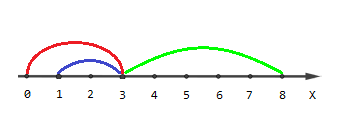
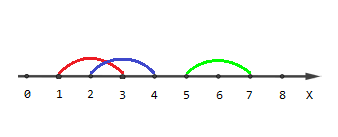
Dados los segmentos y algunos puntos, para cada punto encuentre el número de segmentos que cubren ese punto.
Un segmento (l, r) cubre un punto x si y solo si l < = x < = r .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: Segmentos = {{0, 3}, {1, 3}, {3, 8}},
Puntos = {-1, 3, 8}.
Salida: {0, 3, 1}
Explicación:
- No hay segmentos que pasen por el punto -1
- Todos los segmentos que pasan por el punto 3
- Tramo 3 que pasa por el punto 8
Entrada: Segmentos = {{1, 3}, {2, 4}, {5, 7}},
Puntos = {0, 2, 5}.
Salida: {0, 2, 1}
Explicación:
- No hay segmentos que pasen por el punto 0
- 1er y 2do segmento que pasa por el punto 2
- Tramo 3 que pasa por el punto 5
Acercarse:
- Podemos hacer esto usando una lógica similar a la suma de prefijos.
- Representemos un segmento con (l, r). Forme un vector de pares, para cada segmento empuje dos pares en vector con valores (l, +1) y (r + 1, -1).
- Ordene los puntos en orden ascendente, pero también necesitamos su posición, así que mapéelo con su posición.
- Ordene el vector de segmento en orden descendente porque lo iteramos desde atrás.
- Realice un recuento variable de segmentos, que inicialmente es cero.
- Luego, iteraremos en el punto y sacaremos el par del vector de segmento hasta que su primer valor sea menor que el punto actual y agregaremos su segundo valor al conteo.
- Finalmente, almacene los valores de count en una array en su posición respectiva e imprima la array.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ program to find the number of
// segments covering each points
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print an array
void PrintArray(int n,int arr[])
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
}
// Function prints number of segments
// covering by each points
void NumberOfSegments(vector<pair<int,int> >segments,
vector<int>points, int s, int p)
{
vector< pair<int, int> >pts, seg;
// Pushing points and index in
// vector as a pairs
for(int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
pts.push_back({points[i], i});;
}
for(int i = 0; i < s; i++)
{
// (l,+1)
seg.push_back({segments[i].first, 1});
// (r+1,-1)
seg.push_back({segments[i].second+1, -1});
}
// Sort the vectors
sort(seg.begin(), seg.end(),
greater<pair<int,int>>());
sort(pts.begin(),pts.end());
int count = 0;
int ans[p];
for(int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
int x = pts[i].first;
while(!seg.empty() &&
seg.back().first <= x)
{
count+= seg.back().second;
seg.pop_back();
}
ans[pts[i].second] = count;
}
// Print the answer
PrintArray(p, ans);
}
//Driver code
int main()
{
// Initializing vector of pairs
vector<pair<int,int>>seg;
// Push segments
seg.push_back({0, 3});
seg.push_back({1, 3});
seg.push_back({3, 8});
// Given points
vector<int>point{-1, 3, 7};
int s = seg.size();
int p = point.size();
NumberOfSegments(seg, point, s, p);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find the number of
// segments covering each points
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
// Function to print an array
static void PrintArray(int n,int arr[])
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// Function prints number of segments
// covering by each points
static void NumberOfSegments(ArrayList<int[]> segments,
int[] points, int s, int p)
{
ArrayList<int[]> pts = new ArrayList<>(),
seg = new ArrayList<>();
// Pushing points and index in
// vector as a pairs
for(int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
pts.add(new int[]{points[i], i});
}
for(int i = 0; i < s; i++)
{
// (l,+1)
seg.add(new int[]{segments.get(i)[0], 1});
// (r+1,-1)
seg.add(new int[]{segments.get(i)[1] + 1, -1});
}
// Sort the vectors
Collections.sort(seg, (a, b) -> b[0] - a[0]);
Collections.sort(pts, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int count = 0;
int[] ans = new int[p];
for(int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
int x = pts.get(i)[0];
while (seg.size() != 0 &&
seg.get(seg.size() - 1)[0] <= x)
{
count += seg.get(seg.size() - 1)[1];
seg.remove(seg.size() - 1);
}
ans[pts.get(i)[1]] = count;
}
// Print the answer
PrintArray(p, ans);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing vector of pairs
ArrayList<int[]>seg = new ArrayList<>();
// Push segments
seg.add(new int[]{0, 3});
seg.add(new int[]{1, 3});
seg.add(new int[]{3, 8});
// Given points
int[] point = {-1, 3, 7};
int s = seg.size();
int p = point.length;
NumberOfSegments(seg, point, s, p);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python3 program to find the number # of segments covering each point # Function to print an array def PrintArray(n, arr): for i in range(n): print(arr[i], end = " ") # Function prints number of segments # covering by each points def NumberOfSegments(segments, points, s, p): pts = [] seg = [] # Pushing points and index in # vector as a pairs for i in range(p): pts.append([points[i], i]) for i in range(s): # (l, +1) seg.append([segments[i][0], 1]) # (r+1, -1) seg.append([segments[i][1] + 1, -1]) # Sort the vectors seg.sort(reverse = True) pts.sort(reverse = False) count = 0 ans = [0 for i in range(p)] for i in range(p): x = pts[i][0] while(len(seg) != 0 and seg[len(seg) - 1][0] <= x): count += seg[len(seg) - 1][1] seg.remove(seg[len(seg) - 1]) ans[pts[i][1]] = count # Print the answer PrintArray(p, ans) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': # Initializing vector of pairs seg = [] # Push segments seg.append([ 0, 3 ]) seg.append([ 1, 3 ]) seg.append([ 3, 8 ]) # Given points point = [ -1, 3, 7 ] s = len(seg) p = len(point) NumberOfSegments(seg, point, s, p) # This code is contributed by Bhupendra_Singh
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find the number of
// segments covering each points
// Function to print an array
function PrintArray(n,arr)
{
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
document.write(arr[i]," ");
}
}
// Function prints number of segments
// covering by each points
function NumberOfSegments(segments,points,s,p)
{
let pts = [];
let seg = [];
// Pushing points and index in
// vector as a pairs
for(let i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
pts.push([points[i], i]);
}
for(let i = 0; i < s; i++)
{
// (l,+1)
seg.push([segments[i][0], 1]);
// (r+1,-1)
seg.push([segments[i][1]+1, -1]);
}
// Sort the vectors
seg.sort((a,b) => b[0]-a[0]);
pts.sort((a,b) => a[0]-b[0]);
let count = 0;
let ans = new Array(p);
for(let i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
let x = pts[i][0];
while(seg.length>0 && seg[seg.length-1][0] <= x)
{
count+= seg[seg.length-1][1];
seg.pop();
}
ans[pts[i][1]] = count;
}
// Print the answer
PrintArray(p, ans);
}
// Driver code
// Initializing vector of pairs
let seg = [];
// Push segments
seg.push([0, 3]);
seg.push([1, 3]);
seg.push([3, 8]);
// Given points
let point = [-1, 3, 7];
let s = seg.length;
let p = point.length;
NumberOfSegments(seg, point, s, p);
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra.
</script>
0 3 1
Complejidad temporal: O(s*log(s) + p*log(p)), donde s es el número de segmentos yp es el número de puntos.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(s + p).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por PrakashMishra2 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA