Dada una array NXN (M) rellena con 1 , 0 , 2 , 3 . Encuentre el número mínimo de movimientos necesarios para pasar del origen al destino (sumidero) . mientras atraviesa celdas en blanco solamente. Puede desplazarse hacia arriba, abajo, derecha e izquierda.
Un valor de la celda 1 significa Fuente.
Un valor de la celda 2 significa Destino.
Un valor de celda 3 significa celda en blanco.
Un valor de celda 0 significa Muro en blanco.
Nota : solo hay una fuente única y un destino único. Puede haber más de una ruta desde la fuente hasta el destino (sumidero). Cada movimiento en la array lo consideramos como ‘1’
Ejemplos:
Input : M[3][3] = {{ 0 , 3 , 2 },
{ 3 , 3 , 0 },
{ 1 , 3 , 0 }};
Output : 4
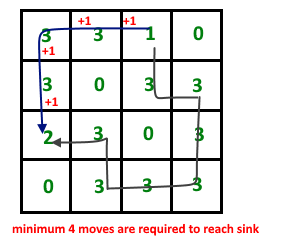
Input : M[4][4] = {{ 3 , 3 , 1 , 0 },
{ 3 , 0 , 3 , 3 },
{ 2 , 3 , 0 , 3 },
{ 0 , 3 , 3 , 3 }};
Output : 4
Preguntado en: Entrevista de Adobe
.
La idea es usar un gráfico de nivel (Breadth First Traversal). Considere cada celda como un Node y cada límite entre dos celdas adyacentes como un borde. por lo que el número total de Nodes es N*N.
- Cree un gráfico vacío que tenga un Node N*N (vértice).
- Inserte todos los Nodes en un gráfico.
- Anota los vértices fuente y sumidero.
- Ahora aplique el concepto de gráfico de nivel (que logramos usando BFS). En el que encontramos el nivel de cada Node desde el vértice de origen. Después de eso, devolvemos ‘Level[d]’ (d es el destino). (que es el movimiento mínimo desde la fuente hasta el sumidero)
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior.
C++
// C++ program to find the minimum numbers
// of moves needed to move from source to
// destination .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
class Graph
{
int V ;
list < int > *adj;
public :
Graph( int V )
{
this->V = V ;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void addEdge( int s , int d ) ;
int BFS ( int s , int d) ;
};
// add edge to graph
void Graph :: addEdge ( int s , int d )
{
adj[s].push_back(d);
adj[d].push_back(s);
}
// Level BFS function to find minimum path
// from source to sink
int Graph :: BFS(int s, int d)
{
// Base case
if (s == d)
return 0;
// make initial distance of all vertex -1
// from source
int *level = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
level[i] = -1 ;
// Create a queue for BFS
list<int> queue;
// Mark the source node level[s] = '0'
level[s] = 0 ;
queue.push_back(s);
// it will be used to get all adjacent
// vertices of a vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
while (!queue.empty())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
s = queue.front();
queue.pop_front();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the
// dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has
// not been visited ( level[i] < '0') ,
// then update level[i] == parent_level[s] + 1
// and enqueue it
for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i)
{
// Else, continue to do BFS
if (level[*i] < 0 || level[*i] > level[s] + 1 )
{
level[*i] = level[s] + 1 ;
queue.push_back(*i);
}
}
}
// return minimum moves from source to sink
return level[d] ;
}
bool isSafe(int i, int j, int M[][N])
{
if ((i < 0 || i >= N) ||
(j < 0 || j >= N ) || M[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Returns minimum numbers of moves from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a destination (a cell with
// value 2)
int MinimumPath(int M[][N])
{
int s , d ; // source and destination
int V = N*N+2;
Graph g(V);
// create graph with n*n node
// each cell consider as node
int k = 1 ; // Number of current vertex
for (int i =0 ; i < N ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0 ; j < N; j++)
{
if (M[i][j] != 0)
{
// connect all 4 adjacent cell to
// current cell
if ( isSafe ( i , j+1 , M ) )
g.addEdge ( k , k+1 );
if ( isSafe ( i , j-1 , M ) )
g.addEdge ( k , k-1 );
if (j< N-1 && isSafe ( i+1 , j , M ) )
g.addEdge ( k , k+N );
if ( i > 0 && isSafe ( i-1 , j , M ) )
g.addEdge ( k , k-N );
}
// source index
if( M[i][j] == 1 )
s = k ;
// destination index
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
// find minimum moves
return g.BFS (s, d) ;
}
// driver program to check above function
int main()
{
int M[N][N] = {{ 3 , 3 , 1 , 0 },
{ 3 , 0 , 3 , 3 },
{ 2 , 3 , 0 , 3 },
{ 0 , 3 , 3 , 3 }
};
cout << MinimumPath(M) << endl;
return 0;
}
Python3
# Python3 program to find the minimum numbers # of moves needed to move from source to # destination . class Graph: def __init__(self, V): self.V = V self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)] # add edge to graph def addEdge (self, s , d ): self.adj[s].append(d) self.adj[d].append(s) # Level BFS function to find minimum # path from source to sink def BFS(self, s, d): # Base case if (s == d): return 0 # make initial distance of all # vertex -1 from source level = [-1] * self.V # Create a queue for BFS queue = [] # Mark the source node level[s] = '0' level[s] = 0 queue.append(s) # it will be used to get all adjacent # vertices of a vertex while (len(queue) != 0): # Dequeue a vertex from queue s = queue.pop() # Get all adjacent vertices of the # dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has # not been visited ( level[i] < '0') , # then update level[i] == parent_level[s] + 1 # and enqueue it i = 0 while i < len(self.adj[s]): # Else, continue to do BFS if (level[self.adj[s][i]] < 0 or level[self.adj[s][i]] > level[s] + 1 ): level[self.adj[s][i]] = level[s] + 1 queue.append(self.adj[s][i]) i += 1 # return minimum moves from source # to sink return level[d] def isSafe(i, j, M): global N if ((i < 0 or i >= N) or (j < 0 or j >= N ) or M[i][j] == 0): return False return True # Returns minimum numbers of moves from a # source (a cell with value 1) to a destination # (a cell with value 2) def MinimumPath(M): global N s , d = None, None # source and destination V = N * N + 2 g = Graph(V) # create graph with n*n node # each cell consider as node k = 1 # Number of current vertex for i in range(N): for j in range(N): if (M[i][j] != 0): # connect all 4 adjacent cell to # current cell if (isSafe (i , j + 1 , M)): g.addEdge (k , k + 1) if (isSafe (i , j - 1 , M)): g.addEdge (k , k - 1) if (j < N - 1 and isSafe (i + 1 , j , M)): g.addEdge (k , k + N) if (i > 0 and isSafe (i - 1 , j , M)): g.addEdge (k , k - N) # source index if(M[i][j] == 1): s = k # destination index if (M[i][j] == 2): d = k k += 1 # find minimum moves return g.BFS (s, d) # Driver Code N = 4 M = [[3 , 3 , 1 , 0 ], [3 , 0 , 3 , 3 ], [2 , 3 , 0 , 3 ], [0 , 3 , 3 , 3]] print(MinimumPath(M)) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# program to find the minimum numbers
// of moves needed to move from source to
// destination .
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Graph {
private int V;
private List<int>[] adj;
// Constructor
public Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List<int>[ v ];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++)
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
// add edge to graph
public void AddEdge(int s, int d)
{
adj[s].Add(d);
adj[d].Add(s);
}
// Level BFS function to find minimum path
// from source to sink
public int BFS(int s, int d)
{
// Base case
if (s == d)
return 0;
// make initial distance of all vertex -1
// from source
int[] level = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
level[i] = -1;
// Create a queue for BFS
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
// Mark the source node level[s] = '0'
level[s] = 0;
queue.Enqueue(s);
while (queue.Count > 0) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
s = queue.Dequeue();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the
// dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has
// not been visited ( level[i] < '0') ,
// then update level[i] == parent_level[s] + 1
// and enqueue it
foreach(int i in adj[s])
{
// Else, continue to do BFS
if (level[i] < 0
|| level[i] > level[s] + 1) {
level[i] = level[s] + 1;
queue.Enqueue(i);
}
}
}
// return minimum moves from source to sink
return level[d];
}
}
public class GFG {
static readonly int N = 4;
static bool IsSafe(int i, int j, int[, ] M)
{
if ((i < 0 || i >= N) || (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| M[i, j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Returns minimum numbers of moves from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a destination (a cell with
// value 2)
static int MinimumPath(int[, ] M)
{
int s = 0, d = 0; // source and destination
int V = N * N + 2;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// create graph with n*n node
// each cell consider as node
int k = 1; // Number of current vertex
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i, j] != 0) {
// connect all 4 adjacent cell to
// current cell
if (IsSafe(i, j + 1, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k + 1);
if (IsSafe(i, j - 1, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k - 1);
if (j < N - 1 && IsSafe(i + 1, j, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && IsSafe(i - 1, j, M))
g.AddEdge(k, k - N);
}
// source index
if (M[i, j] == 1)
s = k;
// destination index
if (M[i, j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
// find minimum moves
return g.BFS(s, d);
}
// driver program to check above function
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] M = { { 3, 3, 1, 0 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 0, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
int ans = MinimumPath(M);
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by cavi4762.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find the minimum numbers
// of moves needed to move from source to
// destination .
class Graph{
constructor(V){
this.V = V
this.adj = new Array(V).fill(0).map(()=>[])
}
// add edge to graph
addEdge (s , d){
this.adj[s].push(d)
this.adj[d].push(s)
}
// Level BFS function to find minimum
// path from source to sink
BFS(s, d){
// Base case
if (s == d)
return 0
// make initial distance of all
// vertex -1 from source
let level = new Array(this.V).fill(-1);
// Create a queue for BFS
let queue = []
// Mark the source node level[s] = '0'
level[s] = 0
queue.push(s)
// it will be used to get all adjacent
// vertices of a vertex
while (queue.length != 0){
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
s = queue.shift()
// Get all adjacent vertices of the
// dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has
// not been visited ( level[i] < '0') ,
// then update level[i] == parent_level[s] + 1
// and enqueue it
let i = 0
while(i < this.adj[s].length){
// Else, continue to do BFS
if (level[this.adj[s][i]] < 0 ||
level[this.adj[s][i]] > level[s] + 1 ){
level[this.adj[s][i]] = level[s] + 1
queue.push(this.adj[s][i])
}
i += 1
}
}
// return minimum moves from source
// to sink
return level[d]
}
}
function isSafe(i, j, M){
if ((i < 0 || i >= N) ||
(j < 0 || j >= N ) || M[i][j] == 0)
return false
return true
}
// Returns minimum numbers of moves from a
// source (a cell with value 1) to a destination
// (a cell with value 2)
function MinimumPath(M){
let s = null, d = null // source and destination
let V = N * N + 2
let g = new Graph(V)
// create graph with n*n node
// each cell consider as node
let k = 1 // Number of current vertex
for(let i=0;i<N;i++){
for(let j=0;j<N;j++){
if (M[i][j] != 0){
// connect all 4 adjacent cell to
// current cell
if (isSafe (i , j + 1 , M))
g.addEdge (k , k + 1)
if (isSafe (i , j - 1 , M))
g.addEdge (k , k - 1)
if (j < N - 1 && isSafe (i + 1 , j , M))
g.addEdge (k , k + N)
if (i > 0 && isSafe (i - 1 , j , M))
g.addEdge (k , k - N)
}
// source index
if(M[i][j] == 1)
s = k
// destination index
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k
k += 1
}
}
// find minimum moves
return g.BFS (s, d)
}
// Driver Code
let N = 4
let M = [[3 , 3 , 1 , 0 ], [3 , 0 , 3 , 3 ],
[2 , 3 , 0 , 3 ], [0 , 3 , 3 , 3]]
document.write(MinimumPath(M))
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
4
Otro Enfoque: (DFS Implementación del problema)
Lo mismo se puede implementar usando DFS donde se compara la ruta completa desde el origen para obtener los movimientos mínimos hacia el destino .
Enfoque :
- Recorra cada elemento en la array de entrada y cree un gráfico a partir de esa array
- Crea un gráfico con N*N vértices.
- Agregue la arista del vértice k a k+1 / k-1 (si la arista está en el elemento izquierdo o derecho en la array) o k a k+N/ kN (si la arista está en el elemento superior o inferior en la array).
- Compruebe siempre si el elemento existe en la array y el elemento != 0.
- if(elemento == 1) mapea el origen if (elemento == 2) mapea el destino.
- Realice DFS al gráfico formado, desde el origen hasta el destino.
- Condición base: si origen==destino devuelve 0 como el número mínimo de movimientos.
- Los movimientos mínimos serán el mínimo (el resultado del DFS realizado en los vértices adyacentes no visitados).
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 4
// To be used in DFS while comparing the
// minimum element
#define MAX (INT_MAX - 1)
using namespace std;
// Graph with the adjacency
// list representationo
class Graph {
private:
int V;
vector<int>* adj;
public:
Graph(int V)
: V{ V }
{
// Initializing the
// adjacency list
adj = new vector<int>[V];
}
// Clearing the memory after
// its use (best practice)
~Graph()
{
delete[] adj;
}
// Adding the element to the
// adjacency list matrix
// representation
void add_edges(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
}
// performing the DFS for the minimum moves
int DFS(int s, int d, unordered_set<int>& visited)
{
// Base condition for the recursion
if (s == d)
return 0;
// Initializing the result
int res{ MAX };
visited.insert(s);
for (int item : adj[s])
if (visited.find(item) ==
visited.end())
// comparing the res with
// the result of DFS
// to get the minimum moves
res = min(res, 1 + DFS(item, d, visited));
return res;
}
};
// ruling out the cases where the element
// to be inserted is outside the matrix
bool is_safe(int arr[][4], int i, int j)
{
if ((i < 0 || i >= N) || (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| arr[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
int min_moves(int arr[][N])
{
int s{ -1 }, d{ -1 }, V{ N * N };
/* k be the variable which represents the
positions( 0 - N*N ) inside the graph.
*/
// k moves from top-left to bottom-right
int k{ 0 };
Graph g{ V };
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// Adding the edge
if (arr[i][j] != 0) {
if (is_safe(arr, i, j + 1))
g.add_edges(k, k + 1); // left
if (is_safe(arr, i, j - 1))
g.add_edges(k, k - 1); // right
if (is_safe(arr, i + 1, j))
g.add_edges(k, k + N); // bottom
if (is_safe(arr, i - 1, j))
g.add_edges(k, k - N); // top
}
// Source from which DFS to be
// performed
if (arr[i][j] == 1)
s = k;
// Destination
else if (arr[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
// Moving k from top-left
// to bottom-right
k++;
}
}
unordered_set<int> visited;
// DFS performed from
// source to destination
return g.DFS(s, d, visited);
}
int32_t main()
{
int arr[][N] = { { 3, 3, 1, 0 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 0, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
// if(min_moves(arr) == MAX) there
// doesn't exist a path
// from source to destination
cout << min_moves(arr) << endl;
return 0;
// the DFS approach and code
// is contributed by Lisho
// Thomas
}
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# To be used in DFS while comparing the
# minimum element
# define MAX (I4T_MAX - 1)
visited = {}
adj = [[] for i in range(16)]
# Performing the DFS for the minimum moves
def add_edges(u, v):
global adj
adj[u].append(v)
def DFS(s, d):
global visited
# Base condition for the recursion
if (s == d):
return 0
# Initializing the result
res = 10**9
visited[s] = 1
for item in adj[s]:
if (item not in visited):
# Comparing the res with
# the result of DFS
# to get the minimum moves
res = min(res, 1 + DFS(item, d))
return res
# Ruling out the cases where the element
# to be inserted is outside the matrix
def is_safe(arr, i, j):
if ((i < 0 or i >= 4) or
(j < 0 or j >= 4) or arr[i][j] == 0):
return False
return True
def min_moves(arr):
s, d, V = -1,-1, 16
# k be the variable which represents the
# positions( 0 - 4*4 ) inside the graph.
# k moves from top-left to bottom-right
k = 0
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
# Adding the edge
if (arr[i][j] != 0):
if (is_safe(arr, i, j + 1)):
add_edges(k, k + 1) # left
if (is_safe(arr, i, j - 1)):
add_edges(k, k - 1) # right
if (is_safe(arr, i + 1, j)):
add_edges(k, k + 4) # bottom
if (is_safe(arr, i - 1, j)):
add_edges(k, k - 4) # top
# Source from which DFS to be
# performed
if (arr[i][j] == 1):
s = k
# Destination
elif (arr[i][j] == 2):
d = k
# Moving k from top-left
# to bottom-right
k += 1
# DFS performed from
# source to destination
return DFS(s, d)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [ [ 3, 3, 1, 0 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 0, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ] ]
# If(min_moves(arr) == MAX) there
# doesn't exist a path
# from source to destination
print(min_moves(arr))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Graph with the adjacency
// list representation
public class Graph {
private List<int>[] adj;
public Graph(int v)
{
// Initializing the
// adjacency list
adj = new List<int>[ v ];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++)
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
// Adding the element to the
// adjacency list matrix
// representation
public void Add_edges(int u, int v) { adj[u].Add(v); }
// performing the DFS for the minimum moves
public int DFS(int s, int d, HashSet<int> visited)
{
// Base condition for the recursion
if (s == d)
return 0;
// Initializing the result
int res = Int32.MaxValue - 1;
visited.Add(s);
foreach(int item in adj[s])
{
if (!visited.Contains(item)) {
// comparing the res with
// the result of DFS
// to get the minimum moves
res = Math.Min(res,
1 + DFS(item, d, visited));
}
}
return res;
}
}
public class GFG
{
static readonly int N = 4;
// ruling out the cases where the element
// to be inserted is outside the matrix
static bool Is_safe(int[, ] arr, int i, int j)
{
if ((i < 0 || i >= N) || (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| arr[i, j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
static int Min_moves(int[, ] arr)
{
int s = -1, d = -1, V = N * N;
/* k be the variable which represents the
positions( 0 - N*N ) inside the graph.
*/
// k moves from top-left to bottom-right
int k = 0;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// Adding the edge
if (arr[i, j] != 0) {
if (Is_safe(arr, i, j + 1))
g.Add_edges(k, k + 1); // left
if (Is_safe(arr, i, j - 1))
g.Add_edges(k, k - 1); // right
if (Is_safe(arr, i + 1, j))
g.Add_edges(k, k + N); // bottom
if (Is_safe(arr, i - 1, j))
g.Add_edges(k, k - N); // top
}
// Source from which DFS to be
// performed
if (arr[i, j] == 1)
s = k;
// Destination
else if (arr[i, j] == 2)
d = k;
// Moving k from top-left
// to bottom-right
k++;
}
}
HashSet<int> visited = new HashSet<int>();
// DFS performed from
// source to destination
return g.DFS(s, d, visited);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] arr = { { 3, 3, 1, 0 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 0, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
int ans = Min_moves(arr);
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
}
4
Este artículo es una contribución de Nishant Singh . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA