Dado un árbol N-ario con raíz en 1 , la tarea es asignar valores del rango [0, N – 1] a cada Node en cualquier orden de modo que la suma de los valores MEX de cada Node en el árbol se maximice e imprima el suma máxima posible de valores MEX de cada Node en el árbol.
El valor MEX del Node V se define como el número positivo faltante más pequeño en un árbol con raíz en el Node V.
Ejemplos:
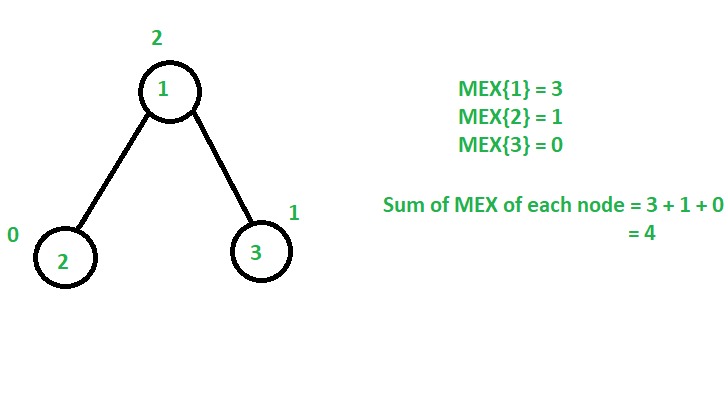
Entrada: N = 3, Edges[] = {{1, 2}, {1, 3}}
Salida: 4
Explicación:Asigne el valor 0 al Node 2, 1 al Node 3 y 2 al Node 1.
Por lo tanto, la suma máxima de MEX de todos los Nodes = MEX{1} + MEX{2} + MEX{3} = 3 + 1 + 0 = 4 .Entrada: N = 7, Edges[] = {1, 5}, {1, 4}, {5, 2}, {5, 3}, {4, 7}, {7, 6}}
Salida: 13
Explicación :Asigne el valor 0 al Node 6, 1 al Node 7, 2 al Node 4, 6 al Node 1, 5 al Node 5, 3 al Node 2 y 4 al Node 3.
Por lo tanto, la suma máxima de MEX de todos los Nodes = MEX{ 1} + MEX{2} + MEX{3} + MEX{4} + MEX{5} + MEX{6} + MEX{7} = 7 + 0 + 0 + 3 + 0 + 1 + 0 = 13.
Enfoque: La idea es realizar DFS Traversal en el árbol N-ario dado y encontrar la suma de MEX para cada subárbol en el árbol. Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Realice la primera búsqueda en profundidad (DFS) en el árbol arraigado en el Node 1 .
- Inicialice una variable mex con 0 y tamaño con 1 .
- Iterar a través de todos los elementos secundarios del Node actual y realizar las siguientes operaciones:
- Llame recursivamente a los hijos del Node actual y almacene la suma máxima de MEX entre todos los subárboles en mex .
- Aumentar el tamaño del árbol enraizado en el Node actual .
- Aumenta el valor de mex por tamaño.
- Después de completar los pasos anteriores, imprima el valor de mex como respuesta.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to create an N-ary Tree
void makeTree(vector<int> tree[],
pair<int, int> edges[],
int N)
{
// Traverse the edges
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
int u = edges[i].first;
int v = edges[i].second;
// Add edges
tree[u].push_back(v);
}
}
// Function to get the maximum sum
// of MEX values of tree rooted at 1
pair<int, int> dfs(int node,
vector<int> tree[])
{
// Initialize mex
int mex = 0;
int size = 1;
// Iterate through all children
// of node
for (int u : tree[node]) {
// Recursively find maximum sum
// of MEX values of each node
// in tree rooted at u
pair<int, int> temp = dfs(u, tree);
// Store the maximum sum of MEX
// of among all subtrees
mex = max(mex, temp.first);
// Increase the size of tree
// rooted at current node
size += temp.second;
}
// Resulting MEX for the current
// node of the recursive call
return { mex + size, size };
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given N nodes
int N = 7;
// Given N-1 edges
pair<int, int> edges[]
= { { 1, 4 }, { 1, 5 }, { 5, 2 }, { 5, 3 }, { 4, 7 }, { 7, 6 } };
// Stores the tree
vector<int> tree[N + 1];
// Generates the tree
makeTree(tree, edges, N);
// Returns maximum sum of MEX
// values of each node
cout << dfs(1, tree).first;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to create an N-ary Tree
static void makeTree(Vector<Integer> tree[],
pair edges[], int N)
{
// Traverse the edges
for(int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
int u = edges[i].first;
int v = edges[i].second;
// Add edges
tree[u].add(v);
}
}
// Function to get the maximum sum
// of MEX values of tree rooted at 1
static pair dfs(int node, Vector<Integer> tree[])
{
// Initialize mex
int mex = 0;
int size = 1;
// Iterate through all children
// of node
for(int u : tree[node])
{
// Recursively find maximum sum
// of MEX values of each node
// in tree rooted at u
pair temp = dfs(u, tree);
// Store the maximum sum of MEX
// of among all subtrees
mex = Math.max(mex, temp.first);
// Increase the size of tree
// rooted at current node
size += temp.second;
}
// Resulting MEX for the current
// node of the recursive call
return new pair(mex + size, size);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given N nodes
int N = 7;
// Given N-1 edges
pair edges[] = { new pair(1, 4),
new pair(1, 5),
new pair(5, 2),
new pair(5, 3),
new pair(4, 7),
new pair(7, 6) };
// Stores the tree
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector<Integer>[] tree = new Vector[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < tree.length; i++)
tree[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
// Generates the tree
makeTree(tree, edges, N);
// Returns maximum sum of MEX
// values of each node
System.out.print((dfs(1, tree).first));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to create an N-ary Tree def makeTree(tree, edges, N): # Traverse the edges for i in range(N - 1): u = edges[i][0] v = edges[i][1] # Add edges tree[u].append(v) return tree # Function to get the maximum sum # of MEX values of tree rooted at 1 def dfs(node, tree): # Initialize mex mex = 0 size = 1 # Iterate through all children # of node for u in tree[node]: # Recursively find maximum sum # of MEX values of each node # in tree rooted at u temp = dfs(u, tree) # Store the maximum sum of MEX # of among all subtrees mex = max(mex, temp[0]) # Increase the size of tree # rooted at current node size += temp[1] # Resulting MEX for the current # node of the recursive call return [mex + size, size] # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Given N nodes N = 7 # Given N-1 edges edges = [ [ 1, 4 ], [ 1, 5 ], [ 5, 2 ], [ 5, 3 ], [ 4, 7 ], [ 7, 6 ] ] # Stores the tree tree = [[] for i in range(N + 1)] # Generates the tree tree = makeTree(tree, edges, N) # Returns maximum sum of MEX # values of each node print(dfs(1, tree)[0]) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
public class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to create an N-ary Tree
static void makeTree(List<int> []tree,
pair []edges, int N)
{
// Traverse the edges
for(int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
int u = edges[i].first;
int v = edges[i].second;
// Add edges
tree[u].Add(v);
}
}
// Function to get the maximum sum
// of MEX values of tree rooted at 1
static pair dfs(int node, List<int> []tree)
{
// Initialize mex
int mex = 0;
int size = 1;
// Iterate through all children
// of node
foreach(int u in tree[node])
{
// Recursively find maximum sum
// of MEX values of each node
// in tree rooted at u
pair temp = dfs(u, tree);
// Store the maximum sum of MEX
// of among all subtrees
mex = Math.Max(mex, temp.first);
// Increase the size of tree
// rooted at current node
size += temp.second;
}
// Resulting MEX for the current
// node of the recursive call
return new pair(mex + size, size);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given N nodes
int N = 7;
// Given N-1 edges
pair []edges = { new pair(1, 4),
new pair(1, 5),
new pair(5, 2),
new pair(5, 3),
new pair(4, 7),
new pair(7, 6) };
// Stores the tree
List<int>[] tree = new List<int>[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < tree.Length; i++)
tree[i] = new List<int>();
// Generates the tree
makeTree(tree, edges, N);
// Returns maximum sum of MEX
// values of each node
Console.Write((dfs(1, tree).first));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Function to create an N-ary Tree
function makeTree(tree, edges, N)
{
// Traverse the edges
for (var i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
var u = edges[i][0];
var v = edges[i][1];
// Add edges
tree[u].push(v);
}
}
// Function to get the maximum sum
// of MEX values of tree rooted at 1
function dfs(node, tree)
{
// Initialize mex
var mex = 0;
var size = 1;
// Iterate through all children
// of node
tree[node].forEach(u => {
// Recursively find maximum sum
// of MEX values of each node
// in tree rooted at u
var temp = dfs(u, tree);
// Store the maximum sum of MEX
// of among all subtrees
mex = Math.max(mex, temp[0]);
// Increase the size of tree
// rooted at current node
size += temp[1];
});
// Resulting MEX for the current
// node of the recursive call
return [mex + size, size ];
}
// Driver Code
// Given N nodes
var N = 7;
// Given N-1 edges
var edges = [ [ 1, 4 ], [ 1, 5 ], [ 5, 2 ],
[ 5, 3 ], [ 4, 7 ], [ 7, 6 ] ];
// Stores the tree
var tree = Array.from(Array(N+1), ()=> Array());
// Generates the tree
makeTree(tree, edges, N);
// Returns maximum sum of MEX
// values of each node
document.write( dfs(1, tree)[0]);
</script>
13
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ManikantaBandla y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA