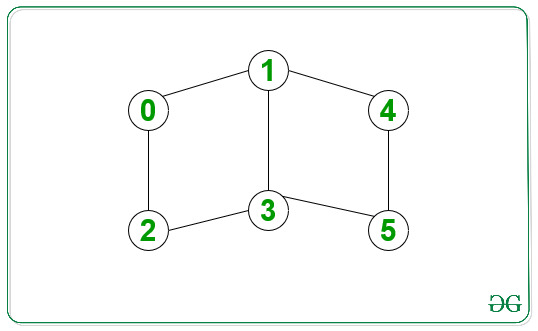
Dado un gráfico no dirigido y no ponderado y dos Nodes como fuente y destino , la tarea es imprimir todas las rutas de menor longitud entre la fuente y el destino dados.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: origen = 0, destino = 5
Salida:
0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 5
0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5
0 -> 1 -> 4 -> 5
Explicación:
Todas las rutas anteriores tienen una longitud de 3, que es la distancia más corta entre 0 y 5.
Entrada: fuente = 0, destino = 4
Salida:
0 -> 1 -> 4
Enfoque: El es hacer un Breadth First Traversal (BFS) para un gráfico. A continuación se muestran los pasos:
- Inicie el recorrido de BFS desde el vértice de origen.
- Mientras realiza BFS, almacene la distancia más corta a cada uno de los otros Nodes y también mantenga un vector principal para cada uno de los Nodes.
- Haga que el padre del Node de origen sea «-1» . Para cada Node, almacenará todos los padres para los que tiene la distancia más corta desde el Node de origen.
- Recupere todas las rutas usando la array principal. En cualquier instante, empujaremos un vértice en la array de ruta y luego llamaremos a todos sus padres.
- Si encontramos «-1» en los pasos anteriores, significa que se ha encontrado una ruta y se puede almacenar en la array de rutas.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
cpp14
// Cpp program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to form edge between
// two vertices src and dest
void add_edge(vector<int> adj[],
int src, int dest)
{
adj[src].push_back(dest);
adj[dest].push_back(src);
}
// Function which finds all the paths
// and stores it in paths array
void find_paths(vector<vector<int> >& paths,
vector<int>& path,
vector<int> parent[],
int n, int u)
{
// Base Case
if (u == -1) {
paths.push_back(path);
return;
}
// Loop for all the parents
// of the given vertex
for (int par : parent[u]) {
// Insert the current
// vertex in path
path.push_back(u);
// Recursive call for its parent
find_paths(paths, path, parent,
n, par);
// Remove the current vertex
path.pop_back();
}
}
// Function which performs bfs
// from the given source vertex
void bfs(vector<int> adj[],
vector<int> parent[],
int n, int start)
{
// dist will contain shortest distance
// from start to every other vertex
vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX);
queue<int> q;
// Insert source vertex in queue and make
// its parent -1 and distance 0
q.push(start);
parent[start] = { -1 };
dist[start] = 0;
// Until Queue is empty
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + 1) {
// A shorter distance is found
// So erase all the previous parents
// and insert new parent u in parent[v]
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
parent[v].clear();
parent[v].push_back(u);
}
else if (dist[v] == dist[u] + 1) {
// Another candidate parent for
// shortes path found
parent[v].push_back(u);
}
}
}
}
// Function which prints all the paths
// from start to end
void print_paths(vector<int> adj[],
int n, int start, int end)
{
vector<vector<int> > paths;
vector<int> path;
vector<int> parent[n];
// Function call to bfs
bfs(adj, parent, n, start);
// Function call to find_paths
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, end);
for (auto v : paths) {
// Since paths contain each
// path in reverse order,
// so reverse it
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
// Print node for the current path
for (int u : v)
cout << u << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 6;
// array of vectors is used
// to store the graph
// in the form of an adjacency list
vector<int> adj[n];
// Given Graph
add_edge(adj, 0, 1);
add_edge(adj, 0, 2);
add_edge(adj, 1, 3);
add_edge(adj, 1, 4);
add_edge(adj, 2, 3);
add_edge(adj, 3, 5);
add_edge(adj, 4, 5);
// Given source and destination
int src = 0;
int dest = n - 1;
// Function Call
print_paths(adj, n, src, dest);
return 0;
}
Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Function to form edge between
// two vertices src and dest
static void add_edge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int src, int dest){
adj.get(src).add(dest);
adj.get(dest).add(src);
}
// Function which finds all the paths
// and stores it in paths array
static void find_paths(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> paths, ArrayList<Integer> path,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> parent, int n, int u) {
// Base Case
if (u == -1) {
paths.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// Loop for all the parents
// of the given vertex
for (int par : parent.get(u)) {
// Insert the current
// vertex in path
path.add(u);
// Recursive call for its parent
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, par);
// Remove the current vertex
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
// Function which performs bfs
// from the given source vertex
static void bfs(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> parent,
int n, int start) {
// dist will contain shortest distance
// from start to every other vertex
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Insert source vertex in queue and make
// its parent -1 and distance 0
q.offer(start);
parent.get(start).clear();
parent.get(start).add(-1);
dist[start] = 0;
// Until Queue is empty
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int u = q.poll();
for (int v : adj.get(u)) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + 1) {
// A shorter distance is found
// So erase all the previous parents
// and insert new parent u in parent[v]
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.offer(v);
parent.get(v).clear();
parent.get(v).add(u);
}
else if (dist[v] == dist[u] + 1) {
// Another candidate parent for
// shortes path found
parent.get(v).add(u);
}
}
}
}
// Function which prints all the paths
// from start to end
static void print_paths(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int n, int start, int end){
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> parent = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
parent.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// Function call to bfs
bfs(adj, parent, n, start);
// Function call to find_paths
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, end);
for (ArrayList<Integer> v : paths) {
// Since paths contain each
// path in reverse order,
// so reverse it
Collections.reverse(v);
// Print node for the current path
for (int u : v)
System.out.print(u + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 6;
// array of vectors is used
// to store the graph
// in the form of an adjacency list
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// Given Graph
add_edge(adj, 0, 1);
add_edge(adj, 0, 2);
add_edge(adj, 1, 3);
add_edge(adj, 1, 4);
add_edge(adj, 2, 3);
add_edge(adj, 3, 5);
add_edge(adj, 4, 5);
// Given source and destination
int src = 0;
int dest = n - 1;
// Function Call
print_paths(adj, n, src, dest);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ayush123ngp.
Python3
# Python program for the above approach # Function to form edge between # two vertices src and dest from typing import List from sys import maxsize from collections import deque def add_edge(adj: List[List[int]], src: int, dest: int) -> None: adj[src].append(dest) adj[dest].append(src) # Function which finds all the paths # and stores it in paths array def find_paths(paths: List[List[int]], path: List[int], parent: List[List[int]], n: int, u: int) -> None: # Base Case if (u == -1): paths.append(path.copy()) return # Loop for all the parents # of the given vertex for par in parent[u]: # Insert the current # vertex in path path.append(u) # Recursive call for its parent find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, par) # Remove the current vertex path.pop() # Function which performs bfs # from the given source vertex def bfs(adj: List[List[int]], parent: List[List[int]], n: int, start: int) -> None: # dist will contain shortest distance # from start to every other vertex dist = [maxsize for _ in range(n)] q = deque() # Insert source vertex in queue and make # its parent -1 and distance 0 q.append(start) parent[start] = [-1] dist[start] = 0 # Until Queue is empty while q: u = q[0] q.popleft() for v in adj[u]: if (dist[v] > dist[u] + 1): # A shorter distance is found # So erase all the previous parents # and insert new parent u in parent[v] dist[v] = dist[u] + 1 q.append(v) parent[v].clear() parent[v].append(u) elif (dist[v] == dist[u] + 1): # Another candidate parent for # shortes path found parent[v].append(u) # Function which prints all the paths # from start to end def print_paths(adj: List[List[int]], n: int, start: int, end: int) -> None: paths = [] path = [] parent = [[] for _ in range(n)] # Function call to bfs bfs(adj, parent, n, start) # Function call to find_paths find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, end) for v in paths: # Since paths contain each # path in reverse order, # so reverse it v = reversed(v) # Print node for the current path for u in v: print(u, end = " ") print() # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": # Number of vertices n = 6 # array of vectors is used # to store the graph # in the form of an adjacency list adj = [[] for _ in range(n)] # Given Graph add_edge(adj, 0, 1) add_edge(adj, 0, 2) add_edge(adj, 1, 3) add_edge(adj, 1, 4) add_edge(adj, 2, 3) add_edge(adj, 3, 5) add_edge(adj, 4, 5) # Given source and destination src = 0 dest = n - 1 # Function Call print_paths(adj, n, src, dest) # This code is contributed by sanjeev2552
C#
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
// Function to form edge between
// two vertices src and dest
static void add_edge(List<List<int>> adj, int src, int dest){
adj[src].Add(dest);
adj[dest].Add(src);
}
// Function which finds all the paths
// and stores it in paths array
static void find_paths(List<List<int>> paths, List<int> path,
List<List<int>> parent, int n, int u) {
// Base Case
if (u == -1) {
paths.Add(new List<int>(path));
return;
}
// Loop for all the parents
// of the given vertex
foreach (int par in parent[u]) {
// Insert the current
// vertex in path
path.Add(u);
// Recursive call for its parent
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, par);
// Remove the current vertex
path.RemoveAt(path.Count-1);
}
}
// Function which performs bfs
// from the given source vertex
static void bfs(List<List<int>> adj, List<List<int>> parent,
int n, int start) {
// dist will contain shortest distance
// from start to every other vertex
int[] dist = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
dist[i] = int.MaxValue;
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
// Insert source vertex in queue and make
// its parent -1 and distance 0
q.Enqueue(start);
parent[start].Clear();
parent[start].Add(-1);
dist[start] = 0;
// Until Queue is empty
while (q.Count!=0) {
int u = q.Dequeue();
foreach (int v in adj[u]) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + 1) {
// A shorter distance is found
// So erase all the previous parents
// and insert new parent u in parent[v]
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.Enqueue(v);
parent[v].Clear();
parent[v].Add(u);
}
else if (dist[v] == dist[u] + 1) {
// Another candidate parent for
// shortes path found
parent[v].Add(u);
}
}
}
}
// Function which prints all the paths
// from start to end
static void print_paths(List<List<int>> adj, int n, int start, int end){
List<List<int>> paths = new List<List<int>>();
List<int> path = new List<int>();
List<List<int>> parent = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
parent.Add(new List<int>());
}
// Function call to bfs
bfs(adj, parent, n, start);
// Function call to find_paths
find_paths(paths, path, parent, n, end);
foreach (List<int> v in paths) {
// Since paths contain each
// path in reverse order,
// so reverse it
v.Reverse();
// Print node for the current path
foreach (int u in v)
Console.Write(u + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 6;
// array of vectors is used
// to store the graph
// in the form of an adjacency list
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
// Given Graph
add_edge(adj, 0, 1);
add_edge(adj, 0, 2);
add_edge(adj, 1, 3);
add_edge(adj, 1, 4);
add_edge(adj, 2, 3);
add_edge(adj, 3, 5);
add_edge(adj, 4, 5);
// Given source and destination
int src = 0;
int dest = n - 1;
// Function Call
print_paths(adj, n, src, dest);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
0 1 3 5 0 2 3 5 0 1 4 5
Complejidad temporal: O(V + E) donde V es el número de vértices y E es el número de aristas.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V) donde V es el número de vértices.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shobhitgupta907 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA