Dada una array arr[] de enteros positivos, la tarea es encontrar la proporción de LCM y GCD de la array dada.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {2, 3, 5, 9}
Salida: 90:1
Explicación:
El GCD de la array dada es 1 y el LCM es 90.
Por lo tanto, la relación se evalúa como 90:1.
Entrada: arr[] = {6, 12, 36}
Salida: 6:1
Explicación:
El GCD de la array dada es 6 y el LCM es 36.
Por lo tanto, la relación se evalúa como 6:1.
Enfoque:
siga los pasos a continuación para resolver los problemas:
- En primer lugar, encontraremos el GCD de la array dada. Para este propósito, podemos usar la función incorporada para GCD proporcionada por STL o podemos usar el algoritmo euclidiano .
- Luego, encontraremos el LCM de la array usando la siguiente fórmula:
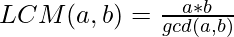
- Por último, encontraremos la proporción requerida.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate and
// return GCD of the given array
int findGCD(int arr[], int n)
{
// Initialise GCD
int gcd = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
gcd = __gcd(arr[i], gcd);
// Once GCD is 1, it
// will always be 1 with
// all other elements
if (gcd == 1) {
return 1;
}
}
// Return GCD
return gcd;
}
// Function to calculate and
// return LCM of the given array
int findLCM(int arr[], int n)
{
// Initialise LCM
int lcm = arr[0];
// LCM of two numbers is
// evaluated as [(a*b)/gcd(a, b)]
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
lcm = (((arr[i] * lcm))
/ (__gcd(arr[i], lcm)));
}
// Return LCM
return lcm;
}
// Function to print the ratio
// of LCM to GCD of the given array
void findRatio(int arr[], int n)
{
int gcd = findGCD(arr, n);
int lcm = findLCM(arr, n);
cout << lcm / gcd << ":"
<< 1 << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 6, 12, 36 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
findRatio(arr, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to implement
// above approach
class GFG{
// Function to calculate and
// return GCD of the given array
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return __gcd(b, a % b);
}
static int findGCD(int arr[], int n)
{
// Initialise GCD
int gcd = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
gcd = __gcd(arr[i], gcd);
// Once GCD is 1, it
// will always be 1 with
// all other elements
if (gcd == 1)
{
return 1;
}
}
// Return GCD
return gcd;
}
// Function to calculate and
// return LCM of the given array
static int findLCM(int arr[], int n)
{
// Initialise LCM
int lcm = arr[0];
// LCM of two numbers is
// evaluated as [(a*b)/gcd(a, b)]
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
lcm = (((arr[i] * lcm)) /
(__gcd(arr[i], lcm)));
}
// Return LCM
return lcm;
}
// Function to print the ratio
// of LCM to GCD of the given array
static void findRatio(int arr[], int n)
{
int gcd = findGCD(arr, n);
int lcm = findLCM(arr, n);
System.out.print((lcm / gcd));
System.out.print(":1");
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = new int[]{ 6, 12, 36 };
int N = 3;
findRatio(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ritik Bansal
Python3
# Python3 program to implement # above approach import math # Function to calculate and # return GCD of the given array def findGCD(arr, n): # Initialise GCD gcd = arr[0] for i in range(1, n): gcd = int(math.gcd(arr[i], gcd)) # Once GCD is 1, it # will always be 1 with # all other elements if (gcd == 1): return 1 # Return GCD return gcd # Function to calculate and # return LCM of the given array def findLCM(arr, n): # Initialise LCM lcm = arr[0] # LCM of two numbers is # evaluated as [(a*b)/gcd(a, b)] for i in range(1, n): lcm = int((((arr[i] * lcm)) / (math.gcd(arr[i], lcm)))) # Return LCM return lcm # Function to print the ratio # of LCM to GCD of the given array def findRatio(arr, n): gcd = findGCD(arr, n) lcm = findLCM(arr, n) print(int(lcm / gcd), ":", "1") # Driver Code arr = [ 6, 12, 36 ] N = len(arr) findRatio(arr, N) # This code is contributed by sanjoy_62
C#
// C# Program to implement
// above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate and
// return GCD of the given array
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return __gcd(b, a % b);
}
static int findGCD(int []arr, int n)
{
// Initialise GCD
int gcd = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
gcd = __gcd(arr[i], gcd);
// Once GCD is 1, it
// will always be 1 with
// all other elements
if (gcd == 1)
{
return 1;
}
}
// Return GCD
return gcd;
}
// Function to calculate and
// return LCM of the given array
static int findLCM(int []arr, int n)
{
// Initialise LCM
int lcm = arr[0];
// LCM of two numbers is
// evaluated as [(a*b)/gcd(a, b)]
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
lcm = (((arr[i] * lcm)) /
(__gcd(arr[i], lcm)));
}
// Return LCM
return lcm;
}
// Function to print the ratio
// of LCM to GCD of the given array
static void findRatio(int []arr, int n)
{
int gcd = findGCD(arr, n);
int lcm = findLCM(arr, n);
Console.Write((lcm / gcd));
Console.Write(":1");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = new int[]{ 6, 12, 36 };
int N = 3;
findRatio(arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Code_Mech
Javascript
<script>
// javascript Program to implement
// above approach
// Function to calculate and
// return GCD of the given array
function __gcd(a , b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return __gcd(b, a % b);
}
function findGCD(arr, n)
{
// Initialise GCD
var gcd = arr[0];
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
gcd = __gcd(arr[i], gcd);
// Once GCD is 1, it
// will always be 1 with
// all other elements
if (gcd == 1) {
return 1;
}
}
// Return GCD
return gcd;
}
// Function to calculate and
// return LCM of the given array
function findLCM(arr, n)
{
// Initialise LCM
var lcm = arr[0];
// LCM of two numbers is
// evaluated as [(a*b)/gcd(a, b)]
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
lcm = (((arr[i] * lcm)) / (__gcd(arr[i], lcm)));
}
// Return LCM
return lcm;
}
// Function to print the ratio
// of LCM to GCD of the given array
function findRatio(arr , n) {
var gcd = findGCD(arr, n);
var lcm = findLCM(arr, n);
document.write((lcm / gcd));
document.write(":1");
}
// Driver Code
var arr = [ 6, 12, 36 ];
var N = 3;
findRatio(arr, N);
// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav.
</script>
6:1
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N * logN)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shauryarehangfg y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA