Dado un número N que es el tamaño del conjunto y un número K , la tarea es encontrar el número de subconjuntos, del conjunto de N elementos, que tiene como máximo K elementos, es decir, el tamaño del subconjunto es menor que o igual a K.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 3, K = 2
Salida: 6
Subconjuntos con 1 elemento en él = {1}, {2}, {3}
Subconjuntos con 2 elementos en él = {1, 2}, {1, 3}, { 1, 2}
Dado que K = 2, solo los subconjuntos anteriores se considerarán para la longitud como máximo K. Por lo tanto, el recuento es 6.
Entrada: N = 5, K = 2
Salida: 15
Acercarse:
- Dado que el número de subconjuntos de exactamente K elementos que se pueden hacer a partir de N elementos es ( N C K ). Por lo tanto, para «como máximo», el conteo requerido será
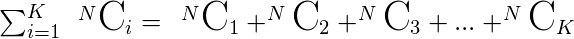
- Para calcular el valor de N C K , se usa el Coeficiente Binomial . Consulte este artículo para ver cómo funciona .
- Entonces, para obtener los subconjuntos requeridos para una longitud máxima de K, ejecute un ciclo de 1 a K y agregue N C i para cada valor de i.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ code to find total number of
// Subsets of size at most K
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to compute the value
// of Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int C[n + 1][k + 1];
int i, j;
// Calculate value of Binomial Coefficient
// in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= min(i, k); j++) {
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i][j] = 1;
// Calculate value using previously
// stored values
else
C[i][j] = C[i - 1][j - 1] + C[i - 1][j];
}
}
return C[n][k];
}
// Function to calculate sum of
// nCj from j = 1 to k
int count(int n, int k)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
// Calling the nCr function
// for each value of j
sum = sum + binomialCoeff(n, j);
}
return sum;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 3, k = 2;
cout << count(n, k) << endl;
n = 5, k = 2;
cout << count(n, k) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code to find total number of
// Subsets of size at most K
import java.lang.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to compute the value
// of Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
public static int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int[][] C = new int[n + 1][k + 1];
int i, j;
// Calculate value of Binomial Coefficient
// in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= Math.min(i, k); j++)
{
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i][j] = 1;
// Calculate value using previously
// stored values
else
C[i][j] = C[i - 1][j - 1] + C[i - 1][j];
}
}
return C[n][k];
}
// Function to calculate sum of
// nCj from j = 1 to k
public static int count(int n, int k)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
{
// Calling the nCr function
// for each value of j
sum = sum + binomialCoeff(n, j);
}
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
GFG g = new GFG();
int n = 3, k = 2;
System.out.print(count(n, k));
int n1 = 5, k1 = 2;
System.out.print(count(n1, k1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondal
Python3
# Python code to find total number of # Subsets of size at most K # Function to compute the value # of Binomial Coefficient C(n, k) def binomialCoeff(n, k): C = [[0 for i in range(k + 1)] for j in range(n + 1)]; i, j = 0, 0; # Calculate value of Binomial Coefficient # in bottom up manner for i in range(n + 1): for j in range( min(i, k) + 1): # Base Cases if (j == 0 or j == i): C[i][j] = 1; # Calculate value using previously # stored values else: C[i][j] = C[i - 1][j - 1] + C[i - 1][j]; return C[n][k]; # Function to calculate sum of # nCj from j = 1 to k def count(n, k): sum = 0; for j in range(1, k+1): # Calling the nCr function # for each value of j sum = sum + binomialCoeff(n, j); return sum; # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': n = 3; k = 2; print(count(n, k), end=""); n1 = 5; k1 = 2; print(count(n1, k1)); # This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
C#
// C# code to find total number of
// Subsets of size at most K
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to compute the value
// of Binomial Coefficient C(n, k)
public static int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int[,] C = new int[n + 1, k + 1];
int i, j;
// Calculate value of Binomial Coefficient
// in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= Math.Min(i, k); j++)
{
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i, j] = 1;
// Calculate value using previously
// stored values
else
C[i, j] = C[i - 1, j - 1] + C[i - 1, j];
}
}
return C[n, k];
}
// Function to calculate sum of
// nCj from j = 1 to k
public static int count(int n, int k)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
{
// Calling the nCr function
// for each value of j
sum = sum + binomialCoeff(n, j);
}
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 3, k = 2;
Console.Write(count(n, k));
int n1 = 5, k1 = 2;
Console.Write(count(n1, k1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the
// above approach
// Function for the binomial coefficient
function binomialCoeff(n, k)
{
var C = new Array(n + 1);
// Loop to create 2D array using 1D array
for (var i = 0; i < C.length; i++) {
C[i] = new Array(k + 1);
}
var i, j;
// Calculate value of Binomial Coefficient
// in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= Math.min(i, k); j++) {
// Base Cases
if (j == 0 || j == i)
C[i][j] = 1;
// Calculate value using previously
// stored values
else
C[i][j] = C[i - 1][j - 1] + C[i - 1][j];
}
}
return C[n][k];
}
// Function to calculate sum of
// nCj from j = 1 to k
function count(n, k)
{
var sum = 0;
for (var j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
// Calling the nCr function
// for each value of j
sum = sum + binomialCoeff(n, j);
}
return sum;
}
// Driver code
var n = 3;
var k = 2;
document.write(count(n, k));
var n = 5;
var k = 2;
document.write(count(n, k));
// This code is contributed by ShubhamSingh10
</script>
Producción
6 15
Complejidad temporal: O(n 2 * k)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n + k)