Dado un número n, encuentre todas las secuencias binarias de longitud 2n tales que la suma de los primeros n bits sea igual a la suma de los últimos n bits.
Ejemplos:
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
La idea es arreglar los bits primero y último y luego repetir para los 2*(n-1) bits restantes. Hay cuatro posibilidades cuando arreglamos los bits primero y último:
- El primer y el último bit son 1, los n – 1 bits restantes en ambos lados también deben tener la misma suma.
- El primer y el último bit son 0, los n – 1 bits restantes en ambos lados también deben tener la misma suma.
- El primer bit es 1 y el último bit es 0, la suma de los n-1 bits restantes en el lado izquierdo debe ser 1 menos que la suma de n-1 bits en el lado derecho.
- El primer bit es 0 y el último bit es 1, la suma de los n-1 bits restantes en el lado izquierdo debe ser 1 más que la suma de n-1 bits en el lado derecho.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior:
C++
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences
// whose sum of first and second half bits is same
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print even length binary sequences
// whose sum of first and second half bits is same
// diff --> difference between sums of first n bits
// and last n bits
// out --> output array
// start --> starting index
// end --> ending index
void findAllSequences(int diff, char* out, int start, int end)
{
// We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits
if (abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2)
return;
// if all bits are filled
if (start > end)
{
// if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same
if (diff == 0)
cout << out << " ";
return;
}
// fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1
out[start] = '0', out[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff + 1, out, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 1
out[start] = out[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff, out, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 0
out[start] = out[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff, out, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0
out[start] = '1', out[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff - 1, out, start + 1, end - 1);
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// input number
int n = 2;
// allocate string containing 2*n characters
char out[2 * n + 1];
// null terminate output array
out[2 * n] = '\0';
findAllSequences(0, out, 0, 2*n - 1);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print even length binary
// sequences whose sum of first and second
// half bits is same
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to print even length binary sequences
// whose sum of first and second half bits is same
// diff --> difference between sums of first n bits
// and last n bits
// out --> output array
// start --> starting index
// end --> ending index
static void findAllSequences(int diff, char out[],
int start, int end)
{
// We can't cover difference of more
// than n with 2n bits
if (Math.abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2)
return;
// if all bits are filled
if (start > end)
{
// if sum of first n bits and
// last n bits are same
if (diff == 0)
{
System.out.print(out);
System.out.print(" ");
}
return;
}
// fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1
out[start] = '0';
out[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff + 1, out, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 1
out[start] = out[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff, out, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 0
out[start] = out[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff, out, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0
out[start] = '1';
out[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff - 1, out, start + 1, end - 1);
}
// Driver program
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// input number
int n = 2;
// allocate string containing 2*n characters
char[] out = new char[2 * n + 1];
// null terminate output array
out[2 * n] = '\0';
findAllSequences(0, out, 0, 2*n - 1);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
Python3
# Python3 program to print even length binary sequences
# whose sum of first and second half bits is same
# Function to print even length binary sequences
# whose sum of first and second half bits is same
# diff --> difference between sums of first n bits
# and last n bits
# out --> output array
# start --> starting index
# end --> ending index
def findAllSequences(diff, out, start, end):
# We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits
if (abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) // 2):
return;
# if all bits are filled
if (start > end):
# if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same
if (diff == 0):
print(''.join(list(out)),end=" ");
return;
# fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1
out[start] = '0';
out[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff + 1, out, start + 1, end - 1);
# fill first and last bits as 1
out[start] = out[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff, out, start + 1, end - 1);
# fill first and last bits as 0
out[start] = out[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff, out, start + 1, end - 1);
# fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0
out[start] = '1';
out[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff - 1, out, start + 1, end - 1);
# Driver program
# input number
n = 2;
# allocate string containing 2*n characters
out=[""]*(2*n);
findAllSequences(0, out, 0, 2*n - 1);
# This code is contributed by mits
C#
// C# program to print even length binary
// sequences whose sum of first and second
// half bits is same
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to print even length binary
// sequences whose sum of first and
// second half bits is same
// diff --> difference between sums of
// first n bits
// and last n bits
// out --> output array
// start --> starting index
// end --> ending index
static void findAllSequences(int diff,
char []outt, int start, int end)
{
// We can't cover difference of
// more than n with 2n bits
if (Math.Abs(diff) > (end - start
+ 1) / 2)
return;
// if all bits are filled
if (start > end)
{
// if sum of first n bits and
// last n bits are same
if (diff == 0)
{
Console.Write(outt);
Console.Write(" ");
}
return;
}
// fill first bit as 0 and last bit
// as 1
outt[start] = '0';
outt[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff + 1, outt,
start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 1
outt[start] = outt[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff, outt,
start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 0
outt[start] = outt[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff, outt,
start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first bit as 1 and last
// bit as 0
outt[start] = '1';
outt[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff - 1, outt,
start + 1, end - 1);
}
// Driver program
public static void Main ()
{
// input number
int n = 2;
// allocate string containing 2*n
// characters
char []outt = new char[2 * n + 1];
// null terminate output array
outt[2 * n] = '\0';
findAllSequences(0, outt, 0, 2*n - 1);
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
PHP
<?php
// PHP program to print even length binary sequences
// whose sum of first and second half bits is same
// Function to print even length binary sequences
// whose sum of first and second half bits is same
// diff --> difference between sums of first n bits
// and last n bits
// out --> output array
// start --> starting index
// end --> ending index
function findAllSequences($diff, $out, $start, $end)
{
// We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits
if (abs($diff) > (int)(($end - $start + 1) / 2))
return;
// if all bits are filled
if ($start > $end)
{
// if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same
if ($diff == 0)
print(implode("",$out)." ");
return;
}
// fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1
$out[$start] = '0';
$out[$end] = '1';
findAllSequences($diff + 1, $out, $start + 1, $end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 1
$out[$start] = $out[$end] = '1';
findAllSequences($diff, $out, $start + 1, $end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 0
$out[$start] = $out[$end] = '0';
findAllSequences($diff, $out, $start + 1, $end - 1);
// fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0
$out[$start] = '1';
$out[$end] = '0';
findAllSequences($diff - 1, $out, $start + 1, $end - 1);
}
// Driver program
// input number
$n = 2;
// allocate string containing 2*n characters
$out=array_fill(0,2*$n,"");
findAllSequences(0, $out, 0, 2*$n - 1);
// This code is contributed by chandan_jnu
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to print even length binary
// sequences whose sum of first and second
// half bits is same
// Function to print even length binary
// sequences whose sum of first and
// second half bits is same
// diff --> difference between sums of
// first n bits
// and last n bits
// out --> output array
// start --> starting index
// end --> ending index
function findAllSequences(diff, outt, start, end)
{
// We can't cover difference of
// more than n with 2n bits
if (Math.abs(diff) > parseInt((end - start + 1) / 2, 10))
return;
// if all bits are filled
if (start > end)
{
// if sum of first n bits and
// last n bits are same
if (diff == 0)
{
document.write(outt.join(""));
document.write(" ");
}
return;
}
// fill first bit as 0 and last bit
// as 1
outt[start] = '0';
outt[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff + 1, outt, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 1
outt[start] = outt[end] = '1';
findAllSequences(diff, outt, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first and last bits as 0
outt[start] = outt[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff, outt, start + 1, end - 1);
// fill first bit as 1 and last
// bit as 0
outt[start] = '1';
outt[end] = '0';
findAllSequences(diff - 1, outt, start + 1, end - 1);
}
// input number
let n = 2;
// allocate string containing 2*n
// characters
let outt = new Array(2 * n + 1);
// null terminate output array
outt[2 * n] = '\0';
findAllSequences(0, outt, 0, 2*n - 1);
</script>
Producción:
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
Complejidad temporal: O(( ![]() )* N)
)* N)
4^N debido a 4 llamadas recursivas y N (simplificado de 2N) por el tiempo dedicado a imprimir strings de tamaño 2N
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)
Existe otro enfoque mediante el cual generamos todas las strings posibles de longitud n y las almacenamos en una lista en un índice que representa su suma. Luego, iteramos a través de cada lista y generamos las strings de tamaño 2n imprimiendo cada string con todas las demás strings en la lista sumando el mismo valor.
C++
// C++ program to implement the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//function that generates the sequence
void generateSequencesWithSum(
int n, vector<vector<string> >& sumToString,
vector<string> sequence, int sumSoFar)
{
// Base case, if there are no more binary digits to
// include
if (n == 0) {
// add permutation to list of sequences with sum
// corresponding to index
string seq = "";
for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++) {
seq = seq + sequence[i];
}
vector<string> x = sumToString[sumSoFar];
x.push_back(seq);
sumToString[sumSoFar] = x;
return;
}
// Generate sequence +0
sequence.push_back("0");
generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1, sumToString, sequence,
sumSoFar);
sequence.erase(sequence.begin());
// Generate sequence +1
sequence.push_back("1");
generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1, sumToString, sequence,
sumSoFar + 1);
sequence.erase(sequence.begin());
}
// function to form permutations of the sequences
void permuteSequences(vector<vector<string> > sumToString)
{
// There are 2^n substring in this list of lists
for (int sumIndexArr = 0;
sumIndexArr < sumToString.size(); sumIndexArr++) {
// Append
for (int sequence1 = 0;
sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].size();
sequence1++) {
for (int sequence2 = 0;
sequence2
< sumToString[sumIndexArr].size();
sequence2++) {
if (sumIndexArr == sumToString.size() - 1
&& sequence1
== sumToString[sumIndexArr]
.size()
- 1
&& sequence2
== sumToString[sumIndexArr]
.size()
- 1) {
cout << "1111 ";
}
else {
cout << sumToString[sumIndexArr]
[sequence1]
+ sumToString[sumIndexArr]
[sequence2]
<< " ";
}
}
}
}
}
// function that finds all the subsequences
void findAllSequences(int n)
{
vector<vector<string> > sumToString;
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
sumToString.push_back(
vector<string>()); // list of strings
// where index
// represents sum
}
generateSequencesWithSum(n, sumToString,
vector<string>(), 0);
permuteSequences(sumToString);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Function Call
findAllSequences(2);
return 0;
}
// this code is contributed by phasing17
Java
// Java program to implement the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// function that finds all the subsequences
static void findAllSequences(int n)
{
ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString
= new ArrayList<ArrayList<String> >();
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
sumToString.add(
new ArrayList<String>()); // list of strings
// where index
// represents sum
}
generateSequencesWithSum(
n, sumToString, new ArrayList<String>(), 0);
permuteSequences(sumToString);
}
static void generateSequencesWithSum(
int n, ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString,
ArrayList<String> sequence, int sumSoFar)
{
// Base case, if there are no more binary digits to
// include
if (n == 0) {
// add permutation to list of sequences with sum
// corresponding to index
String seq = "";
for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++) {
seq = seq + sequence.get(i);
}
ArrayList<String> x = sumToString.get(sumSoFar);
x.add(seq);
sumToString.set(sumSoFar, x);
return;
}
// Generate sequence +0
sequence.add("0");
generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1, sumToString,
sequence, sumSoFar);
sequence.remove(0);
// Generate sequence +1
sequence.add("1");
generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1, sumToString,
sequence, sumSoFar + 1);
sequence.remove(0);
}
// function to form permutations of the sequences
static void permuteSequences(
ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString)
{
// There are 2^n substring in this list of lists
for (int sumIndexArr = 0;
sumIndexArr < sumToString.size();
sumIndexArr++) {
// Append
for (int sequence1 = 0;
sequence1
< sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size();
sequence1++) {
for (int sequence2 = 0;
sequence2
< sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size();
sequence2++) {
if (sumIndexArr
== sumToString.size() - 1
&& sequence1
== sumToString
.get(sumIndexArr)
.size()
- 1
&& sequence2
== sumToString
.get(sumIndexArr)
.size()
- 1) {
System.out.print("1111");
}
else {
System.out.println(
sumToString.get(sumIndexArr)
.get(sequence1)
+ sumToString.get(sumIndexArr)
.get(sequence2));
}
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Function Call
findAllSequences(2);
}
// this code is contributed by phasing17
}
Python3
def findAllSequences(n):
sumToString = [[] for x in range(n+1)] # list of strings where index represents sum
generateSequencesWithSum(n, sumToString, [], 0)
permuteSequences(sumToString)
def generateSequencesWithSum(n, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar):
#Base case, if there are no more binary digits to include
if n == 0:
sumToString[sumSoFar].append("".join(sequence)) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index
return
#Generate sequence +0
sequence.append("0")
generateSequencesWithSum(n-1, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar)
sequence.pop()
#Generate sequence +1
sequence.append("1")
generateSequencesWithSum(n-1, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar+1)
sequence.pop()
def permuteSequences(sumToString):
#There are 2^n substring in this list of lists
for sumIndexArr in sumToString:
# Append
for sequence1 in sumIndexArr:
for sequence2 in sumIndexArr:
print(sequence1 + sequence2)
findAllSequences(2)
#Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static void findAllSequences(int n)
{
List<List<string>> sumToString = new List<List<string>>();
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
sumToString.Add(new List<string>()); // list of strings where index represents sum
}
generateSequencesWithSum(n, sumToString, new List<string>(), 0);
permuteSequences(sumToString);
}
static void generateSequencesWithSum(int n, List<List<string>> sumToString, List<string> sequence, int sumSoFar)
{
// Base case, if there are no more binary digits to include
if(n == 0)
{
//add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index
string seq = "";
for(int i = 0; i < sequence.Count; i++)
{
seq = seq + sequence[i];
}
sumToString[sumSoFar].Add(seq);
return;
}
// Generate sequence +0
sequence.Add("0");
generateSequencesWithSum(n-1, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar);
sequence.RemoveAt(0);
// Generate sequence +1
sequence.Add("1");
generateSequencesWithSum(n-1, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar+1);
sequence.RemoveAt(0);
}
static void permuteSequences(List<List<string>> sumToString)
{
// There are 2^n substring in this list of lists
for(int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.Count; sumIndexArr++)
{
// Append
for(int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence1++)
{
for(int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence2++)
{
if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.Count-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1)
{
Console.Write("1111");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2]);
}
}
}
}
}
static void Main() {
findAllSequences(2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Javascript
<script>
function findAllSequences(n)
{
let sumToString = [];
for(let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
sumToString.push([]); // list of strings where index represents sum
}
generateSequencesWithSum(n, sumToString, [], 0);
permuteSequences(sumToString);
}
function generateSequencesWithSum(n, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar)
{
// Base case, if there are no more binary digits to include
if(n == 0)
{
//add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index
sumToString[sumSoFar].push(sequence.join(""));
return;
}
// Generate sequence +0
sequence.push("0");
generateSequencesWithSum(n-1, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar);
sequence.shift();
// Generate sequence +1
sequence.push("1");
generateSequencesWithSum(n-1, sumToString, sequence, sumSoFar+1);
sequence.shift();
}
function permuteSequences(sumToString)
{
// There are 2^n substring in this list of lists
for(let sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.length; sumIndexArr++)
{
// Append
for(let sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence1++)
{
for(let sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence2++)
{
if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.length-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1)
{
document.write("1111");
}
else
{
document.write(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2] + "</br>");
}
}
}
}
}
findAllSequences(2);
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
</script>
Producción:
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Análisis de la complejidad del tiempo:
generar secuencias con suma = O ((2 N ) * N)
- 2 N : generamos todas las permutaciones de strings binarias de tamaño N
- N: convierte la lista de caracteres en una string y la almacena en una array. Esto se hace en el caso base.
permuteSequences = O((2 N ) * N!/(N/2)! 2 * N)
- 2 N : iteramos a través de toda la string generada de tamaño n
- N!/(N/2)! 2 : Este es un poco difícil de explicar
Tomemos N = 2 como ejemplo. Nuestro arreglo de posibles secuencias de tamaño n sería:
| índice de array | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| lista de strings | 00 | 01,10 | 11 |
En la lista de strings cuyo índice representa la suma, obtenemos el recuento de strings de tamaño 2n usando la fórmula «n elige k». En nuestro caso sería nCk *nCk donde k representa el número de 1s en cada mitad de la string de tamaño 2n:
k = 0, tenemos (2C0)^2 = 1 string (0000)
k = 1, tenemos (2C1)^2 string = 4 strings (0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2, tenemos (2c2)^2 = 1 string (1111)
Obtenemos nuestra lista más larga de strings cuando k = N/2, por lo tanto, N C N/2 = N!/[(N/2)! * (N – N/2)!] que se simplifica a N C N/2 = N!/(N/2)! 2
Por lo tanto, para cada elemento, debemos iterar, como máximo, N C N/2 para formar strings de longitud 2N
Sin prueba formal, si graficamos 2^N y N!/(N/2)! 2 , vemos que 2 N tiene una tasa de crecimiento más rápida que la última. Por lo tanto O(2 N * N!/(N/2) 2 ) < O(2 N *2 N ) = O(2 2n ) = O(4 N )
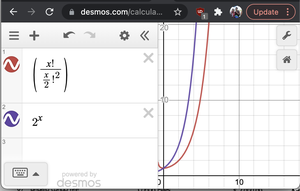
Gráfica de 2^x y nC(n/2)
- N: debemos imprimir cada string de tamaño 2N
Finalmente, podemos ignorar la complejidad temporal de generarSequencesWithSum porque permuteSequence es el término principal
Complejidad temporal: O(2 N * N!/(N/2)! 2 * N) (mejor que la primera solución de O((4^N) * N, consulte la explicación anterior para obtener más detalles)
Espacio auxiliar : O(2 N ) porque almacenamos todas las permutaciones de strings binarias de tamaño N
Este artículo es aportado por Aditya Goel y mejorado por Xavier Jean Baptiste . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA