Nos dan dos arrays ordenadas. Necesitamos fusionar estas dos arrays de modo que los números iniciales (después de la clasificación completa) estén en la primera array y los números restantes estén en la segunda array. Se permite espacio extra en O(1).
Ejemplo:
Input: ar1[] = {10};
ar2[] = {2, 3};
Output: ar1[] = {2}
ar2[] = {3, 10}
Input: ar1[] = {1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20};
ar2[] = {2, 3, 8, 13};
Output: ar1[] = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9}
ar2[] = {10, 13, 15, 20}
Esta tarea es simple y O(m+n) si se nos permite usar espacio adicional. Pero se vuelve realmente complicado cuando no se permite espacio adicional y no parece posible en menos de O(m*n) en el peor de los casos. Aunque son posibles más optimizaciones,
la idea es comenzar desde el último elemento de ar2[] y buscarlo en ar1[]. Si hay un elemento mayor en ar1[], movemos el último elemento de ar1[] a ar2[]. Para mantener ordenados ar1[] y ar2[], necesitamos colocar el último elemento de ar2[] en el lugar correcto en ar1[]. Podemos usar el tipo de inserción Ordenar por inserción para esto.
1. Método 1
Algoritmo:
1) Iterate through every element of ar2[] starting from last
element. Do following for every element ar2[i]
a) Store last element of ar1[i]: last = ar1[i]
b) Loop from last element of ar1[] while element ar1[j] is
greater than ar2[i].
ar1[j+1] = ar1[j] // Move element one position ahead
j--
c) If any element of ar1[] was moved
ar1[j+1] = ar2[i]
ar2[i] = last
En el ciclo anterior, los elementos en ar1[] y ar2[] siempre se mantienen ordenados.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del algoritmo anterior.
C++
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra
// space.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Merge ar1[] and ar2[] with O(1) extra space
void merge(int ar1[], int ar2[], int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements
// of ar2[] starting from the last element
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i].
// Move all elements one position ahead till the
// smallest greater element is not found */
int j, last = ar1[m - 1];
for (j = m - 2; j >= 0 && ar1[j] > ar2[i]; j--)
ar1[j + 1] = ar1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > ar2[i]) {
ar1[j + 1] = ar2[i];
ar2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
C
// C program to merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra
// space.
#include <stdio.h>
// Merge ar1[] and ar2[] with O(1) extra space
void merge(int ar1[], int ar2[], int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements
// of ar2[] starting from the last element
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i].
// Move all elements one position ahead till the
// smallest greater element is not found */
int j, last = ar1[m - 1];
for (j = m - 2; j >= 0 && ar1[j] > ar2[i]; j--)
ar1[j + 1] = ar1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > ar2[i]) {
ar1[j + 1] = ar2[i];
ar2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
printf("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
printf("%d ", ar1[i]);
printf("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", ar2[i]);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
Java
// Java program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
import java.util.Arrays;
class Test
{
static int arr1[] = new int[]{1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20};
static int arr2[] = new int[]{2, 3, 8, 13};
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting from
// the last element
for (int i=n-1; i>=0; i--)
{
/* Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i]. Move all
elements one position ahead till the smallest greater
element is not found */
int j, last = arr1[m-1];
for (j=m-2; j >= 0 && arr1[j] > arr2[i]; j--)
arr1[j+1] = arr1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > arr2[i])
{
arr1[j+1] = arr2[i];
arr2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.length,arr2.length);
System.out.print("After Merging nFirst Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.print("Second Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
Python3
# Python program to merge
# two sorted arrays
# with O(1) extra space.
# Merge ar1[] and ar2[]
# with O(1) extra space
def merge(ar1, ar2, m, n):
# Iterate through all
# elements of ar2[] starting from
# the last element
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
# Find the smallest element
# greater than ar2[i]. Move all
# elements one position ahead
# till the smallest greater
# element is not found
last = ar1[m-1]
j=m-2
while(j >= 0 and ar1[j] > ar2[i]):
ar1[j+1] = ar1[j]
j-=1
# If there was a greater element
if (last > ar2[i]):
ar1[j+1] = ar2[i]
ar2[i] = last
# Driver program
ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
m = len(ar1)
n = len(ar2)
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n)
print("After Merging \nFirst Array:", end="")
for i in range(m):
print(ar1[i] , " ", end="")
print("\nSecond Array: ", end="")
for i in range(n):
print(ar2[i] , " ", end="")
# This code is contributed
# by Anant Agarwal.
C#
// C# program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
using System;
// Java program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
public class Test
{
static int []arr1 = new int[]{1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20};
static int []arr2 = new int[]{2, 3, 8, 13};
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting from
// the last element
for (int i=n-1; i>=0; i--)
{
/* Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i]. Move all
elements one position ahead till the smallest greater
element is not found */
int j, last = arr1[m-1];
for (j=m-2; j >= 0 && arr1[j] > arr2[i]; j--)
arr1[j+1] = arr1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > arr2[i])
{
arr1[j+1] = arr2[i];
arr2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void Main()
{
merge(arr1.Length,arr2.Length);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for(int i =0; i< arr1.Length;i++){
Console.Write(arr1[i]+" ");
}
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for(int i =0; i< arr2.Length;i++){
Console.Write(arr2[i]+" ");
}
}
}
/*This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar*/
PHP
<?php
// PHP program to merge two sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
// Merge ar1[] and ar2[] with O(1) extra space
function merge(&$ar1, &$ar2, $m, $n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting from
// the last element
for ($i = $n-1; $i >= 0; $i--)
{
/* Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i]. Move all
elements one position ahead till the smallest greater
element is not found */
$last = $ar1[$m-1];
for ($j = $m-2; $j >= 0 && $ar1[$j] > $ar2[$i]; $j--)
$ar1[$j+1] = $ar1[$j];
// If there was a greater element
if ($last > $ar2[$i])
{
$ar1[$j+1] = $ar2[$i];
$ar2[$i] = $last;
}
}
}
// Driver program
$ar1 = array(1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20);
$ar2 = array(2, 3, 8, 13);
$m = sizeof($ar1)/sizeof($ar1[0]);
$n = sizeof($ar2)/sizeof($ar2[0]);
merge($ar1, $ar2, $m, $n);
echo "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for ($i=0; $i<$m; $i++)
echo $ar1[$i] . " ";
echo "\nSecond Array: ";
for ($i=0; $i<$n; $i++)
echo $ar2[$i] ." ";
return 0;
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to merge two
// sorted arrays with O(1) extra space.
let arr1=[1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20];
let arr2=[2, 3, 8, 13];
function merge(m,n)
{
// Iterate through all elements of ar2[] starting from
// the last element
for (let i=n-1; i>=0; i--)
{
/* Find the smallest element greater than ar2[i]. Move all
elements one position ahead till the smallest greater
element is not found */
let j, last = arr1[m-1];
for (j=m-2; j >= 0 && arr1[j] > arr2[i]; j--)
arr1[j+1] = arr1[j];
// If there was a greater element
if (last > arr2[i])
{
arr1[j+1] = arr2[i];
arr2[i] = last;
}
}
}
// Driver method to test the above function
merge(arr1.length,arr2.length);
document.write("After Merging <br>First Array: ");
for(let i=0;i<arr1.length;i++)
{
document.write(arr1[i]+" ");
}
document.write("<br>Second Array: ");
for(let i=0;i<arr2.length;i++)
{
document.write(arr2[i]+" ");
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
After Merging First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9 Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Complejidad de tiempo: la complejidad de tiempo del código/algoritmo en el peor de los casos es O(m*n). El peor caso ocurre cuando todos los elementos de ar1[] son mayores que todos los elementos de ar2[].
Ilustración:
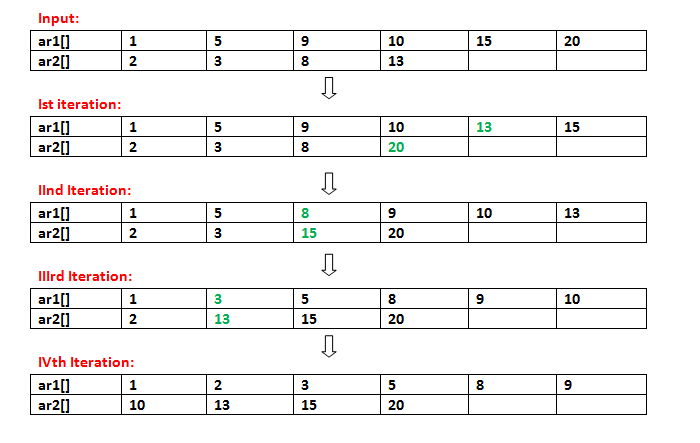
<!— Arrays iniciales:
ar1[] = {1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20};
ar2[] = {2, 3, 8, 13 };
Después de la primera iteración:
ar1[] = {1, 5, 9, 10, 13, 15};
ar2[] = {2, 3, 8 , 20};
// 20 se mueve de ar1[] a ar2[]
// 13 de ar2[] se inserta en ar1[]
Después de la segunda iteración:
ar1[] = {1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 13};
ar2[] = {2, 3 , 15, 20};
// 15 se mueve de ar1[] a ar2[]
// 8 de ar2[] se inserta en ar1[]
Después de la tercera iteración:
ar1[] = {1, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10};
ar2[] = { 2 , 13, 15, 20};
// 13 se mueve de ar1[] a ar2[]
// 3 de ar2[] se inserta en ar1[]
Después de la Cuarta Iteración:
ar1[] = {1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9};
ar2[] = {10, 13, 15, 20};
// 10 se mueve de ar1[] a ar2[]
// 2 de ar2[] se inserta en ar1[]
—!>
Método 2:
La solución se puede optimizar aún más al observar que mientras se recorren los dos arreglos ordenados en forma paralela, si encontramos que el j-ésimo segundo elemento del arreglo es más pequeño que el i-ésimo primer elemento del arreglo, entonces el j-ésimo elemento se debe incluir y reemplazar algún k-ésimo elemento en el primer arreglo. Esta observación nos ayuda con el siguiente algoritmo
Algoritmo
1) Initialize i,j,k as 0,0,n-1 where n is size of arr1
2) Iterate through every element of arr1 and arr2 using two pointers i and j respectively
if arr1[i] is less than arr2[j]
increment i
else
swap the arr2[j] and arr1[k]
increment j and decrement k
3) Sort both arr1 and arr2
A continuación se muestra la implementación del algoritmo anterior.
C++
// CPP program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to merge two arrays
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = n - 1;
// Until i less than equal to k
// or j is less than m
while (i <= k && j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
swap(arr2[j++], arr1[k--]);
}
}
// Sort first array
sort(arr1, arr1 + n);
// Sort second array
sort(arr2, arr2 + m);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
static int arr1[] = new int[] { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int arr2[] = new int[] { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
// Function to merge two arrays
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = m - 1;
while (i <= k && j < n) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
int temp = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = arr1[k];
arr1[k] = temp;
j++;
k--;
}
}
Arrays.sort(arr1);
Arrays.sort(arr2);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.print("Second Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
Python3
# Python program for the above approach
arr1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
arr2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
# Function to merge two arrays
def merge(n, m):
i = 0
j = 0
k = n - 1
while (i <= k and j < m):
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j]):
i += 1
else:
temp = arr2[j]
arr2[j] = arr1[k]
arr1[k] = temp
j += 1
k -= 1
arr1.sort()
arr2.sort()
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
merge(len(arr1), len(arr2))
print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ")
print(','.join(str(x) for x in arr1))
print("Second Array: ")
print(','.join(str(x) for x in arr2))
# This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG {
static int []arr1 ={ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int []arr2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
// Function to merge two arrays
static void merge(int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = n - 1;
while (i <= k && j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
int temp = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = arr1[k];
arr1[k] = temp;
j++;
k--;
}
}
Array.Sort(arr1);
Array.Sort(arr2);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.Length, arr2.Length);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr1){
Console.Write(i+" ");
}
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr2){
Console.Write(i+" ");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program for the above approach
var arr1 = [ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var arr2 = [ 2, 3, 8, 13 ];
// Function to merge two arrays
function merge(m , n) {
var i = 0, j = 0, k = n - 1;
while (i <= k && j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else {
var temp = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = arr1[k];
arr1[k] = temp;
j++;
k--;
}
}
arr1.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
arr2.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
}
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
document.write("After Merging <br/>First Array:<br/> ");
for(var a of arr1)
document.write(a+" ");
document.write("<br/>Second Array: <br/> ");
for(var a of arr2)
document.write(a+" ");
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
After Merging First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9 Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Complejidades:
Complejidad de tiempo: La complejidad de tiempo al atravesar las arrays en el ciclo while es O(n+m) en el peor de los casos y la clasificación es O(nlog(n) + mlog(m)). Entonces, la complejidad temporal general del código se convierte en O((n+m)log(n+m)).
Complejidad del espacio: como la función no usa ningún arreglo extra para ninguna operación, la complejidad del espacio es O(1).
Método 3:
Algoritmo:
1) Initialize i with 0
2) Iterate while loop until last element of array 1 is greater than first element of array 2
if arr1[i] greater than first element of arr2
swap arr1[i] with arr2[0]
sort arr2
incrementing i
C++
#include<iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m) {
int i=0;
// while loop till last element of array 1(sorted) is greater than
// first element of array 2(sorted)
while(arr1[n-1]>arr2[0])
{
if(arr1[i]>arr2[0])
{
// swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
sort(arr2,arr2+m);
}
i++;
}
}
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG{
static int arr1[] = new int[]{ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int arr2[] = new int[]{ 2, 3, 8, 13 };
static void merge(int n, int m)
{
int i = 0;
int temp = 0;
// While loop till last element
// of array 1(sorted)
// is greater than first element
// of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0])
{
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0])
{
// Swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
// swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[0];
arr2[0] = temp;
Arrays.sort(arr2);
}
i++;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.print("Second Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Tiwari(nighteagle)
Python3
arr1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
arr2 =[ 2, 3, 8, 13 ];
def merge(n, m):
i = 0;
temp = 0;
# While loop till last element
# of array 1(sorted)
# is greater than first element
# of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]):
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]):
# Swap arr1[i] with first element
# of arr2 and sorting the updated
# arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
# swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[0];
arr2[0] = temp;
arr2.sort();
i+=1;
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
merge(len(arr1), len(arr2));
print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
print((arr1));
print("Second Array: ");
print((arr2));
# This code contributed by gauravrajput1
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static int []arr1 = new int[] { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
static int []arr2 = new int[] { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
static void merge(int n, int m) {
int i = 0;
int temp = 0;
// While loop till last element
// of array 1(sorted)
// is greater than first element
// of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]) {
// Swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
// swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[0];
arr2[0] = temp;
Array.Sort(arr2);
}
i++;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
merge(arr1.Length, arr2.Length);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr1)
Console.Write(i+" ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
foreach(int i in arr2)
Console.Write(i+" ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
var arr1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var arr2 =[2, 3, 8, 13 ];
function merge(n , m) {
var i = 0;
var temp = 0;
// While loop till last element
// of array 1(sorted)
// is greater than first element
// of array 2(sorted)
while (arr1[n - 1] > arr2[0]) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[0]) {
// Swap arr1[i] with first element
// of arr2 and sorting the updated
// arr2(arr1 is already sorted)
// swap(arr1[i],arr2[0]);
temp = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[0];
arr2[0] = temp;
arr2.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
}
i++;
}
}
// Driver code
merge(arr1.length, arr2.length);
document.write("After Merging <br\>First Array: ");
document.write(arr1.toString());
document.write("<br\>Second Array: ");
document.write(arr2.toString());
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
After Merging First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9 Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Fusión eficiente de dos arrays ordenadas con O (1) espacio adicional
Método 4: Deje que la longitud de la array más corta sea ‘m’ y la array más grande sea ‘n’
Paso 1 : seleccione la array más corta y busque el índice en el que se debe realizar la partición. Similar a este https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/median-of-two-sorted-arrays-of- different-sizes/
Paso 1 : Divida la array más corta en su mediana (l1) .
Paso 2 : seleccione los primeros elementos n-l1 de la segunda array.

Paso 3 : Compare los elementos del borde, es decir
si l1 < r2 y l2 < r2 hemos encontrado el índice
de lo contrario, si l1 > r2 tenemos que buscar en el subarreglo izquierdo
de lo contrario, tenemos que buscar en el subarreglo correcto
NOTA: este paso almacenará todos los elementos más pequeños en la array más corta.
Paso 2 : Intercambie todos los elementos directamente al índice (i) de la array más corta con los primeros ni elementos de la array más grande.
Paso 3 : ordene ambas arrays.
::::: if len(arr1) > len(arr2) todos los elementos más pequeños se almacenan en arr2 por lo que tenemos que mover todos los elementos en arr1 ya que tenemos que imprimir arr1 primero.
Paso 4 : Gire la array más grande (arr1) m veces en sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj.
Paso 5 : Intercambie los primeros m elementos de ambas arrays.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void rotate(int a[], int n, int idx)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[idx - 1 - i]);
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - (i - idx)]);
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - i]);
}
void sol(int a1[], int a2[], int n, int m)
{
int l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
//---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h) {
// select the median of the remaining subarray
int c1 = (l + h) / 2;
// select the first elements from the larger array
// equal to the size of remaining portion to the
// right of the smaller array
int c2 = n - c1 - 1;
int l1 = a1[c1];
int l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
int r1 = c1 == n - 1 ? INT_MAX : a1[c1 + 1];
int r2 = c2 == m ? INT_MAX : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
}
else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
}
else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++)
swap(a1[i], a2[i - idx]);
sort(a1, a1 + n);
sort(a2, a2 + m);
}
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
swap(arr2[i], arr1[i]);
}
else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
static void rotate(int a[], int n, int idx)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[idx - 1 - i]);
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - (i - idx)]);
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - i]);
}
static void sol(int a1[], int a2[], int n, int m)
{
int l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
//---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h) {
// select the median of the remaining subarray
int c1 = (int)(l + h) / 2;
// select the first elements from the larger array
// equal to the size of remaining portion to the
// right of the smaller array
int c2 = n - c1 - 1;
int l1 = a1[c1];
int l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
int r1 = (c1 == n - 1) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : a1[c1 + 1];
int r2 = (c2 == m) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
}
else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
}
else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++)
swap(a1[i], a2[i - idx]);
Arrays.sort(a1);
Arrays.sort(a2);
}
static void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
swap(arr2[i], arr1[i]);
}
else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.length;
int n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
System.out.print(ar1[i] + " ");
System.out.print("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62.
Python3
# Python program to merge
# two sorted arrays
# with O(1) extra space.
# Merge ar1[] and ar2[]
# with O(1) extra space
def rotate(a, n, idx):
for i in range((int)(idx/2)):
a[i], a[idx-1-i] = a[idx-1-i], a[i]
for i in range(idx, (int)((n+idx)/2)):
a[i], a[n-1-(i-idx)] = a[n-1-(i-idx)], a[i]
for i in range((int)(n/2)):
a[i], a[n-1-i] = a[n-1-i], a[i]
def sol(a1, a2, n, m):
l = 0
h = n-1
idx = 0
while (l <= h):
c1 = (int)((l+h)/2)
c2 = n-c1-1
l1 = a1[c1]
l2 = a2[c2-1]
r1 = sys.maxint if c1 == n-1 else a1[c1+1]
r2 = sys.maxint if c2 == m else a2[c2]
if l1 > r2:
h = c1-1
if h == -1:
idx = 0
elif l2 > r1:
l = c1+1
if l == n-1:
idx = n
else:
idx = c1+1
break
for i in range(idx, n):
a1[i], a2[i-idx] = a2[i-idx], a1[i]
a1.sort()
a2.sort()
def merge(a1, a2, n, m):
if n > m:
sol(a2, a1, m, n)
rotate(a1, n, n-m)
for i in range(m):
a1[i], a2[i] = a2[i], a1[i]
else:
sol(a1, a2, n, m)
# Driver program
ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
m = len(ar1)
n = len(ar2)
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n)
print("After Merging \nFirst Array:", end="")
for i in range(m):
print(ar1[i], " ", end="")
print("\nSecond Array: ", end="")
for i in range(n):
print(ar2[i], " ", end="")
# This code is contributed
# by Aditya Anand.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static void swap(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
static void rotate(int []a, int n, int idx) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[idx - 1 - i]);
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - (i - idx)]);
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
swap(a[i], a[n - 1 - i]);
}
static void sol(int []a1, int []a2, int n, int m) {
int l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
// ---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h) {
// select the median of the remaining subarray
int c1 = (int) (l + h) / 2;
// select the first elements from the larger array
// equal to the size of remaining portion to the
// right of the smaller array
int c2 = n - c1 - 1;
int l1 = a1[c1];
int l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
int r1 = (c1 == n - 1) ? int.MaxValue : a1[c1 + 1];
int r2 = (c2 == m) ? int.MaxValue : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
} else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
} else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++)
swap(a1[i], a2[i - idx]);
Array.Sort(a1);
Array.Sort(a2);
}
static void merge(int []arr1, int []arr2, int n, int m) {
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
swap(arr2[i], arr1[i]);
} else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []ar1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int []ar2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.Length;
int n = ar2.Length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
Console.Write(ar1[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program for the above approach
function swap(a , b) {
var temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
function rotate(a , n , idx) {
var i;
for (i = 0; i < idx / 2; i++)
{
var temp =a[i]
a[i]= a[idx - 1 - i];
a[idx - 1 - i] = temp;
}
for (i = idx; i < (n + idx) / 2; i++)
{
var temp =a[i]
a[i]= a[n - 1 - (i - idx)];
a[n - 1 - (i - idx)] = temp;
}
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
var temp =a[i]
a[i]= a[n - 1 - i];
a[n - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
function sol(a1 , a2 , n , m) {
var l = 0, h = n - 1, idx = 0;
// ---------------------------------------------------------
while (l <= h)
{
// select the median of the remaining subarray
var c1 = parseInt( (l + h) / 2);
// select the first elements from the larger array
// equal to the size of remaining portion to the
// right of the smaller array
var c2 = n - c1 - 1;
var l1 = a1[c1];
var l2 = a2[c2 - 1];
var r1 = (c1 == n - 1) ? Number.MAX_VALUE : a1[c1 + 1];
var r2 = (c2 == m) ? Number.MAX_VALUE : a2[c2];
// compare the border elements and check for the
// target index
if (l1 > r2) {
h = c1 - 1;
if (h == -1)
idx = 0;
} else if (l2 > r1) {
l = c1 + 1;
if (l == n - 1)
idx = n;
} else {
idx = c1 + 1;
break;
}
}
for (i = idx; i < n; i++)
{
var temp =a1[i]
a1[i]= a2[i - idx];
a2[i - idx] = temp;
}
a1.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
a2.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
}
function merge(arr1 , arr2 , n , m) {
// code here
if (n > m) {
sol(arr2, arr1, m, n);
rotate(arr1, n, n - m);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
var temp =arr2[i]
arr2[i]= arr1[i];
arr1[i] = temp;
}
} else {
sol(arr1, arr2, n, m);
}
}
// Driver Code
var ar1 = [ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var ar2 = [ 2, 3, 8, 13 ];
var m = ar1.length;
var n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
document.write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
document.write(ar1[i] + " ");
document.write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(ar2[i] + " ");
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
After Merging First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9 Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Complejidad de tiempo: O(min(nlogn, mlogm))
Método 5 [Ordenar por inserción con combinación simultánea]
Acercarse:
1. ordenar la lista 1 comparándola siempre con el encabezado/primero de la lista 2 e intercambiar si es necesario
2. después de cada encabezado/primer intercambio, realice la inserción del elemento intercambiado en la posición correcta en la lista 2, lo que finalmente clasificará la lista 2 al final.Para cada elemento intercambiado de la lista 1, realice una ordenación por inserción en la lista 2 para encontrar su posición correcta, de modo que cuando se ordene la lista 1, la lista 2 también se ordene.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// two pointer to iterate
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is already
// sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
}
else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap both
// element so that arr1[i] become smaller means
// arr1[] become sorted then we check that
// arr2[j] is smaller than all other element in
// right side of arr2[j] if arr2[] is not sorted
// then we linearly do sorting
// means while adjacent element are less than
// new arr2[j] we do sorting like by changing
// position of element by shifting one position
// toward left
swap(arr1[i], arr2[j]);
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
int temp = arr2[j];
int tempj = j + 1;
while (arr2[tempj] < temp && tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// two pointer to iterate
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m)
{
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is already
// sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
}
else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j])
{
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap both
// element so that arr1[i] become smaller means
// arr1[] become sorted then we check that
// arr2[j] is smaller than all other element in
// right side of arr2[j] if arr2[] is not sorted
// then we linearly do sorting
// means while adjacent element are less than
// new arr2[j] we do sorting like by changing
// position of element by shifting one position
// toward left
int t = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = t;
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
int temp = arr2[j];
int tempj = j + 1;
while (tempj<m && arr2[tempj] < temp && tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.length;
int n =ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
System.out.print(ar1[i]+ " ");
System.out.print("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(ar2[i]+ " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Python3
# code contributed by mahee96 # "Insertion sort of list 2 with swaps from list 1" # # swap elements to get list 1 correctly, meanwhile # place the swapped item in correct position of list 2 # eventually list 2 is also sorted # Time = O(m*n) or O(n*m) # AUX = O(1) def merge(arr1, arr2): x = arr1; y = arr2 end = len(arr1) i = 0 while(i < end): # O(m) or O(n) if(x[i] > y[0]): swap(x,y,i,0) insert(y,0) # O(n) or O(m) number of shifts i+=1 # O(n): def insert(y, i): orig = y[i] i+=1 while (i<len(y) and y[i]<orig): y[i-1] = y[i] i+=1 y[i-1] = orig def swap(x,y,i,j): temp = x[i] x[i] = y[j] y[j] = temp def test(): c1 = [2, 3, 8, 13] c2 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ] for _ in range(2): merge(c1,c2) print(c1,c2) c1, c2 = c2, c1 test()
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static void merge(int []arr1, int []arr2, int n, int m) {
// two pointer to iterate
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is already
// sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap both
// element so that arr1[i] become smaller means
// arr1[] become sorted then we check that
// arr2[j] is smaller than all other element in
// right side of arr2[j] if arr2[] is not sorted
// then we linearly do sorting
// means while adjacent element are less than
// new arr2[j] we do sorting like by changing
// position of element by shifting one position
// toward left
int t = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = t;
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
int temp = arr2[j];
int tempj = j + 1;
while (tempj < m && arr2[tempj] < temp && tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []ar1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int []ar2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.Length;
int n = ar2.Length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
Console.Write(ar1[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
function merge(arr1 , arr2 , n , m) {
// two pointer to iterate
var i = 0;
var j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
// if arr1[i] <= arr2[j] then both array is already
// sorted
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
i++;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// if arr1[i]>arr2[j] then first we swap both
// element so that arr1[i] become smaller means
// arr1 become sorted then we check that
// arr2[j] is smaller than all other element in
// right side of arr2[j] if arr2 is not sorted
// then we linearly do sorting
// means while adjacent element are less than
// new arr2[j] we do sorting like by changing
// position of element by shifting one position
// toward left
var t = arr1[i];
arr1[i] = arr2[j];
arr2[j] = t;
i++;
if (j < m - 1 && arr2[j + 1] < arr2[j]) {
var temp = arr2[j];
var tempj = j + 1;
while (tempj < m && arr2[tempj] < temp && tempj < m) {
arr2[tempj - 1] = arr2[tempj];
tempj++;
}
arr2[tempj - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
var ar1 = [ 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 ];
var ar2 = [ 2, 3, 8, 13 ];
var m = ar1.length;
var n = ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
document.write("After Merging <br/>First Array: <br/>");
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
document.write(ar1[i] + " ");
document.write("<br/>Second Array: <br/>");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(ar2[i] + " ");
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
After Merging First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9 Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Complejidad de tiempo: O(m*n) lista 1 recorrido y lista 2 inserciones
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Si m == n: Tiempo = O(n^2) complejidad de clasificación de inserción
Método-6 [Usando el lema de división euclidiana]
Acercarse:
Simplemente fusione las dos arrays como lo hacemos en la ordenación por fusión, mientras usa simultáneamente el lema de división euclidiana, es decir (((Operación en la array) % x) * x). Y al menos después de fusionar, divida ambas arrays con x. Donde x debe ser un número mayor que todos los elementos de la array. Aquí en este caso x, (según las restricciones) puede ser 10e7 + 1.
C++
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays without using extra space
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
int x = 10e7 + 1;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if none elements are modified
else {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exchausted
while (j < n && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m)) {
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else {
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n) {
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m) {
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
int main()
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = sizeof(ar1) / sizeof(ar1[0]);
int n = sizeof(ar2) / sizeof(ar2[0]);
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
cout << "After Merging \nFirst Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
cout << ar1[i] << " ";
cout << "\nSecond Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar2[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by @ancientmoon8 (Mayank Kashyap)
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static void merge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
int x=10000000+7;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if none elements are modified
else {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exchausted
while (j < n && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else
{
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n) {
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m) {
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int ar2[] = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.length;
int n =ar2.length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
System.out.print("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
System.out.print(ar1[i]+ " ");
System.out.print("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(ar2[i]+ " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
Python3
# Python program to merge two sorted arrays without using extra space
def merge(arr1, arr2, n, m):
# three pointers to iterate
i = 0
j = 0
k = 0
# for euclid's division lemma
x = 10e7 + 1
# in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while i < n and (j < n and k < m):
# if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if arr1[j] >= x and arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr1 elements are modified
elif arr1[j] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr2 elements are modified
elif arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if none elements are modified
else:
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k]:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
i += 1
# we can copy the elements directly as the other array
# is exchausted
while j < n and i < n:
arr1[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
i += 1
j += 1
while k < m and i < n:
arr1[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
i += 1
k += 1
# we need to reset i
i = 0
# in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while i < m and (j < n and k < m):
# if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if arr1[j] >= x and arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr1 elements are modified
elif arr1[j] >= x:
if arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
# if only arr2 elements are modified
elif arr2[k] >= x:
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
else:
# if none elements are modified
if arr1[j] <= arr2[k]:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
j += 1
else:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
k += 1
i += 1
# we can copy the elements directly as the other array
# is exhausted
while j < n and i < m:
arr2[i] += (arr1[j] % x) * x
i += 1
j += 1
while k < m and i < m:
arr2[i] += (arr2[k] % x) * x
i += 1
k += 1
# we need to reset i
i = 0
# we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while i < n:
arr1[i] /= x
i += 1
# we need to reset i
i = 0
# we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while i < m:
arr2[i] /= x
i += 1
# Driver program
ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20]
ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13]
m = len(ar1)
n = len(ar2)
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n)
print("After Merging \nFirst Array:", end=" ")
for i in range(m):
print(int(ar1[i]), end=" ")
print("\nSecond Array:", end=" ")
for i in range(n):
print(int(ar2[i]), end=" ")
# This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420)
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static void merge(int []arr1, int []arr2, int n, int m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
int x = 10000000 + 1;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if none elements are modified
else {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exchausted
while (j < n && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n) {
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr1 elements are modified
else if (arr1[j] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
// if only arr2 elements are modified
else if (arr2[k] >= x) {
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else
{
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k]) {
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else {
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m) {
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n) {
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m) {
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []ar1 = { 1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20 };
int []ar2 = { 2, 3, 8, 13 };
int m = ar1.Length;
int n = ar2.Length;
merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
Console.Write("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
Console.Write(ar1[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\nSecond Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(ar2[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
Javascript
// JavaScript program to merge two sorted arrays without using extra space
static merge(arr1, arr2, n, m)
{
// three pointers to iterate
var i = 0;
var j = 0;
var k = 0;
// for euclid's division lemma
var x = 10000000 + 7;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr1
while (i < n && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr1[j] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k])
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else
{
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k])
{
arr1[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr1[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exchausted
while (j < n && i < n)
{
arr1[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < n)
{
arr1[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// in this loop we are rearranging the elements of arr2
while (i < m && (j < n && k < m))
{
// if both arr1 and arr2 elements are modified
if (arr1[j] >= x && arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr1[j] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] % x <= arr2[k])
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else if (arr2[k] >= x)
{
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k] % x)
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
else
{
// if none elements are modified
if (arr1[j] <= arr2[k])
{
arr2[i] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
else
{
arr2[i] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
}
i++;
}
// we can copy the elements directly as the other array
// is exhausted
while (j < n && i < m)
{
arr2[i++] += (arr1[j++] % x) * x;
}
while (k < m && i < m)
{
arr2[i++] += (arr2[k++] % x) * x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr1 by x
while (i < n)
{
arr1[i++] /= x;
}
// we need to reset i
i = 0;
// we need to divide the whole arr2 by x
while (i < m)
{
arr2[i++] /= x;
}
}
var ar1 = [1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20];
var ar2 = [2, 3, 8, 13];
var m = ar1.length;
var n = ar2.length;
GFG.merge(ar1, ar2, m, n);
console.log("After Merging \nFirst Array: ");
for (var i=0; i < m; i++)
{
console.log(parseInt(ar1[i]) + " ");
}
console.log("\nSecond Array: ");
for (var i=0; i < n; i++)
{
console.log(parseInt(ar2[i]) + " ");
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
After Merging First Array: 1 2 3 5 8 9 Second Array: 10 13 15 20
Tiempo Complejidad: O(m + n)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Artículos relacionados:
Combinar dos arrays ordenadas
Combinar k arrays ordenadas | Conjunto 1
Gracias a Shubham Chauhan por sugerir la primera solución ya Himanshu Kaushik por la segunda solución. Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
