Prerrequisitos: Clustering de OPTICS
Este artículo demostrará cómo implementar la técnica de agrupamiento OPTICS usando Sklearn en Python. El conjunto de datos utilizado para la demostración son los datos de segmentación de clientes del centro comercial que se pueden descargar de Kaggle .
Paso 1: Importación de las bibliotecas requeridas
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import gridspec from sklearn.cluster import OPTICS, cluster_optics_dbscan from sklearn.preprocessing import normalize, StandardScaler
Paso 2: cargando los datos
# Changing the working location to the location of the data
cd C:\Users\Dev\Desktop\Kaggle\Customer Segmentation
X = pd.read_csv('Mall_Customers.csv')
# Dropping irrelevant columns
drop_features = ['CustomerID', 'Gender']
X = X.drop(drop_features, axis = 1)
# Handling the missing values if any
X.fillna(method ='ffill', inplace = True)
X.head()
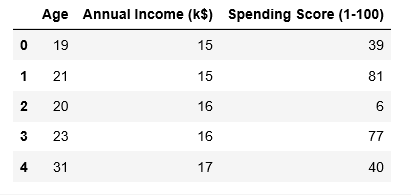
Paso 3: preprocesamiento de los datos
# Scaling the data to bring all the attributes to a comparable level scaler = StandardScaler() X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X) # Normalizing the data so that the data # approximately follows a Gaussian distribution X_normalized = normalize(X_scaled) # Converting the numpy array into a pandas DataFrame X_normalized = pd.DataFrame(X_normalized) # Renaming the columns X_normalized.columns = X.columns X_normalized.head()
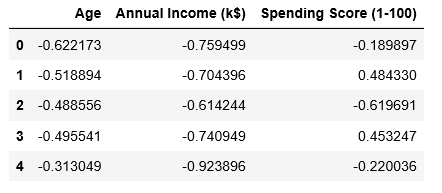
Paso 4: Construcción del modelo de agrupamiento
# Building the OPTICS Clustering model optics_model = OPTICS(min_samples = 10, xi = 0.05, min_cluster_size = 0.05) # Training the model optics_model.fit(X_normalized)
Paso 5: Almacenamiento de los resultados del entrenamiento
# Producing the labels according to the DBSCAN technique with eps = 0.5 labels1 = cluster_optics_dbscan(reachability = optics_model.reachability_, core_distances = optics_model.core_distances_, ordering = optics_model.ordering_, eps = 0.5) # Producing the labels according to the DBSCAN technique with eps = 2.0 labels2 = cluster_optics_dbscan(reachability = optics_model.reachability_, core_distances = optics_model.core_distances_, ordering = optics_model.ordering_, eps = 2) # Creating a numpy array with numbers at equal spaces till # the specified range space = np.arange(len(X_normalized)) # Storing the reachability distance of each point reachability = optics_model.reachability_[optics_model.ordering_] # Storing the cluster labels of each point labels = optics_model.labels_[optics_model.ordering_] print(labels)
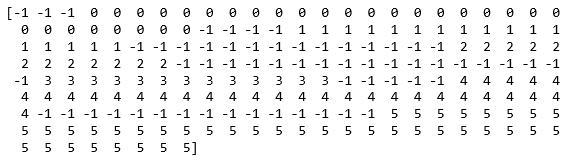
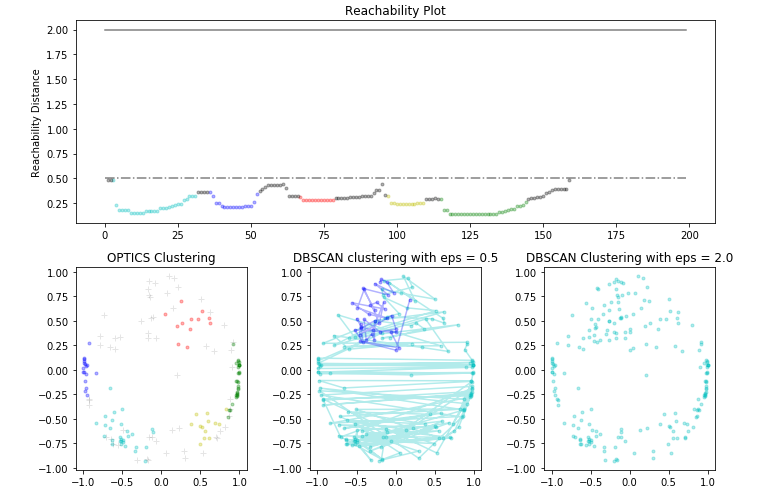
Paso 6: Visualización de los resultados
# Defining the framework of the visualization
plt.figure(figsize =(10, 7))
G = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 3)
ax1 = plt.subplot(G[0, :])
ax2 = plt.subplot(G[1, 0])
ax3 = plt.subplot(G[1, 1])
ax4 = plt.subplot(G[1, 2])
# Plotting the Reachability-Distance Plot
colors = ['c.', 'b.', 'r.', 'y.', 'g.']
for Class, colour in zip(range(0, 5), colors):
Xk = space[labels == Class]
Rk = reachability[labels == Class]
ax1.plot(Xk, Rk, colour, alpha = 0.3)
ax1.plot(space[labels == -1], reachability[labels == -1], 'k.', alpha = 0.3)
ax1.plot(space, np.full_like(space, 2., dtype = float), 'k-', alpha = 0.5)
ax1.plot(space, np.full_like(space, 0.5, dtype = float), 'k-.', alpha = 0.5)
ax1.set_ylabel('Reachability Distance')
ax1.set_title('Reachability Plot')
# Plotting the OPTICS Clustering
colors = ['c.', 'b.', 'r.', 'y.', 'g.']
for Class, colour in zip(range(0, 5), colors):
Xk = X_normalized[optics_model.labels_ == Class]
ax2.plot(Xk.iloc[:, 0], Xk.iloc[:, 1], colour, alpha = 0.3)
ax2.plot(X_normalized.iloc[optics_model.labels_ == -1, 0],
X_normalized.iloc[optics_model.labels_ == -1, 1],
'k+', alpha = 0.1)
ax2.set_title('OPTICS Clustering')
# Plotting the DBSCAN Clustering with eps = 0.5
colors = ['c', 'b', 'r', 'y', 'g', 'greenyellow']
for Class, colour in zip(range(0, 6), colors):
Xk = X_normalized[labels1 == Class]
ax3.plot(Xk.iloc[:, 0], Xk.iloc[:, 1], colour, alpha = 0.3, marker ='.')
ax3.plot(X_normalized.iloc[labels1 == -1, 0],
X_normalized.iloc[labels1 == -1, 1],
'k+', alpha = 0.1)
ax3.set_title('DBSCAN clustering with eps = 0.5')
# Plotting the DBSCAN Clustering with eps = 2.0
colors = ['c.', 'y.', 'm.', 'g.']
for Class, colour in zip(range(0, 4), colors):
Xk = X_normalized.iloc[labels2 == Class]
ax4.plot(Xk.iloc[:, 0], Xk.iloc[:, 1], colour, alpha = 0.3)
ax4.plot(X_normalized.iloc[labels2 == -1, 0],
X_normalized.iloc[labels2 == -1, 1],
'k+', alpha = 0.1)
ax4.set_title('DBSCAN Clustering with eps = 2.0')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por AlindGupta y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA