Dadas las intersecciones de una línea recta en ambos ejes como m y n . La tarea es encontrar la longitud de la normal en esta línea recta desde el origen.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: m = 5, n = 3
Salida: 2,57248
Entrada: m = 13, n = 9
Salida: 7,39973
Aproximación: Una normal a una línea es un segmento de línea dibujado desde un punto perpendicular a la línea dada.
Sea p la longitud de la normal trazada desde el origen hasta una línea que subtiende un ángulo Θ con la dirección positiva del eje x de la siguiente manera.
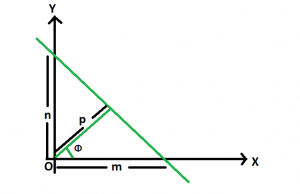
Entonces, tenemos cos Θ = p / m y sen Θ = p / n
Ya que, sen 2 Θ + cos 2 Θ = 1
Entonces, (p / m) 2 + (p / n) 2 = 1
Obtenemos, p = m * n / √(m 2 + n 2 )
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the normal
// of the straight line
float normal(float m, float n)
{
// Length of the normal
float N = (fabsf(m) * fabsf(n))
/ sqrt((fabsf(m) * fabsf(m))
+ (fabsf(n) * fabsf(n)));
return N;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
float m = -5, n = 3;
cout << normal(m, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Function to find the normal
// of the straight line
static float normal(float m, float n)
{
// Length of the normal
float N = (float) ((Math.abs(m) * Math.abs(n))
/ Math.sqrt((Math.abs(m) * Math.abs(m))
+ (Math.abs(n) * Math.abs(n))));
return N;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float m = -5, n = 3;
System.out.println(normal(m, n));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach import math; # Function to find the normal # of the straight line def normal(m, n): # Length of the normal N = ((abs(m) * abs(n)) / math.sqrt((abs(m) * abs(m)) + (abs(n) * abs(n)))); return N; # Driver code m = -5; n = 3; print(normal(m, n)); # This code is contributed # by Akanksha Rai
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the normal
// of the straight line
static float normal(float m, float n)
{
// Length of the normal
float N = (float)((Math.Abs(m) * Math.Abs(n)) /
Math.Sqrt((Math.Abs(m) * Math.Abs(m)) +
(Math.Abs(n) * Math.Abs(n))));
return N;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
float m = -5, n = 3;
Console.Write(normal(m, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Akanksha Rai
PHP
<?php
// PHP implementation of the approach
// Function to find the normal
// of the straight line
function normal($m, $n)
{
// Length of the normal
$N = (abs($m) * abs($n)) /
sqrt((abs($m) * abs($m)) +
(abs($n) * abs($n)));
return $N;
}
// Driver code
$m = -5; $n = 3;
echo normal($m, $n);
// This code is contributed by Ryuga
?>
Javascript
<script>
// javascript implementation of the approach
// Function to find the normal
// of the straight line
function normal(m , n)
{
// Length of the normal
var N = ((Math.abs(m) * Math.abs(n))
/ Math.sqrt((Math.abs(m) * Math.abs(m))
+ (Math.abs(n) * Math.abs(n))));
return N;
}
// Driver code
var m = -5, n = 3;
document.write(normal(m, n).toFixed(5));
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
</script>
2.57248
Tiempo Complejidad: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por IshwarGupta y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA