Dado un tablero de ajedrez N*M . La tarea es encontrar el número máximo de caballos que se pueden colocar en el tablero de ajedrez dado de modo que ningún caballo ataque a otro caballo.
Ejemplo
Entrada: N = 1, M = 4
Salida: 4
Coloque un caballo en cada celda del tablero de ajedrez.Entrada: N = 4, M = 5
Salida: 10
Planteamiento: Como sabemos que un caballero puede atacar de dos formas. Estos son los lugares que puede atacar.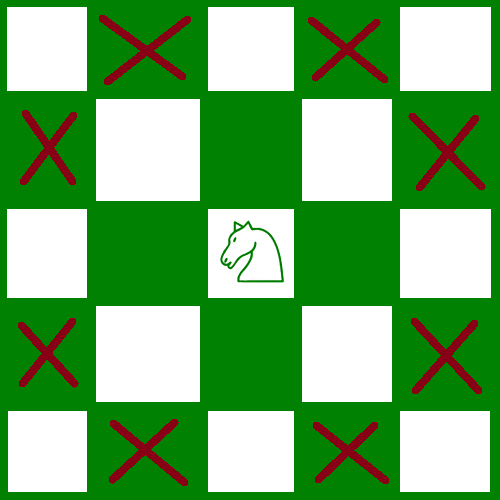
Aquí, en la imagen, el caballo está en color blanco y ataca solo al color negro. De este modo. llegamos a la conclusión de que un caballo puede atacar solo en un color diferente.
Podemos tomar la ayuda de este hecho y usarlo para nuestro propósito. Ahora que sabemos que los caballeros atacan en diferentes colores, podemos mantener a todos los caballeros en el mismo color, es decir, todos en blanco o todos en negro. Haciendo así el mayor número de caballos que se pueden colocar.
Para encontrar el número de blanco o negro, es simplemente la mitad del total de bloques a bordo.
Bloques totales = n * m
Bloques del mismo color = (n * m) / 2
Casos de esquina:
- Si solo hay una sola fila o columna. Entonces todos los bloques pueden ser llenados por caballeros ya que un caballero no puede atacar en la misma fila o columna.

- Si solo hay dos filas o columnas. Luego, cada dos columnas (o filas) se llenarán de caballos y cada dos columnas (o filas) consecutivas permanecerán vacías. Como se demuestra en la imagen.
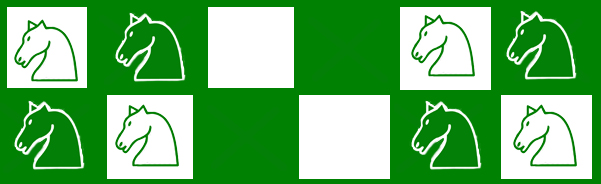
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std; // Function to return the maximum number of// knights that can be placed on the given// chessboard such that no two// knights attack each otherint max_knight(int n, int m){ // Check for corner case #1 // If row or column is 1 if (m == 1 || n == 1) { // If yes, then simply print total blocks // which will be the max of row or column return max(m, n); } // Check for corner case #2 // If row or column is 2 else if (m == 2 || n == 2) { // If yes, then simply calculate // consecutive 2 rows or columns int c = 0; c = (max(m, n) / 4) * 4; if (max(m, n) % 4 == 1) { c += 2; } else if (max(m, n) % 4 > 1) { c += 4; } return c; } // For general case, just print the // half of total blocks else { return (((m * n) + 1) / 2); }} // Driver codeint main(){ int n = 4, m = 5; cout << max_knight(n, m); return 0;} |
Java
// Java implementation of the approach import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return the maximum number of // knights that can be placed on the given // chessboard such that no two // knights attack each other static int max_knight(int n, int m) { // Check for corner case #1 // If row or column is 1 if (m == 1 || n == 1) { // If yes, then simply print total blocks // which will be the max of row or column return Math.max(m, n); } // Check for corner case #2 // If row or column is 2 else if (m == 2 || n == 2) { // If yes, then simply calculate // consecutive 2 rows or columns int c = 0; c = (Math.max(m, n) / 4) * 4; if (Math.max(m, n) % 4 == 1) { c += 2; } else if (Math.max(m, n) % 4 > 1) { c += 4; } return c; } // For general case, just print the // half of total blocks else { return (((m * n) + 1) / 2); } } // Driver code public static void main (String[] args) { int n = 4, m = 5; System.out.println (max_knight(n, m)); }} // This code is contributed by ajit |
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach # Function to return the maximum number of # knights that can be placed on the given # chessboard such that no two # knights attack each other def max_knight(n, m) : # Check for corner case #1 # If row or column is 1 if (m == 1 or n == 1) : # If yes, then simply print total blocks # which will be the max of row or column return max(m, n); # Check for corner case #2 # If row or column is 2 elif (m == 2 or n == 2) : # If yes, then simply calculate # consecutive 2 rows or columns c = 0; c = (max(m, n) // 4) * 4; if (max(m, n) % 4 == 1) : c += 2; elif (max(m, n) % 4 > 1) : c += 4; return c; # For general case, just print the # half of total blocks else : return (((m * n) + 1) // 2); # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__" : n = 4; m = 5; print(max_knight(n, m)); # This code is contributed by AnkitRai01 |
C#
// C# implementation of the approach using System; class GFG{ // Function to return the maximum number of // knights that can be placed on the given // chessboard such that no two // knights attack each other static int max_knight(int n, int m) { // Check for corner case #1 // If row or column is 1 if (m == 1 || n == 1) { // If yes, then simply print total blocks // which will be the max of row or column return Math.Max(m, n); } // Check for corner case #2 // If row or column is 2 else if (m == 2 || n == 2) { // If yes, then simply calculate // consecutive 2 rows or columns int c = 0; c = (Math.Max(m, n) / 4) * 4; if (Math.Max(m, n) % 4 == 1) { c += 2; } else if (Math.Max(m, n) % 4 > 1) { c += 4; } return c; } // For general case, just print the // half of total blocks else { return (((m * n) + 1) / 2); } } // Driver code static public void Main(){ int n = 4, m = 5; Console.Write(max_knight(n, m)); }} // This code is contributed by Tushil. |
10
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ShivamChauhan5 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA