Dada una array A[] de tamaño N , la tarea es encontrar los elementos de la array que son factores de la suma del elemento restante. Entonces simplemente seleccione un elemento de una array y tome la suma de los elementos restantes y verifique si la suma es perfectamente divisible por el elemento seleccionado o no. Si es divisible, devuelve el elemento.
Ejemplos:
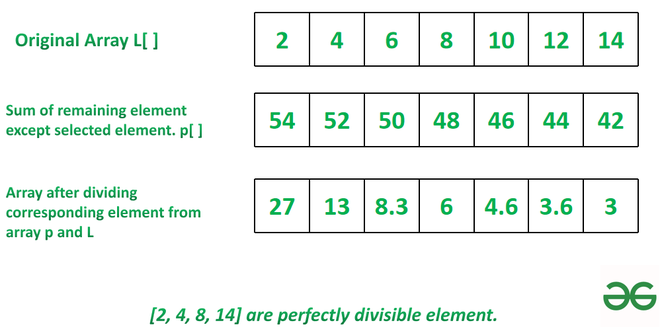
Entrada: A[] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14}
Salida: [2, 4, 8, 14]
Explicación:
1. Tome la suma del elemento restante excepto el seleccionado.
2. Para el elemento 2, la suma del elemento restante es 4+6+8+10+12+14=54
3. De manera similar para la array completa: [54, 52, 50, 48, 46, 44, 42]
3. 54/ 2, 52/4, 48/8, 42/14 son perfectamente divisibles por lo que los elementos resultantes son [2, 4, 8, 14]
Entrada: A[]= {3, 6, 8, 10, 7, 15}
Salida: [7]
Enfoque ingenuo: tome la suma de todos los elementos de la array. Ahora reste cada elemento uno por uno de la suma y agréguelo a la nueva array p []. Divida cada suma por el elemento de índice correspondiente de una array dada y agréguelo a la nueva array q[]. Multiplique el elemento correspondiente de la array A[] y la array q[] y compárelo con elementos indexados similares de la array p[] . Si son iguales, agréguelo a una nueva array z[ ] . Si no se encuentra tal elemento, devuelve -1.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// c++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find element
vector<int> Factor(vector<int> A)
{
// Sum of all element
int s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++)
{
s += A[i];
}
// Subtract each element from sum
vector<int> p;
for (int i : A)
p.push_back(s - i);
// Divide corresponding element
// from array p and l
vector<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++)
q.push_back(p[i] / A[i]);
// Check sum is divisible by
// corresponding element or not
vector<int> z;
for (int i = 0; i < q.size(); i++)
{
// First we divided element now multiple
// to check perfect divisibility of element
if (q[i] * A[i] == p[i])
z.push_back(A[i]);
}
return z;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector<int> A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14};
// Calling function
vector<int> b = Factor(A);
// Print required array
for (auto i : b)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
}
// This code is contributed by amreshkumar3.
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.ArrayList;
class GFG{
// Function to find element
static ArrayList<Integer> Factor(int[] A)
{
// Sum of all element
int s = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i++)
{
s += A[i];
}
// Subtract each element from sum
ArrayList<Integer> p = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i : A)
p.add(s - i);
// Divide corresponding element
// from array p and l
ArrayList<Integer> q = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i++)
q.add((int) Math.floor(p.get(i) / A[i]));
// Check sum is divisible by
// corresponding element or not
ArrayList<Integer> z = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < q.size(); i++)
{
// First we divided element now multiple
// to check perfect divisibility of element
if (q.get(i) * A[i] == p.get(i))
z.add(A[i]);
}
// If no such element found return -1
if (z.size() == 0)
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
return z;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[] A = { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
// Calling function
ArrayList<Integer> b = Factor(A);
// Print required array
System.out.println(b);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gfgking
Python3
# Python program for the above approach # Function to find element def Factor(A): # Sum of all element s = sum(A) # Subtract each element from sum p =[] for i in A: p.append(s-i) # Divide corresponding element # from array p and l q =[] for i in range(len(A)): q.append(p[i]//A[i]) # Check sum is divisible by # corresponding element or not z =[] for i in range(len(q)): # First we divided element now multiple # to check perfect divisibility of element if q[i]*A[i]== p[i]: z.append(A[i]) # If no such element found return -1 if len(z)== 0: return -1 return z A = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14] # Calling function b = Factor(A) # Print required array print(b)
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
// Function to find element
static List<int> Factor(int[] A)
{
// Sum of all element
int s = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < A.Length; i++)
{
s += A[i];
}
// Subtract each element from sum
List<int> p = new List<int>();
foreach(int i in A)
p.Add(s - i);
// Divide corresponding element
// from array p and l
List<int> q = new List<int>();
for(int i = 0; i < A.Length; i++)
q.Add((int) Math.Floor((double)p[i] / A[i]));
// Check sum is divisible by
// corresponding element or not
List<int> z = new List<int>();
for(int i = 0; i < q.Count; i++)
{
// First we divided element now multiple
// to check perfect divisibility of element
if (q[i] * A[i] == p[i])
z.Add(A[i]);
}
// If no such element found return -1
if (z.Count == 0)
return new List<int>();
return z;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int[] A = { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
// Calling function
List<int> b = Factor(A);
// Print required array
foreach(int i in b)
Console.Write(i+", ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code for the above approach
// Function to find element
function Factor(A) {
// Sum of all element
let s = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
s += A[i]
}
// Subtract each element from sum
p = []
for (i of A)
p.push(s - i)
// Divide corresponding element
// from array p and l
q = []
for (i = 0; i < A.length; i++)
q.push(Math.floor(p[i] / A[i]))
// Check sum is divisible by
// corresponding element or not
z = []
for (let i = 0; i < q.length; i++) {
// First we divided element now multiple
// to check perfect divisibility of element
if (q[i] * A[i] == p[i])
z.push(A[i])
}
// If no such element found return -1
if (z.length == 0)
return -1
return z
}
A = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14]
// Calling function
b = Factor(A)
// Print required array
document.write(b)
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh
</script>
[2, 4, 8, 14]
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Enfoque eficiente: en este enfoque, no es necesario utilizar múltiples bucles y múltiples arrays. por lo que la complejidad del espacio y la complejidad del tiempo disminuirán. En esto, todas las operaciones de resta, división y multiplicación se realizan en un solo ciclo. Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice la variable s como la suma de la array A[].
- Inicialice la array z[] para almacenar el resultado.
- Iterar sobre el rango [0, len(A)) usando las variables i y realizar las siguientes tareas:
- Inicialice la variable a como sl[i], b como a/A[i].
- Si b*A[i] es igual a a , agregue A[i] a z[].
- Después de realizar los pasos anteriores, imprima -1 si la array resultante está vacía; de lo contrario, imprima los elementos de la array z[] como respuesta.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find sum of all elements of an array
int sum(vector<int>& A)
{
int res = 0;
for (auto it : A)
res += it;
return res;
}
// Function to find element
vector<int> Factor(vector<int>& A)
{
// Sum of all element
int s = sum(A);
vector<int> z;
// Loop to find the factors of sum.
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); ++i) {
// a is sum of remaining elements.
int a = s - A[i];
// b is integer value or factor of b.
int b = a / A[i];
// Check the divisibility
if (b * A[i] == a)
z.push_back(A[i]);
}
// If no element found return -1
if (z.size() == 0)
return { -1 };
return z;
}
// Drive Code
int main()
{
vector<int> A = { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
// Calling function
vector<int> b = Factor(A);
// Print resultant element
for (auto it : b)
cout << it << " ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rakeshsahni
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to find sum of all elements of an array
static int sum(int[] A)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
res += A[i];
}
return res;
}
// Function to find element
static ArrayList<Integer> Factor(int[] A)
{
// Sum of all element
int s = sum(A);
ArrayList<Integer> z = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Loop to find the factors of sum.
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; ++i) {
// a is sum of remaining elements.
int a = s - A[i];
// b is integer value or factor of b.
int b = a / A[i];
// Check the divisibility
if (b * A[i] == a){
z.add(A[i]);
}
}
// If no element found return -1
if (z.size() == 0){
ArrayList<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
l1.add(-1);
return l1;
}
return z;
}
// Drive Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int A[] = new int[] { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
// Calling function
ArrayList<Integer> b = Factor(A);
// Print resultant element
System.out.println(b);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shubham Singh
Python3
# Python program for the above approach # Function to find element def Factor(A): # Sum of all element s = sum(A) z = [] # Loop to find the factors of sum. for i in range(len(A)): # a is sum of remaining elements. a = s-A[i] # b is integer value or factor of b. b = a//A[i] # Check the divisibility if b * A[i] == a: z.append(A[i]) # If no element found return -1 if len(z) == 0: return -1 return z A = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14] # Calling function b = Factor(A) # Print resultant element print(b)
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Function to find sum of all elements of an array
static int sum(List<int> A)
{
int res = 0;
foreach(int it in A) res += it;
return res;
}
// Function to find element
static List<int> Factor(List<int> A)
{
// Sum of all element
int s = sum(A);
List<int> z = new List<int>();
// Loop to find the factors of sum.
for (int i = 0; i < A.Count; ++i) {
// a is sum of remaining elements.
int a = s - A[i];
// b is integer value or factor of b.
int b = a / A[i];
// Check the divisibility
if (b * A[i] == a)
z.Add(A[i]);
}
// If no element found return -1
if (z.Count == 0)
return new List<int>() { -1 };
return z;
}
// Drive Code
public static void Main()
{
List<int> A
= new List<int>() { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 };
// Calling function
List<int> b = Factor(A);
// Print resultant element
Console.Write("[ ");
int it;
for (it = 0; it < b.Count - 1; it++) {
Console.Write(b[it] + ", ");
}
Console.Write(b[it] + " ]");
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Function to find sum of all elements of an array
function sum(A)
{
var res = 0;
for (var it of A){
res += parseInt(it);}
return res;
}
// Function to find element
function Factor(A)
{
// Sum of all element
var s = sum(A);
var z =[];
// Loop to find the factors of sum.
for (var i = 0; i < A.length; ++i) {
// a is sum of remaining elements.
var a = s - A[i];
// b is integer value or factor of b.
var b = parseInt(a / A[i]);
// Check the divisibility
if (b * A[i] == a)
z.push(A[i]);
}
// If no element found return -1
if (z.length == 0)
return [ -1 ];
return z;
}
// Drive Code
A = [ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 ];
// Calling function
b = Factor(A);
// Print resultant element
for (var it of b)
document.write(it + " ");
//This code is contributed by Shubham Singh
</script>
[2, 4, 8, 14]
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por harshdeepmahajan88 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA