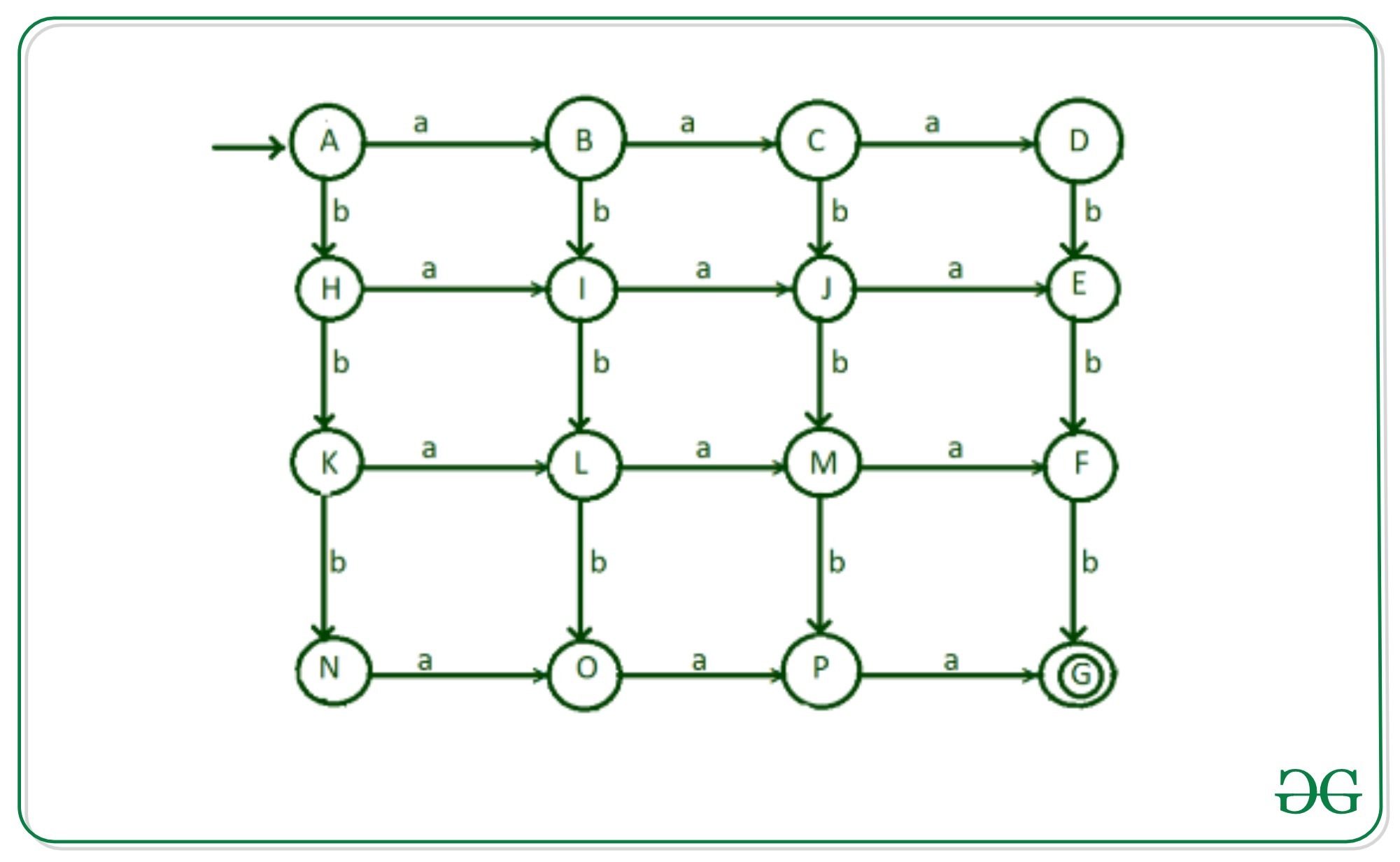
Paso 9: ahora ingrese el alfabeto ‘a’ de los estados D, E, F, G y ‘b’ de los estados G, N, O, P quedan para las transiciones. la transición restante irá a los estados muertos “Q1″ y Q2”.
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «D» al estado muerto «Q1»
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «E» al estado muerto «Q1»
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «F» al estado muerto «Q1»
- La transición de la entrada ‘a’ del estado «G» al estado muerto «Q1»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «G» al estado muerto «Q2»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «N» al estado muerto «Q2»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «O» al estado muerto «Q2»
- La transición de la entrada ‘b’ del estado «P» al estado muerto «Q2»

Tabla de transición de DFA anterior
| ESTADOS | ENTRADA (a) | ENTRADA (b) |
|---|---|---|
| —> A (estado inicial) | B | H |
| B | C | yo |
| C | D | j |
| D | Q2 (estado muerto) | mi |
| mi | Q2 (estado muerto) | F |
| F | Q2 (estado muerto) | G*(estado final) |
| G* (estado final) | Q2 (estado muerto) | Q1 (estado muerto) |
| H | yo | k |
| yo | j | L |
| j | mi | METRO |
| k | L | norte |
| L | METRO | O |
| METRO | F | PAGS |
| norte | O | Q1 (estado muerto) |
| O | PAGS | Q1 (estado muerto) |
| PAGS | G* (estado final) | Q1 (estado muerto) |
A continuación se muestra la implementación del DFA:
C++
// C++ implementation of the
// DFA of permutation of three
// a's and three b's
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// declaration of state functions
void stateA(string),stateB(string),stateC(string),stateD(string);
void stateE(string),stateF(string),stateG(string),stateH(string);
void stateI(string),stateJ(string),stateK(string),stateL(string);
void stateM(string),stateN(string),stateO(string),stateP(string);
void stateQ1(string),stateQ2(string);
// State A
void stateA(string n)
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateB(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
{
stateH(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State B
void stateB(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateC(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateI(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State C
void stateC(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateD(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateJ(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State D
void stateD(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateE(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State E
void stateE(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateF(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State F
void stateF(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateG(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State G
void stateG(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ2(n);
}
}
// State H
void stateH(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateI(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateK(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State I
void stateI(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateJ(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateL(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State J
void stateJ(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateE(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateM(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State K
void stateK(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateL(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateN(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State L
void stateL(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateM(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateO(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State M
void stateM(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateF(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateP(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State N
void stateN(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
if (n[0] =='a')
stateO(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
// State Q
void stateO(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateP(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
}
// State P
void stateP(string n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
cout << "string Not Accepted";
else
{
if (n[0] == 'a')
stateG(n.substr(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n.substr(1));
}
}
// State Q1
void stateQ1(string n)
{
cout << "string Not Accepted";
}
// State Q2
void stateQ2(string n)
{
cout << "string Not Accepted";
}
int main()
{
string n = "abaabb";
// call stateA
// to check the input
stateA(n);
}
Java
// Java implementation of the
// DFA of permutation of three
// a's and three b's
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// State A
static void stateA(String n)
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateB(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
{
stateH(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State B
static void stateB(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateC(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateI(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State C
static void stateC(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateD(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateJ(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State D
static void stateD(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateE(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State E
static void stateE(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateF(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State F
static void stateF(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateG(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State G
static void stateG(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ2(n);
}
}
// State H
static void stateH(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateI(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateK(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State I
static void stateI(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateJ(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateL(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State J
static void stateJ(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateE(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateM(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State K
static void stateK(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateL(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateN(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State L
static void stateL(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateM(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateO(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State M
static void stateM(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateF(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateP(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State N
static void stateN(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
if (n.charAt(0) =='a')
stateO(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
// State Q
static void stateO(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateP(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
}
// State P
static void stateP(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateG(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ1(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State Q1
static void stateQ1(String n)
{
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
}
// State Q2
static void stateQ2(String n)
{
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Take String input
String n = "abaabb";
// Call stateA
// to check the input
stateA(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the
# DFA of permutation of three
# a's and three b's
# State A
def stateA(n):
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateB(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateH(n[1:])
# State B
def stateB(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateC(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateI(n[1:])
# State C
def stateC(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateD(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateJ(n[1:])
# State D
def stateD(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n)
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateE(n[1:])
# State E
def stateE(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n)
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateF(n[1:])
# State F
def stateF(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateG(n[1:])
# State G
def stateG(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n)
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ2(n)
# State H
def stateH(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateI(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateK(n[1:])
# State I
def stateI(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateJ(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateL(n[1:])
# State J
def stateJ(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateE(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateM(n[1:])
# State K
def stateK(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateL(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateN(n[1:])
# State L
def stateL(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateM(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateO(n[1:])
# State M
def stateM(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateF(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateP(n[1:])
# State N
def stateN(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateO(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ1(n)
# State Q
def stateO(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateP(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ1(n)
# State P
def stateP(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateG(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ1(n[1:])
# State Q1
def stateQ1(n):
print("String Not Accepted")
# State Q2
def stateQ2(n):
print("String Not Accepted")
# take string input
n = "abaabb"
# call stateA
# to check the input
stateA(n)
C#
// C# implementation of the
// DFA of permutation of three
// a's and three b's
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG{
// State A
static void stateA(string n)
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateB(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
{
stateH(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State B
static void stateB(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateC(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateI(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State C
static void stateC(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateD(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateJ(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State D
static void stateD(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateE(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State E
static void stateE(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateF(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State F
static void stateF(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateG(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State G
static void stateG(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ2(n);
}
}
// State H
static void stateH(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateI(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateK(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State I
static void stateI(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateJ(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateL(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State J
static void stateJ(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateE(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateM(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State K
static void stateK(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateL(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateN(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State L
static void stateL(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateM(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateO(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State M
static void stateM(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateF(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateP(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State N
static void stateN(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
if(n[0] =='a')
stateO(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
// State Q
static void stateO(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateP(n.Substring(1));
else if(n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
}
// State P
static void stateP(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateG(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State Q1
static void stateQ1(string n)
{
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
}
// State Q2
static void stateQ2(string n)
{
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main (string[] args)
{
// Take string input
string n = "abaabb";
// Call stateA
// to check the input
stateA(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation of the
// DFA of permutation of three
// a's and three b's
// State A
function stateA(n) {
if (n[0] === "a") stateB(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") {
stateH(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State B
function stateB(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateC(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateI(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State C
function stateC(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateD(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateJ(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State D
function stateD(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] === "b") stateE(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State E
function stateE(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] === "b") stateF(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State F
function stateF(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateQ2(nsubstring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateG(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State G
function stateG(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] === "b") staseQ2(n);
}
}
// State H
function stateH(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateI(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateK(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State I
function stateI(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateJ(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateL(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State J
function stateJ(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateE(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateM(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State K
function stateK(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateL(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateN(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State L
function stateL(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateM(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateO(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State M
function stateM(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateF(n.substring(1));
else if (s[0] === "b") stateP((n.Substr = ing(s)));
}
}
// State N
function stateN(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else if (n[0] === "a") stateO(n.substring(1));
else if (n[s] === "b") stateQ1(n);
}
// Stste Q
function stateO(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateP(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") staseQ1(n);
}
}
// State P
function stateP(n) {
if (n.length === 0)
document.write("String Not Accepted");
else {
if (n[0] === "a") stateG(n.substring(1));
else if (n[0] === "b") stateQ1(nsSubstring(1));
}
}
// State Q1
function stateQ1(n) {
document.write("String Not Accepted");
}
// State Q2
function stateQ2(n) {
document.write("String Not Accepted");
}
// Driver code
// Take string input
var n = "abaabb";
// Call stateA
// to check the input
stateA(n);
</script>
String Accepted
Tiempo Complejidad : O(N)
Espacio Auxiliar : O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por _tanya_sri_ y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA