Dadas dos arrays ordenadas, la tarea es fusionarlas de manera ordenada.
Ejemplos:
Entrada : arr1[] = { 1, 3, 4, 5}, arr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8}
Salida : arr3[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8}
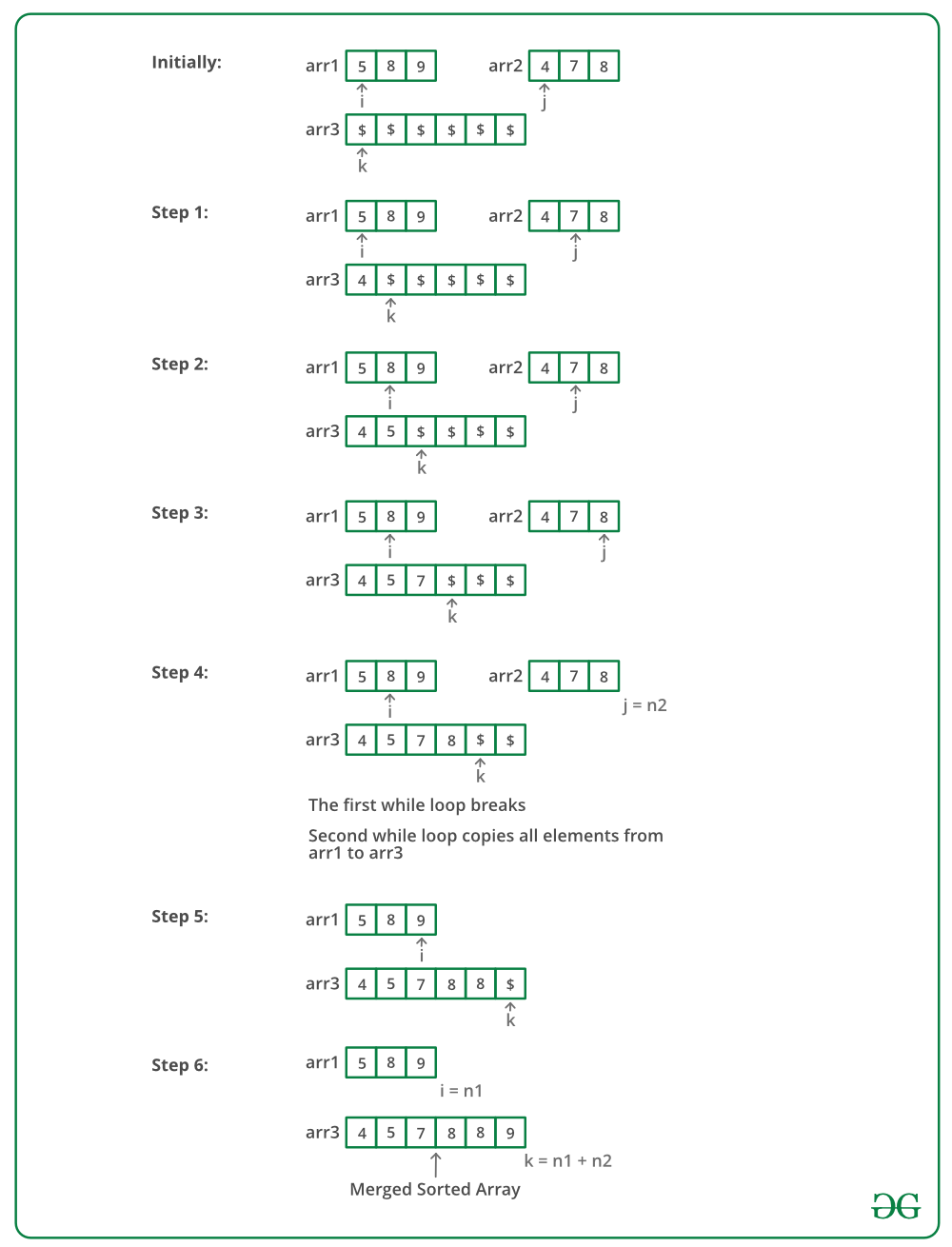
Entrada : arr1[] = { 5, 8, 9}, arr2[] = {4, 7, 8}
Salida : arr3[] = {4, 5, 7, 8, 8, 9}Método 1 (O(n1 * n2) Tiempo y O(n1+n2) Espacio Extra)
- Cree una array arr3[] de tamaño n1 + n2.
- Copie todos los elementos n1 de arr1[] a arr3[]
- Atraviese arr2[] e inserte elementos uno por uno (como ordenar por inserción ) de arr3[] a arr1[]. Este paso toma O(n1 * n2) tiempo.
Hemos discutido la implementación del método anterior en Merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space
Method 2 (O(n1 + n2) Time and O(n1 + n2) Extra Space)
La idea es usar la función Merge de Merge sort .
- Cree una array arr3[] de tamaño n1 + n2.
- Atraviese simultáneamente arr1[] y arr2[].
- Elija los elementos actuales más pequeños en arr1[] y arr2[], copie este elemento más pequeño a la siguiente posición en arr3[] y avance en arr3[] y la array cuyo elemento se selecciona.
- Si quedan elementos en arr1[] o arr2[], cópielos también en arr3[].
La imagen de abajo es una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays/#include<iostream>usingnamespacestd;// Merge arr1[0..n1-1] and arr2[0..n2-1] into// arr3[0..n1+n2-1]voidmergeArrays(intarr1[],intarr2[],intn1,intn2,intarr3[]){inti = 0, j = 0, k = 0;// Traverse both arraywhile(i<n1 && j <n2){// Check if current element of first// array is smaller than current element// of second array. If yes, store first// array element and increment first array// index. Otherwise do same with second arrayif(arr1[i] < arr2[j])arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];elsearr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}// Store remaining elements of first arraywhile(i < n1)arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];// Store remaining elements of second arraywhile(j < n2)arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}// Driver codeintmain(){intarr1[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};intn1 =sizeof(arr1) /sizeof(arr1[0]);intarr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};intn2 =sizeof(arr2) /sizeof(arr2[0]);intarr3[n1+n2];mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);cout <<"Array after merging"<<endl;for(inti=0; i < n1+n2; i++)cout << arr3[i] <<" ";return0;}Java
// Java program to merge two sorted arraysimportjava.util.*;importjava.lang.*;importjava.io.*;classMergeTwoSorted{// Merge arr1[0..n1-1] and arr2[0..n2-1]// into arr3[0..n1+n2-1]publicstaticvoidmergeArrays(int[] arr1,int[] arr2,intn1,intn2,int[] arr3){inti =0, j =0, k =0;// Traverse both arraywhile(i<n1 && j <n2){// Check if current element of first// array is smaller than current element// of second array. If yes, store first// array element and increment first array// index. Otherwise do same with second arrayif(arr1[i] < arr2[j])arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];elsearr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}// Store remaining elements of first arraywhile(i < n1)arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];// Store remaining elements of second arraywhile(j < n2)arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}publicstaticvoidmain (String[] args){int[] arr1 = {1,3,5,7};intn1 = arr1.length;int[] arr2 = {2,4,6,8};intn2 = arr2.length;int[] arr3 =newint[n1+n2];mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);System.out.println("Array after merging");for(inti=0; i < n1+n2; i++)System.out.print(arr3[i] +" ");}}/* This code is contributed by Mr. Somesh Awasthi */Python 3
# Python program to merge# two sorted arrays# Merge arr1[0..n1-1] and# arr2[0..n2-1] into# arr3[0..n1+n2-1]defmergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2):arr3=[None]*(n1+n2)i=0j=0k=0# Traverse both arraywhilei < n1andj < n2:# Check if current element# of first array is smaller# than current element of# second array. If yes,# store first array element# and increment first array# index. Otherwise do same# with second arrayifarr1[i] < arr2[j]:arr3[k]=arr1[i]k=k+1i=i+1else:arr3[k]=arr2[j]k=k+1j=j+1# Store remaining elements# of first arraywhilei < n1:arr3[k]=arr1[i];k=k+1i=i+1# Store remaining elements# of second arraywhilej < n2:arr3[k]=arr2[j];k=k+1j=j+1("Array after merging")foriinrange(n1+n2):(str(arr3[i]), end=" ")# Driver codearr1=[1,3,5,7]n1=len(arr1)arr2=[2,4,6,8]n2=len(arr2)mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2);# This code is contributed# by ChitraNayalC#
// C# program to merge// two sorted arraysusingSystem;classGFG{// Merge arr1[0..n1-1] and// arr2[0..n2-1] into// arr3[0..n1+n2-1]publicstaticvoidmergeArrays(int[] arr1,int[] arr2,intn1,intn2,int[] arr3){inti = 0, j = 0, k = 0;// Traverse both arraywhile(i < n1 && j < n2){// Check if current element// of first array is smaller// than current element// of second array. If yes,// store first array element// and increment first array// index. Otherwise do same// with second arrayif(arr1[i] < arr2[j])arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];elsearr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}// Store remaining// elements of first arraywhile(i < n1)arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];// Store remaining elements// of second arraywhile(j < n2)arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}// Driver codepublicstaticvoidMain(){int[] arr1 = {1, 3, 5, 7};intn1 = arr1.Length;int[] arr2 = {2, 4, 6, 8};intn2 = arr2.Length;int[] arr3 =newint[n1+n2];mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);Console.Write("Array after merging\n");for(inti = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++)Console.Write(arr3[i] +" ");}}// This code is contributed// by ChitraNayalPHP
<?php// PHP program to merge// two sorted arrays// Merge $arr1[0..$n1-1] and// $arr2[0..$n2-1] into// $arr3[0..$n1+$n2-1]functionmergeArrays(&$arr1, &$arr2,$n1,$n2, &$arr3){$i= 0;$j= 0;$k= 0;// Traverse both arraywhile($i<$n1&&$j<$n2){// Check if current element// of first array is smaller// than current element of// second array. If yes,// store first array element// and increment first array// index. Otherwise do same// with second arrayif($arr1[$i] <$arr2[$j])$arr3[$k++] =$arr1[$i++];else$arr3[$k++] =$arr2[$j++];}// Store remaining elements// of first arraywhile($i<$n1)$arr3[$k++] =$arr1[$i++];// Store remaining elements// of second arraywhile($j<$n2)$arr3[$k++] =$arr2[$j++];}// Driver code$arr1=array(1, 3, 5, 7);$n1= sizeof($arr1);$arr2=array(2, 4, 6, 8);$n2= sizeof($arr2);$arr3[$n1+$n2] =array();mergeArrays($arr1,$arr2,$n1,$n2,$arr3);echo"Array after merging \n";for($i= 0;$i<$n1+$n2;$i++)echo$arr3[$i] ." ";// This code is contributed// by ChitraNayal?>JavaScript
<script>// javascript program to merge two sorted arrays// Merge arr1[0..n1-1] and arr2[0..n2-1]// into arr3[0..n1+n2-1]functionmergeArrays(arr1, arr2 , n1 , n2, arr3) {vari = 0, j = 0, k = 0;// Traverse both arraywhile(i < n1 && j < n2) {// Check if current element of first// array is smaller than current element// of second array. If yes, store first// array element and increment first array// index. Otherwise do same with second arrayif(arr1[i] < arr2[j])arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];elsearr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}// Store remaining elements of first arraywhile(i < n1)arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];// Store remaining elements of second arraywhile(j < n2)arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];}vararr1 = [ 1, 3, 5, 7 ];varn1 = arr1.length;vararr2 = [ 2, 4, 6, 8 ];varn2 = arr2.length;vararr3 = Array(n1 + n2).fill(0);mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);document.write("Array after merging<br/>");for(i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++)document.write(arr3[i] +" ");// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji</script>Producción:
Array after merging 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Complejidad de tiempo: O(n1 + n2)
Espacio auxiliar: O(n1 + n2)
Método 3: Uso de mapas (O(nlog(n) + mlog(m)) Tiempo y O(N) Espacio extra)
- Inserte elementos de ambas arrays en un mapa como claves.
- Imprime las claves del mapa.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
CPP
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays//using maps#include<bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespacestd;// Function to merge arraysvoidmergeArrays(inta[],intb[],intn,intm){// Declaring a map.// using map as a inbuilt tool// to store elements in sorted order.map<int,bool> mp;// Inserting values to a map.for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)mp[a[i]] =true;for(inti = 0;i < m;i++)mp[b[i]] =true;// Printing keys of the map.for(autoi: mp)cout<< i.first <<" ";}// Driver Codeintmain(){inta[] = {1, 3, 5, 7}, b[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};intsize =sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);intsize1 =sizeof(b)/sizeof(int);// Function callmergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);return0;}//This code is contributed by yashbeersingh42Java
// Java program to merge two sorted arrays//using mapsimportjava.io.*;importjava.util.*;classGFG {// Function to merge arraysstaticvoidmergeArrays(inta[],intb[],intn,intm){// Declaring a map.// using map as a inbuilt tool// to store elements in sorted order.Map<Integer,Boolean> mp =newTreeMap<Integer,Boolean>();// Inserting values to a map.for(inti =0; i < n; i++){mp.put(a[i],true);}for(inti =0;i < m;i++){mp.put(b[i],true);}// Printing keys of the map.for(Map.Entry<Integer,Boolean> me : mp.entrySet()){System.out.print(me.getKey() +" ");}}// Driver Codepublicstaticvoidmain (String[] args){inta[] = {1,3,5,7}, b[] = {2,4,6,8};intsize = a.length;intsize1 = b.length;// Function callmergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);}}// This code is contributed by rag2127Python3
# Python program to merge two sorted arrays# using mapsimportbisect# Function to merge arraysdefmergeArrays(a, b, n, m):# Declaring a map.# using map as a inbuilt tool# to store elements in sorted order.mp=[]# Inserting values to a map.foriinrange(n):bisect.insort(mp, a[i])foriinrange(m):bisect.insort(mp, b[i])# Printing keys of the map.foriinmp:(i,end=' ')# Driver codearr1=[1,3,5,7]arr2=[2,4,6,8]size=len(arr1)size1=len(arr2)# Function callmergeArrays(arr1, arr2, size, size1)# This code is contributed by Pushpesh RajC#
// C# program to merge two sorted arrays//using mapsusingSystem;usingSystem.Collections.Generic;publicclassGFG {// Function to merge arraysstaticvoidmergeArrays(int[]a,int[]b,intn,intm){// Declaring a map.// using map as a inbuilt tool// to store elements in sorted order.SortedDictionary<int, Boolean> mp =newSortedDictionary<int, Boolean>();// Inserting values to a map.for(inti = 0; i < n; i++) {mp.Add(a[i],true);}for(inti = 0; i < m; i++) {mp.Add(b[i],true);}// Printing keys of the map.foreach(KeyValuePair<int, Boolean> meinmp) {Console.Write(me.Key +" ");}}// Driver CodepublicstaticvoidMain(String[] args) {int[]a = { 1, 3, 5, 7 };int[]b = { 2, 4, 6, 8 };intsize = a.Length;intsize1 = b.Length;// Function callmergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);}}// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1JavaScript
<script>// javascript program to merge two sorted arrays//using maps// Function to merge arraysfunctionmergeArrays(a , b , n , m){// Declaring a map.// using map as a inbuilt tool// to store elements in sorted order.varmp =newMap();// Inserting values to a map.for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {mp.set(a[i],true);}for(i = 0; i < m; i++) {mp.set(b[i],true);}vara = [];// Printing keys of the map.for( me of mp.keys()) {a.push(me);}a.sort();for( me of a) {document.write(me +" ");}}// Driver Codevara = [ 1, 3, 5, 7 ], b = [ 2, 4, 6, 8 ];varsize = a.length;varsize1 = b.length;// Function callmergeArrays(a, b, size, size1);// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1</script>Producción:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Complejidad de tiempo: O( nlog(n) + mlog(m) )
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Brocade , Goldman-Sachs , Juniper , Linkedin , Microsoft , Quikr , Snapdeal , Synopsys , Zoho
Artículos relacionados :
Combinar dos arreglos ordenados con O (1) espacio adicional
Fusionar k arrays ordenadas | Conjunto 1
Este artículo es una contribución de Sahil Chhabra . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.orgo envíe su artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA