Los números de Euler Zigzag son una secuencia de números enteros que es un número de arreglos de esos números de modo que cada entrada sea alternativamente mayor o menor que la entrada anterior.
c1, c2, c3, c4 es una permutación alterna donde
c1 < c2
c3 < c2
c3 < c4… los
números en zigzag son los siguientes 1, 1, 1, 2, 5, 16, 61, 272, 1385, 7936, 50521 ……
Para un entero N dado. La tarea es imprimir una secuencia de hasta N términos.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 10
Salida: 1 1 1 2 5 16 61 272 1385 7936
Entrada: N = 14
Salida: 1 1 1 2 5 16 61 272 1385 7936 50521 353792 2702765 22368256
Enfoque:
El número de zigzag (n+1) es: 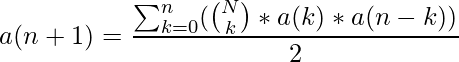
Encontraremos el factorial hasta n y los almacenaremos en una array y también crearemos una segunda array para almacenar el i-ésimo número de zigzag y aplicaremos la fórmula indicada anteriormente para encontrar todos los n números en zigzag.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// CPP program to find zigzag sequence
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print first n zigzag numbers
void ZigZag(int n)
{
// To store factorial and n'th zig zag number
long long fact[n + 1], zig[n + 1] = { 0 };
// Initialize factorial upto n
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
// Set first two zig zag numbers
zig[0] = 1;
zig[1] = 1;
cout << "zig zag numbers: ";
// Print first two zig zag number
cout << zig[0] << " " << zig[1] << " ";
// Print the rest zig zag numbers
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
long long sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k <= i - 1; k++)
{
// Binomial(n, k)*a(k)*a(n-k)
sum += (fact[i - 1]/(fact[i - 1 - k]*fact[k]))
*zig[k] * zig[i - 1 - k];
}
// Store the value
zig[i] = sum / 2;
// Print the number
cout << sum / 2 << " ";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 10;
// Function call
ZigZag(n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find zigzag sequence
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to print first n zigzag numbers
static void ZigZag(int n)
{
// To store factorial and n'th zig zag number
long[] fact= new long[n + 1];
long[] zig = new long[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
zig[i] = 0;
// Initialize factorial upto n
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
// Set first two zig zag numbers
zig[0] = 1;
zig[1] = 1;
System.out.print("zig zag numbers: ");
// Print first two zig zag number
System.out.print(zig[0] + " " + zig[1] + " ");
// Print the rest zig zag numbers
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
long sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k <= i - 1; k++)
{
// Binomial(n, k)*a(k)*a(n-k)
sum += (fact[i - 1] / (fact[i - 1 - k] *
fact[k])) * zig[k] * zig[i - 1 - k];
}
// Store the value
zig[i] = sum / 2;
// Print the number
System.out.print(sum / 2 + " " );
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
throws java.lang.Exception
{
int n = 10;
// Function call
ZigZag(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by nidhiva
Python3
# Python3 program to find zigzag sequence
# Function to print first n zigzag numbers
def ZigZag(n):
# To store factorial and
# n'th zig zag number
fact = [0 for i in range(n + 1)]
zig = [0 for i in range(n + 1)]
# Initialize factorial upto n
fact[0] = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i
# Set first two zig zag numbers
zig[0] = 1
zig[1] = 1
print("zig zag numbers: ", end = " ")
# Print first two zig zag number
print(zig[0], zig[1], end = " ")
# Print the rest zig zag numbers
for i in range(2, n):
sum = 0
for k in range(0, i):
# Binomial(n, k)*a(k)*a(n-k)
sum += ((fact[i - 1] //
(fact[i - 1 - k] * fact[k])) *
zig[k] * zig[i - 1 - k])
# Store the value
zig[i] = sum // 2
# Print the number
print(sum // 2, end = " ")
# Driver code
n = 10
# Function call
ZigZag(n)
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar
C#
// C# program to find zigzag sequence
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to print first n zigzag numbers
static void ZigZag(int n)
{
// To store factorial and n'th zig zag number
long[] fact= new long[n + 1];
long[] zig = new long[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
zig[i] = 0;
// Initialize factorial upto n
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
// Set first two zig zag numbers
zig[0] = 1;
zig[1] = 1;
Console.Write("zig zag numbers: ");
// Print first two zig zag number
Console.Write(zig[0] + " " + zig[1] + " ");
// Print the rest zig zag numbers
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
long sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k <= i - 1; k++)
{
// Binomial(n, k)*a(k)*a(n-k)
sum += (fact[i - 1] / (fact[i - 1 - k] *
fact[k])) * zig[k] * zig[i - 1 - k];
}
// Store the value
zig[i] = sum / 2;
// Print the number
Console.Write(sum / 2 + " " );
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
int n = 10;
// Function call
ZigZag(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to find zigzag sequence
// Function to print first n zigzag numbers
function ZigZag(n)
{
// To store factorial and n'th zig zag number
var fact = Array(n+1).fill(0);
var zig = Array(n+1).fill(0);
// Initialize factorial upto n
fact[0] = 1;
for (var i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
// Set first two zig zag numbers
zig[0] = 1;
zig[1] = 1;
document.write( "zig zag numbers: ");
// Print first two zig zag number
document.write( zig[0] + " " + zig[1] + " ");
// Print the rest zig zag numbers
for (var i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
var sum = 0;
for (var k = 0; k <= i - 1; k++)
{
// Binomial(n, k)*a(k)*a(n-k)
sum += parseInt(fact[i - 1]/(fact[i - 1 - k]*fact[k]))
*zig[k] * zig[i - 1 - k];
}
// Store the value
zig[i] = parseInt(sum / 2);
// Print the number
document.write( parseInt(sum / 2) + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
var n = 10;
// Function call
ZigZag(n);
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
</script>
Producción:
zig zag numbers: 1 1 1 2 5 16 61 272 1385 7936
Complejidad temporal: O(n 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n)
Referencia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alternating_permutation
https://oeis.org/A000111
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por andrew1234 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA