Dados N artículos con pesos W[0..n-1] , valores V[0..n-1] y una mochila con capacidad C , seleccione los artículos tales que:
- La suma de los pesos llevados a la mochila es menor o igual a C.
- La suma de valores de los elementos de la mochila es máxima entre todas las combinaciones posibles.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 4, C = 15, V[]= {10, 10, 12, 18}, W[]= {2, 4, 6, 9} Salida: Los elementos que se llevan
a
la mochila son
1 1 0 1
Máximo el beneficio es 38
Explicación:
1 en la salida indica que el artículo está incluido en la mochila mientras que 0 indica que el artículo está excluido.
Dado que el costo máximo posible permitido es 15, las formas de seleccionar artículos son:
(1 1 0 1) -> Costo = 2 + 4 + 9 = 15, Beneficio = 10 + 10 + 18 = 38.
(0 0 1 1) -> Costo = 6 + 9 = 15, Beneficio = 12 + 18 = 30
(1 1 1 0) -> Costo = 2 + 4 + 6 = 12, Beneficio = 32
Por lo tanto, el beneficio máximo posible dentro de un costo de 15 es 38
Entrada: N = 4, C = 21, V[]= {18, 20, 14, 18}, W[]= {6, 3, 5, 9} Salida :
Los artículos que se llevan a la mochila son
1 1 0 1
La ganancia máxima es 56
Explicación:
Costo = 6 + 3 + 9 = 18
Ganancia = 18 + 20 + 18 = 56
Enfoque: En esta publicación, se analiza
la implementación del método Branch and Bound utilizando el costo mínimo (LC) para el problema de la mochila 0/1 .
Branch and Bound se puede resolver utilizando estrategias FIFO , LIFO y LC . El menor costo (LC) se considera el más inteligente, ya que selecciona el siguiente Node en función de una función de costo heurística . Escoge el que tiene el menor costo.
Como 0/1 Mochila se trata de maximizar el valor total, no podemos usar directamente LC Branch and Boundtécnica para resolver esto. En su lugar, convertimos esto en un problema de minimización tomando negativos de los valores dados.
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Ordene los elementos según su relación valor/peso (V/W) .
- Inserte un Node ficticio en la cola de prioridad .
- Repita los siguientes pasos hasta que la cola de prioridad esté vacía:
- Extraiga el elemento de vista previa de la cola de prioridad y asígnelo al Node actual .
- Si el límite superior del Node actual es menor que minLB , el límite inferior mínimo de todos los Nodes explorados, entonces no hay punto de exploración. Entonces, continúe con el siguiente elemento. La razón para no considerar los Nodes cuyo límite superior es mayor que minLB es que el límite superior almacena el mejor valor que se puede lograr. Si el mejor valor en sí mismo no es óptimo que minLB , entonces explorar ese camino no sirve de nada.
- Actualice la array de ruta .
- Si el nivel del Node actual es N , compruebe si el límite inferior del Node actual es menor que finalLB , el límite inferior mínimo de todas las rutas que alcanzaron el nivel final. Si es cierto, actualice finalPath y finalLB . De lo contrario, continúe con el siguiente elemento.
- Calcule los límites inferior y superior del hijo derecho del Node actual.
- Si el elemento actual se puede insertar en la mochila, calcule el límite inferior y superior del elemento secundario izquierdo del Node actual.
- Actualice minLB e inserte los hijos si su límite superior es menor que minLB .
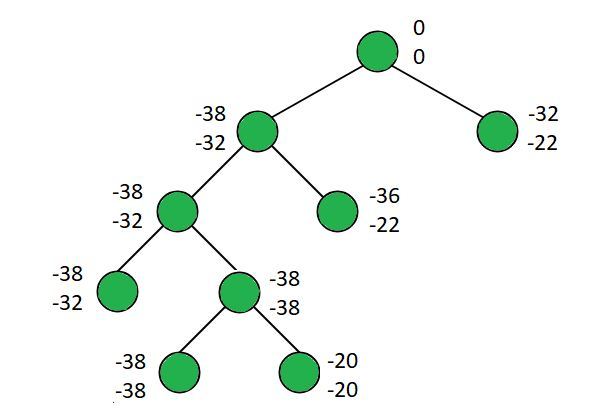
Ilustración:
N = 4, C = 15, V[]= {10 10 12 18}, W[]= {2 4 6 9}
La rama izquierda y la rama derecha en el i- ésimo nivel almacenan el máximo obtenido incluyendo y excluyendo el i- ésimo elemento.
La siguiente imagen muestra el estado de la cola de prioridad después de cada paso:
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement 0/1
// knapsack using LC Branch and Bound
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Stores the number of items
int size;
// Stores the knapsack capacity
float capacity;
typedef struct Item {
// Stores the weight of items
float weight;
// Stores the value of items
int value;
// Stores the index of items
int idx;
} Item;
typedef struct Node {
// Upper Bound: Best case
// (Fractional Knapsack)
float ub;
// Lower Bound: Worst case (0/1)
float lb;
// Level of the node
// in the decision tree
int level;
// Stores if the current item is
// selected or not
bool flag;
// Total Value: Stores the sum of the
// values of the items included
float tv;
// Total Weight: Stores the sum of the
// weights of the items included
float tw;
} Node;
// Function to calculate upper bound
// (includes fractional part of the items)
float upper_bound(float tv, float tw,
int idx, vector<Item>& arr)
{
float value = tv;
float weight = tw;
for (int i = idx; i < size; i++) {
if (weight + arr[i].weight
<= capacity) {
weight += arr[i].weight;
value -= arr[i].value;
}
else {
value -= (float)(capacity
- weight)
/ arr[i].weight
* arr[i].value;
break;
}
}
return value;
}
// Function to calculate lower bound (doesn't
// include fractional part of the items)
float lower_bound(float tv, float tw,
int idx, vector<Item>& arr)
{
float value = tv;
float weight = tw;
for (int i = idx; i < size; i++) {
if (weight + arr[i].weight
<= capacity) {
weight += arr[i].weight;
value -= arr[i].value;
}
else {
break;
}
}
return value;
}
class comp {
public:
bool operator()(Node a, Node b)
{
return a.lb > b.lb;
}
};
void assign(Node& a, float ub, float lb,
int level, bool flag,
float tv, float tw)
{
a.ub = ub;
a.lb = lb;
a.level = level;
a.flag = flag;
a.tv = tv;
a.tw = tw;
}
void knapsack(vector<Item>& arr)
{
// Sort the items based on the
// profit/weight ratio
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(),
[&](Item& a, Item& b) {
return a.value / a.weight
> b.value / b.weight;
});
// min_lb -> Minimum lower bound
// of all the nodes explored
// final_lb -> Minimum lower bound
// of all the paths that reached
// the final level
float min_lb = 0, final_lb = INT_MAX;
// curr_path -> Boolean array to store
// at every index if the element is
// included or not
// final_path -> Boolean array to store
// the result of selection array when
// it reached the last level
bool curr_path[size], final_path[size];
// Priority queue to store the nodes
// based on lower bounds
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>,
comp>
pq;
Node current, left, right;
current.lb = current.ub = current.tw
= current.tv = current.level
= current.flag = 0;
// Insert a dummy node
pq.push(current);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
curr_path[i] = final_path[i]
= false;
while (!pq.empty()) {
current = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (current.ub > min_lb
|| current.ub >= final_lb) {
// If the current node's best case
// value is not optimal than min_lb,
// then there is no reason to explore
// that path including final_lb
// eliminates all those paths whose
// best values is equal to final_lb
continue;
}
// update the path
if (current.level != 0)
curr_path[current.level - 1]
= current.flag;
if (current.level == size) {
// Reached last level
if (current.lb < final_lb)
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
final_path[arr[i].idx]
= curr_path[i];
final_lb = min(current.lb, final_lb);
continue;
}
int level = current.level;
// right node -> Excludes current item
// Hence, cp, cw will obtain the value
// of that of parent
assign(right,
upper_bound(current.tv,
current.tw, level + 1,
arr),
lower_bound(current.tv, current.tw,
level + 1, arr),
level + 1, false,
current.tv, current.tw);
// Check whether adding the current
// item will not exceed the knapsack weight
if (current.tw + arr[current.level].weight
<= capacity) {
// left node -> includes current item
// c and lb should be calculated
// including the current item.
left.ub
= upper_bound(
current.tv
- arr[level].value,
current.tw
+ arr[level].weight,
level + 1, arr);
left.lb
= lower_bound(
current.tv
- arr[level].value,
current.tw
+ arr[level].weight,
level + 1, arr);
assign(left, left.ub, left.lb,
level + 1, true,
current.tv - arr[level].value,
current.tw
+ arr[level].weight);
}
// If Left node cannot be inserted
else {
// Stop the left node from
// getting added to the
// priority queue
left.ub = left.lb = 1;
}
// Update the lower bound
min_lb = min(min_lb, left.lb);
min_lb = min(min_lb, right.lb);
// Exploring nodes whose
// upper bound is greater than
// min_lb will never give
// the optimal result
if (min_lb >= left.ub)
pq.push(left);
if (min_lb >= right.ub)
pq.push(right);
}
cout << "Items taken into the"
<< " knapsack are : \n";
if (final_lb == INT_MAX)
final_lb = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << final_path[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
cout << "Maximum profit is : "
<< (-final_lb) << "\n";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
size = 4;
capacity = 15;
vector<Item> arr;
arr.push_back({ 2, 10, 0 });
arr.push_back({ 4, 10, 1 });
arr.push_back({ 6, 12, 2 });
arr.push_back({ 9, 18, 3 });
knapsack(arr);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to implement
// 0/1 knapsack using LC
// Branch and Bound
import java.util.*;
class Item {
// Stores the weight
// of items
float weight;
// Stores the values
// of items
int value;
// Stores the index
// of items
int idx;
public Item() {}
public Item(int value, float weight,
int idx)
{
this.value = value;
this.weight = weight;
this.idx = idx;
}
}
class Node {
// Upper Bound: Best case
// (Fractional Knapsack)
float ub;
// Lower Bound: Worst case
// (0/1)
float lb;
// Level of the node in
// the decision tree
int level;
// Stores if the current
// item is selected or not
boolean flag;
// Total Value: Stores the
// sum of the values of the
// items included
float tv;
// Total Weight: Stores the sum of
// the weights of included items
float tw;
public Node() {}
public Node(Node cpy)
{
this.tv = cpy.tv;
this.tw = cpy.tw;
this.ub = cpy.ub;
this.lb = cpy.lb;
this.level = cpy.level;
this.flag = cpy.flag;
}
}
// Comparator to sort based on lower bound
class sortByC implements Comparator<Node> {
public int compare(Node a, Node b)
{
boolean temp = a.lb > b.lb;
return temp ? 1 : -1;
}
}
class sortByRatio implements Comparator<Item> {
public int compare(Item a, Item b)
{
boolean temp = (float)a.value
/ a.weight
> (float)b.value
/ b.weight;
return temp ? -1 : 1;
}
}
class knapsack {
private static int size;
private static float capacity;
// Function to calculate upper bound
// (includes fractional part of the items)
static float upperBound(float tv, float tw,
int idx, Item arr[])
{
float value = tv;
float weight = tw;
for (int i = idx; i < size; i++) {
if (weight + arr[i].weight
<= capacity) {
weight += arr[i].weight;
value -= arr[i].value;
}
else {
value -= (float)(capacity
- weight)
/ arr[i].weight
* arr[i].value;
break;
}
}
return value;
}
// Calculate lower bound (doesn't
// include fractional part of items)
static float lowerBound(float tv, float tw,
int idx, Item arr[])
{
float value = tv;
float weight = tw;
for (int i = idx; i < size; i++) {
if (weight + arr[i].weight
<= capacity) {
weight += arr[i].weight;
value -= arr[i].value;
}
else {
break;
}
}
return value;
}
static void assign(Node a, float ub, float lb,
int level, boolean flag,
float tv, float tw)
{
a.ub = ub;
a.lb = lb;
a.level = level;
a.flag = flag;
a.tv = tv;
a.tw = tw;
}
public static void solve(Item arr[])
{
// Sort the items based on the
// profit/weight ratio
Arrays.sort(arr, new sortByRatio());
Node current, left, right;
current = new Node();
left = new Node();
right = new Node();
// min_lb -> Minimum lower bound
// of all the nodes explored
// final_lb -> Minimum lower bound
// of all the paths that reached
// the final level
float minLB = 0, finalLB
= Integer.MAX_VALUE;
current.tv = current.tw = current.ub
= current.lb = 0;
current.level = 0;
current.flag = false;
// Priority queue to store elements
// based on lower bounds
PriorityQueue<Node> pq
= new PriorityQueue<Node>(
new sortByC());
// Insert a dummy node
pq.add(current);
// curr_path -> Boolean array to store
// at every index if the element is
// included or not
// final_path -> Boolean array to store
// the result of selection array when
// it reached the last level
boolean currPath[] = new boolean[size];
boolean finalPath[] = new boolean[size];
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
current = pq.poll();
if (current.ub > minLB
|| current.ub >= finalLB) {
// if the current node's best case
// value is not optimal than minLB,
// then there is no reason to
// explore that node. Including
// finalLB eliminates all those
// paths whose best values is equal
// to the finalLB
continue;
}
if (current.level != 0)
currPath[current.level - 1]
= current.flag;
if (current.level == size) {
if (current.lb < finalLB) {
// Reached last level
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
finalPath[arr[i].idx]
= currPath[i];
finalLB = current.lb;
}
continue;
}
int level = current.level;
// right node -> Excludes current item
// Hence, cp, cw will obtain the value
// of that of parent
assign(right, upperBound(current.tv,
current.tw,
level + 1, arr),
lowerBound(current.tv, current.tw,
level + 1, arr),
level + 1, false,
current.tv, current.tw);
if (current.tw + arr[current.level].weight
<= capacity) {
// left node -> includes current item
// c and lb should be calculated
// including the current item.
left.ub = upperBound(
current.tv
- arr[level].value,
current.tw
+ arr[level].weight,
level + 1, arr);
left.lb = lowerBound(
current.tv
- arr[level].value,
current.tw
+ arr[level].weight,
level + 1,
arr);
assign(left, left.ub, left.lb,
level + 1, true,
current.tv - arr[level].value,
current.tw
+ arr[level].weight);
}
// If the left node cannot
// be inserted
else {
// Stop the left node from
// getting added to the
// priority queue
left.ub = left.lb = 1;
}
// Update minLB
minLB = Math.min(minLB, left.lb);
minLB = Math.min(minLB, right.lb);
if (minLB >= left.ub)
pq.add(new Node(left));
if (minLB >= right.ub)
pq.add(new Node(right));
}
System.out.println("Items taken"
+ "into the knapsack are");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (finalPath[i])
System.out.print("1 ");
else
System.out.print("0 ");
}
System.out.println("\nMaximum profit"
+ " is " + (-finalLB));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
size = 4;
capacity = 15;
Item arr[] = new Item[size];
arr[0] = new Item(10, 2, 0);
arr[1] = new Item(10, 4, 1);
arr[2] = new Item(12, 6, 2);
arr[3] = new Item(18, 9, 3);
solve(arr);
}
}
Items taken into the knapsack are : 1 1 0 1 Maximum profit is : 38
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por udaykumar12381 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA