Dados dos enteros P y Q , la tarea es encontrar dos enteros cuyo máximo común divisor (MCD) sea P y la diferencia entre sus cuadrados sea Q. Si no existen tales enteros, imprima «-1» .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: P = 3, Q = 27
Salida: 6 3
Explicación:
Considere los dos números como 6, 3. Ahora, el MCD (6, 3) = 3 y 6*6 – 3*3 = 27 que satisface la condición.Entrada: P = 1, Q = 100
Salida: -1
Enfoque: El problema dado se puede resolver usando en base a las siguientes observaciones:
La ecuación dada también se puede escribir como:
=>
=>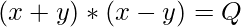
Ahora para una solución integral de la ecuación dada:
(x+y)(xy) siempre es un número entero
=> (x+y)(xy) son divisores de Q
Sean (x + y) = p1 y (x + y) = p2
las dos ecuaciones donde p1 y p2 son los divisores de Q
tales que p1 * p2 = Q.
Resolviendo las dos ecuaciones anteriores tenemos:
=>
y
De los cálculos anteriores, para que x e y sean integrales, entonces la suma de los divisores debe ser par . Dado que hay 4 valores posibles para dos valores de x e y como (+x, +y), (+x, -y), (-x, +y) y (-x, -y) .
Por lo tanto, el número total de posibles soluciones viene dado por 4*(cuenta pares de divisores con suma par) .
Ahora, entre estos pares, encuentre el par con GCD como P e imprima el par. Si no existe tal par, imprima -1.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print a valid pair with
// the given criteria
int printValidPair(int P, int Q)
{
// Iterate over the divisors of Q
for (int i = 1; i * i <= Q; i++) {
// check if Q is a multiple of i
if (Q % i == 0) {
// L = (A - B) <- 1st equation
// R = (A + B) <- 2nd equation
int L = i;
int R = Q / i;
// Calculate value of A
int A = (L + R) / 2;
// Calculate value of B
int B = (R - L) / 2;
// As A and B both are integers
// so the parity of L and R
// should be the same
if (L % 2 != R % 2) {
continue;
}
// Check the first condition
if (__gcd(A, B) == P) {
cout << A << " " << B;
return 0;
}
}
}
// If no such A, B exist
cout << -1;
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int P = 3, Q = 27;
printValidPair(P, Q);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to print a valid pair with
// the given criteria
static int printValidPair(int P, int Q)
{
// Iterate over the divisors of Q
for (int i = 1; i * i <= Q; i++) {
// check if Q is a multiple of i
if (Q % i == 0) {
// L = (A - B) <- 1st equation
// R = (A + B) <- 2nd equation
int L = i;
int R = Q / i;
// Calculate value of A
int A = (L + R) / 2;
// Calculate value of B
int B = (R - L) / 2;
// As A and B both are integers
// so the parity of L and R
// should be the same
if (L % 2 != R % 2) {
continue;
}
// Check the first condition
if (__gcd(A, B) == P) {
System.out.print(A+ " " + B);
return 0;
}
}
}
// If no such A, B exist
System.out.print(-1);
return 0;
}
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b == 0? a:__gcd(b, a % b);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int P = 3, Q = 27;
printValidPair(P, Q);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python3
# python program for the above approach
import math
# Function to print a valid pair with
# the given criteria
def printValidPair(P, Q):
# Iterate over the divisors of Q
for i in range(1, int(math.sqrt(Q)) + 1):
# check if Q is a multiple of i
if (Q % i == 0):
# L = (A - B) <- 1st equation
# R = (A + B) <- 2nd equation
L = i
R = Q // i
# Calculate value of A
A = (L + R) // 2
# Calculate value of B
B = (R - L) // 2
# As A and B both are integers
# so the parity of L and R
# should be the same
if (L % 2 != R % 2):
continue
# Check the first condition
if (math.gcd(A, B) == P):
print(f"{A} {B}")
return 0
# If no such A, B exist
print(-1)
return 0
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
P = 3
Q = 27
printValidPair(P, Q)
# This code is contributed by rakeshsahni
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to print a valid pair with
// the given criteria
static int printValidPair(int P, int Q)
{
// Iterate over the divisors of Q
for (int i = 1; i * i <= Q; i++)
{
// check if Q is a multiple of i
if (Q % i == 0)
{
// L = (A - B) <- 1st equation
// R = (A + B) <- 2nd equation
int L = i;
int R = Q / i;
// Calculate value of A
int A = (L + R) / 2;
// Calculate value of B
int B = (R - L) / 2;
// As A and B both are integers
// so the parity of L and R
// should be the same
if (L % 2 != R % 2)
{
continue;
}
// Check the first condition
if (__gcd(A, B) == P)
{
Console.Write(A + " " + B);
return 0;
}
}
}
// If no such A, B exist
Console.Write(-1);
return 0;
}
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b == 0 ? a : __gcd(b, a % b);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int P = 3, Q = 27;
printValidPair(P, Q);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gfgking
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code for the above approach
// Recursive function to return gcd of a and b
function __gcd(a, b) {
// Everything divides 0
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
// base case
if (a == b)
return a;
// a is greater
if (a > b)
return __gcd(a - b, b);
return __gcd(a, b - a);
}
// Function to print a valid pair with
// the given criteria
function printValidPair(P, Q) {
// Iterate over the divisors of Q
for (let i = 1; i * i <= Q; i++) {
// check if Q is a multiple of i
if (Q % i == 0) {
// L = (A - B) <- 1st equation
// R = (A + B) <- 2nd equation
let L = i;
let R = Q / i;
// Calculate value of A
let A = (L + R) / 2;
// Calculate value of B
let B = (R - L) / 2;
// As A and B both are integers
// so the parity of L and R
// should be the same
if (L % 2 != R % 2) {
continue;
}
// Check the first condition
if (__gcd(A, B) == P) {
document.write(A + " " + B);
return 0;
}
}
}
// If no such A, B exist
document.write(-1);
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
let P = 3, Q = 27;
printValidPair(P, Q);
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh
</script>
6 3
Complejidad de tiempo: O(sqrt(Q))
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por kartikmodi y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA