Dada una array mat[][] de dimensión N * M , la tarea es contar el número mínimo de decrementos de distintos elementos de la array necesarios para que no haya dos elementos de array adyacentes iguales.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: mat[][] = { {2, 3, 4}, {2, 5, 4} }
Salida: 3
Explicación: Disminuye los elementos de la array arr[0][0], arr[0][1], y arr[0][2] por 1 cada uno. La array se modifica a {{1, 2, 3}, {2, 5, 4}}. Por lo tanto, todos los pares de elementos de array adyacentes se vuelven diferentes.Entrada: mat[][] = { {1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 3} }
Salida: 3
Explicación: Disminuya cada elemento presente en la segunda fila de la array en 1. La array tendrá todos los elementos adyacentes diferentes como se muestra a continuación:
1 2 3
0 1 2
1 2 3
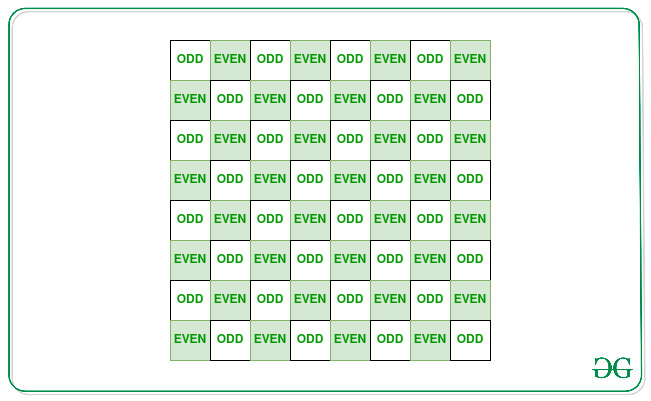
Enfoque: La idea principal es resolver el problema dado asumiendo la array como una cuadrícula de ajedrez que se muestra a continuación:
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Atraviesa la array
- Para cada elemento de la array, se presentan los siguientes dos casos:
- Caso 1: Si (i + j) es par, mat[i][j] debería ser par. De lo contrario, mat[i][j] debería ser impar.
- Caso 2: si (i + j) es par, el valor en mat[i][j] debería ser par. De lo contrario, el valor en mat[i][j] debería ser impar.
- Por lo tanto, calcule el número de operaciones requeridas en ambos casos.
- Imprime el mínimo de las dos cuentas obtenidas.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Matrix dimensions
const int n = 3;
const int m = 3;
// Function to count minimum
// number of operations required
void countDecrements(long long arr[][m])
{
int count_1 = 0;
int count_2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// Case 1:
if ((i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2)
count_1++;
// Case 2:
if (1 - (i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2)
count_2++;
}
}
// Print the minimum number
// of operations required
cout << min(count_1, count_2);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// The given matrix
long long arr[][m]
= { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 } };
// Function Call to count
// the minimum number of
// decrements required
countDecrements(arr);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Function to count minimum
// number of operations required
static void countDecrements(long arr[][])
{
// Matrix dimensions
int n = arr.length;
int m = arr[0].length;
int count_1 = 0;
int count_2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// Case 1:
if ((i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2)
count_1++;
// Case 2:
if (1 - (i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2)
count_2++;
}
}
// Print the minimum number
// of operations required
System.out.println(Math.min(count_1, count_2));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// The given matrix
long arr[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 } };
// Function Call to count
// the minimum number of
// decrements required
countDecrements(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash.
Python3
# Python program for # the above approach # Matrix dimensions n = 3 m = 3 # Function to count minimum # number of operations required def countDecrements(arr): count_1 = 0 count_2 = 0 for i in range(n): for j in range(m): # Case 1: if ((i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2): count_1 += 1 # Case 2: if (1 - (i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2): count_2 += 1 # Print the minimum number # of operations required print(min(count_1, count_2)) # Driver Code # The given matrix arr = [[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]] # Function Call to count # the minimum number of # decrements required countDecrements(arr) # This code is contributed by souravmahato348.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to count minimum
// number of operations required
static void countDecrements(long[,] arr)
{
// Matrix dimensions
int n = arr.GetLength(0);
int m = arr.GetLength(1);
int count_1 = 0;
int count_2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
// Case 1:
if ((i + j) % 2 == arr[i, j] % 2)
count_1++;
// Case 2:
if (1 - (i + j) % 2 == arr[i, j] % 2)
count_2++;
}
}
// Print the minimum number
// of operations required
Console.WriteLine(Math.Min(count_1, count_2));
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// The given matrix
long[,] arr = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 } };
// Function Call to count
// the minimum number of
// decrements required
countDecrements(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for
// the above approach
// Matrix dimensions
const n = 3;
const m = 3;
// Function to count minimum
// number of operations required
function countDecrements(arr)
{
let count_1 = 0;
let count_2 = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(let j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
// Case 1:
if ((i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2)
count_1++;
// Case 2:
if (1 - (i + j) % 2 == arr[i][j] % 2)
count_2++;
}
}
// Print the minimum number
// of operations required
document.write(Math.min(count_1, count_2));
}
// Driver Code
// The given matrix
let arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 1, 2, 3 ] ];
// Function Call to count
// the minimum number of
// decrements required
countDecrements(arr);
// This code is contributed by subhammahato348
</script>
3
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(N 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por aimformohan y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA