Dado un número entero N que denota un tablero de ajedrez N * N , la tarea es contar el número de formas de colocar dos reinas en el tablero de modo que no se ataquen entre sí.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 9
Salida: 2184
Explicación:
Hay 2184 formas de colocar dos reinas en un tablero de ajedrez de 9 * 9.
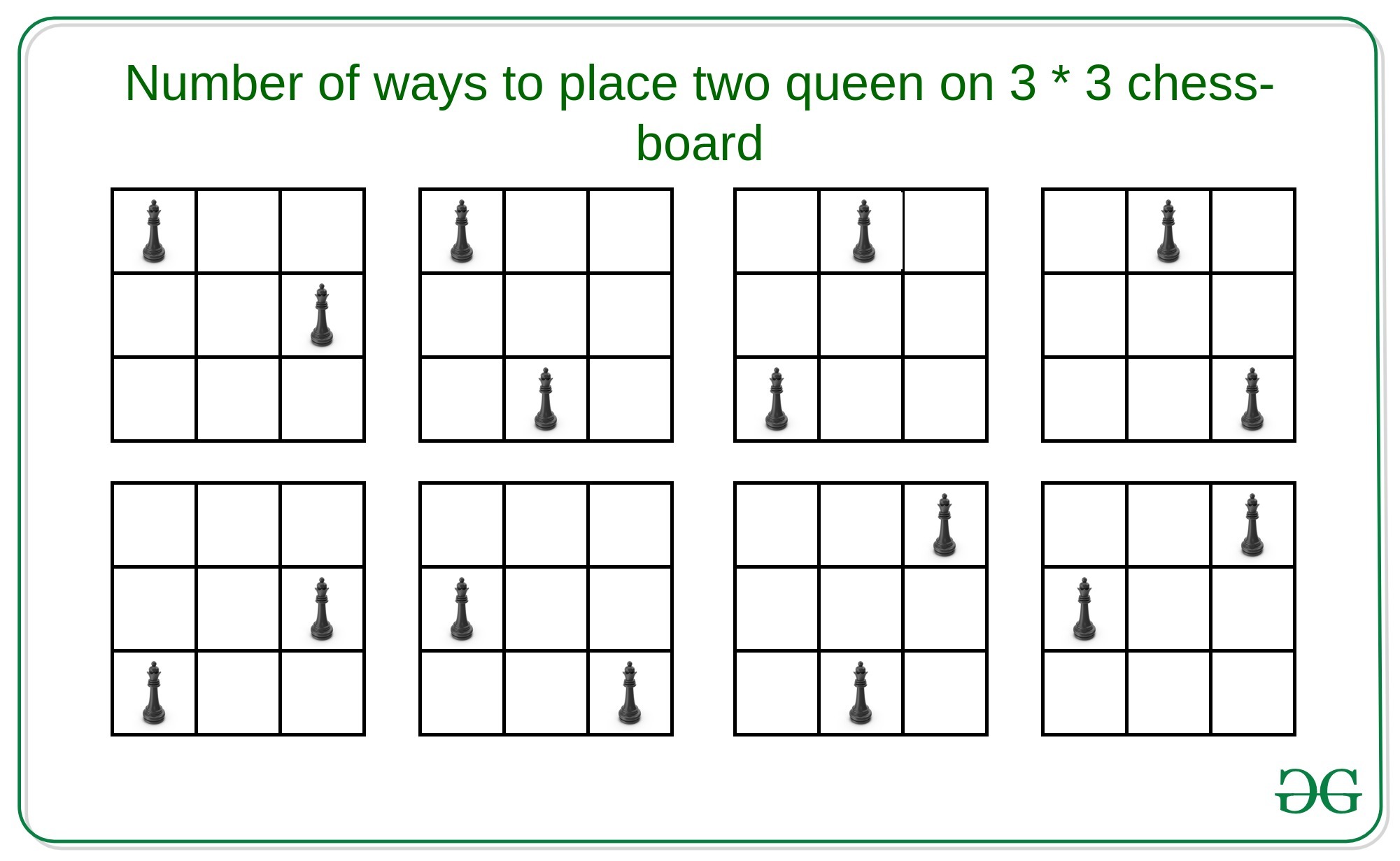
Entrada: N = 3
Salida: 8
Explicación:
Hay 8 formas de colocar dos reinas en un tablero de ajedrez de 3 * 3.
Enfoque ingenuo: una solución simple será elegir dos de cada posición posible para las dos reinas en la array N * N y verificar que no estén en horizontal, vertical, diagonal positiva o diagonal negativa. En caso afirmativo, incremente el conteo en 1.
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N 4 )
Enfoque eficiente: La idea es usar combinaciones para calcular las posibles posiciones de las reinas de modo que no se ataquen entre sí. Una observación útil es que es bastante fácil calcular el número de posiciones que ataca una sola dama. Eso es –
Number of positions a queen attack =
(N - 1) + (N - 1) + (D - 1)
Here,
// First N-1 denotes positions in horizontal direction
// Second N-1 denotes positions in vertical direction
// D = Number of positions in
positive and negative diagonal
Si no colocamos la reina en la última fila y última columna, la respuesta será simplemente el número de posiciones a colocar en un tablero de ajedrez ![]() , mientras que si colocamos en la última columna y última fila, las posiciones posibles para las reinas serán
, mientras que si colocamos en la última columna y última fila, las posiciones posibles para las reinas serán ![]() y atacando en las
y atacando en las ![]() posiciones. Por lo tanto, las posiciones posibles para la otra reina para cada posición de la reina serán
posiciones. Por lo tanto, las posiciones posibles para la otra reina para cada posición de la reina serán ![]() . Finalmente, hay
. Finalmente, hay ![]() combinaciones donde ambas reinas están en la última fila y última columna. Por tanto, la relación de recurrencia será:
combinaciones donde ambas reinas están en la última fila y última columna. Por tanto, la relación de recurrencia será:
// By Induction
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// number of ways to place two
// queens on the N * N chess board
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
// Function to find number of valid
// positions for two queens in the
// N * N chess board
ll possiblePositions(ll n)
{
ll term1 = pow(n, 4);
ll term2 = pow(n, 3);
ll term3 = pow(n, 2);
ll term4 = n / 3;
ll ans = (ceil)(term1) / 2 -
(ceil)(5 * term2) / 3 +
(ceil)(3 * term3) / 2 - term4;
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
ll n;
n = 3;
// Function Call
ll ans = possiblePositions(n);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find the
// number of ways to place two
// queens on the N * N chess board
class GFG{
// Function to find number of valid
// positions for two queens in the
// N * N chess board
static double possiblePositions(double n)
{
double term1 = Math.pow(n, 4);
double term2 = Math.pow(n, 3);
double term3 = Math.pow(n, 2);
double term4 = n / 3;
double ans = (Math.ceil(term1 / 2)) -
(Math.ceil(5 * term2) / 3) +
(Math.ceil(3 * term3) / 2) - term4;
return (long)ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double n;
n = 3;
// Function Call
double ans = possiblePositions(n);
System.out.print(ans + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the # number of ways to place two # queens on the N * N chess board import math # Function to find number of valid # positions for two queens in the # N * N chess board def possiblePositions(n): term1 = pow(n, 4); term2 = pow(n, 3); term3 = pow(n, 2); term4 = n / 3; ans = ((math.ceil(term1)) / 2 - (math.ceil(5 * term2)) / 3 + (math.ceil(3 * term3)) / 2 - term4); return ans; # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': n = 3 # Function call ans = possiblePositions(n) print(int(ans)) # This code is contributed by jana_sayantan
C#
// C# implementation to find the
// number of ways to place two
// queens on the N * N chess board
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find number of valid
// positions for two queens in the
// N * N chess board
static double possiblePositions(double n)
{
double term1 = Math.Pow(n, 4);
double term2 = Math.Pow(n, 3);
double term3 = Math.Pow(n, 2);
double term4 = n / 3;
double ans = (Math.Ceiling(term1 / 2)) -
(Math.Ceiling(5 * term2) / 3) +
(Math.Ceiling(3 * term3) / 2) - term4;
return (long)ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
double n;
n = 3;
// Function Call
double ans = possiblePositions(n);
Console.Write(ans + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to find the
// number of ways to place two
// queens on the N * N chess board
// Function to find number of valid
// positions for two queens in the
// N * N chess board
function possiblePositions(n)
{
let term1 = Math.pow(n, 4);
let term2 = Math.pow(n, 3);
let term3 = Math.pow(n, 2);
let term4 = n / 3;
let ans = (Math.ceil(term1 / 2)) -
(Math.ceil(5 * term2) / 3) +
(Math.ceil(3 * term3) / 2) - term4;
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
let n;
n = 3;
// Function Call
let ans = possiblePositions(n);
document.write(Math.floor(ans));
// This code is contributed by souravghosh0416.
</script>
8
Complejidad de tiempo: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por mridulkumar y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA