En este artículo, se analizan dos tipos de Radix Sort :
- LSD Radix Sort: comienza a clasificar desde el final de las strings (el dígito menos significativo ).
- MSD Radix Sort: comienza a ordenar desde el principio de las strings (el dígito más significativo ).
En este artículo, la tarea es discutir el MSD Radix Sort y compararlo con el LSD Radix Sort.
Planteamiento: La idea es realizar los siguientes pasos para cada dígito i donde el valor de i varía del dígito más significativo al dígito menos significativo:
- Almacene elementos en diferentes cubos de acuerdo con su i- ésimo dígito.
- Ordene recursivamente cada cubo que tenga más de un elemento.
Clasificación Radix de dígitos más vs. menos significativos :
- La idea es ordenar los enteros de longitud fija, MSD es más eficiente que LSD porque es posible que no tenga que examinar cada dígito de cada entero:
LSD Radix Clasificación:
Ordenación Radix MSD :
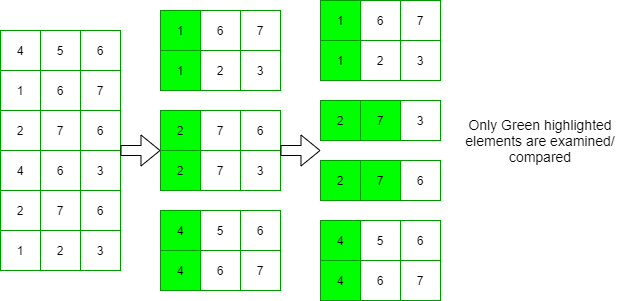
Clasificación MSD Radix
- MSD se puede utilizar para ordenar strings de longitud variable, a diferencia de LSD. LSD tiene que ser estable para funcionar correctamente, pero MSD puede hacerse estable o inestable y MSD puede funcionar con strings aleatorias.
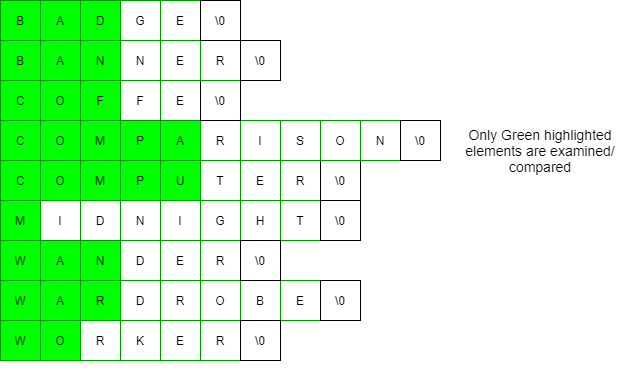
MSD Radix ordenar string de longitud variable
- Complejidad del tiempo:
- LSD Radix sort: la complejidad temporal en el mejor y el peor de los casos es O(N*M) donde M = longitud de la string más larga.
Clasificación MSD Radix: la complejidad temporal del mejor caso es O(N) y la complejidad temporal del peor caso es O(N*M) donde M = la longitud media de las strings.
- LSD Radix sort: la complejidad temporal en el mejor y el peor de los casos es O(N*M) donde M = longitud de la string más larga.
- Espacio Auxiliar:
- LSD Radix tipo: O (N + B)
- MSD Radix sort: O(N + MB ), donde M = longitud de la string más larga y B = tamaño de la raíz (B=10 números posibles o B=256 caracteres o B=2 para binario).
- MSD usa recursividad , por lo que requiere más espacio que LSD. Esto significa que MSD es mucho más lento que LSD cuando se trabaja con pocas entradas.
Implementación de MSD Radix Sort :
Uso de lista enlazada : esta implementación es para números enteros que usan lista enlazada. Una array de longitud fija para cada Node requerirá una gran cantidad de almacenamiento.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de MSD Radix Sort usando una lista enlazada:
C++
// C++ program for the implementation
// of MSD Radix Sort using linked list
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Linked list node structure
struct node {
vector<int> arr;
struct node* nxt[10];
};
// Function to create a new node of
// the Linked List
struct node* new_node(void)
{
struct node* tempNode = new node;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
tempNode->nxt[i] = NULL;
}
// Return the created node
return tempNode;
}
// Function to sort the given array
// using MSD Radix Sort recursively
void msd_sort(struct node* root, int exp,
vector<int>& sorted_arr)
{
if (exp <= 0) {
return;
}
int j;
// Stores the numbers in different
// buckets according their MSD
for (int i = 0;
i < root->arr.size();
i++) {
// Get the MSD in j
j = (root->arr[i] / exp) % 10;
// If j-th index in the node
// array is empty create and
// link a new node in index
if (root->nxt[j] == NULL) {
root->nxt[j] = new_node();
}
// Store the number in j-th node
root->nxt[j]->arr.push_back(
root->arr[i]);
}
// Sort again every child node that
// has more than one number
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// If root->next is NULL
if (root->nxt[i] != NULL) {
if (root->nxt[i]->arr.size()
> 1) {
// Sort recursively
msd_sort(root->nxt[i],
exp / 10,
sorted_arr);
}
// If any node have only
// one number then it means
// the number is sorted
else {
sorted_arr.push_back(
root->nxt[i]->arr[0]);
}
}
}
}
// Function to calculate the MSD of the
// maximum value in the array
int get_max_exp(vector<int> arr)
{
// Stores the maximum element
int mx = arr[0];
// Traverse the given array
for (int i = 1; i < arr.size(); i++) {
// Update the value of maximum
if (arr[i] > mx) {
mx = arr[i];
}
}
int exp = 1;
while (mx > 10) {
mx /= 10;
exp *= 10;
}
// Return the resultant value
return exp;
}
// Function to print an array
void print(vector<int> arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// create the root node
struct node* root = new_node();
// Stores the unsorted array
// in the root node
root->arr.insert(root->arr.end(),
{ 9330, 9950, 718,
8977, 6790, 95,
9807, 741, 8586,
5710 });
cout << "Unsorted array : ";
// Print the unsorted array
print(root->arr);
// Find the optimal longest exponent
int exp = get_max_exp(root->arr);
// Stores the sorted numbers
vector<int> sorted_arr;
// Function Call
msd_sort(root, exp, sorted_arr);
cout << "Sorted array : ";
// Print the sorted array
print(sorted_arr);
return 0;
}
C
// C program for the implementation
// of MSD Radix Sort using linked list
// Linked list node structure
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // For using malloc
#include <string.h> // For using memset
// Output array filled length
int sorted_array_length = 0;
struct node {
int arr[100];
int arr_length;
struct node* nxt[10];
};
// Function to create a new node of
// the Linked List
struct node* new_node(void)
{
struct node* tempNode
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
tempNode->arr_length = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
tempNode->nxt[i] = NULL;
}
// Return the created node
return tempNode;
}
// Function to sort the given array
// using MSD Radix Sort recursively
void msd_sort(struct node* root, int exp, int* sorted_arr)
{
if (exp <= 0) {
return;
}
int j;
// Stores the numbers in different
// buckets according their MSD
for (int i = 0; i < root->arr_length; i++) {
// Get the MSD in j
j = (root->arr[i] / exp) % 10;
// If j-th index in the node
// array is empty create and
// link a new node in index
if (root->nxt[j] == NULL) {
root->nxt[j] = new_node();
}
// Store the number in j-th node
root->nxt[j]->arr[root->nxt[j]->arr_length++]
= root->arr[i];
}
// Sort again every child node that
// has more than one number
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// If root->next is NULL
if (root->nxt[i] != NULL) {
if (root->nxt[i]->arr_length > 1) {
// Sort recursively
msd_sort(root->nxt[i], exp / 10,
sorted_arr);
}
// If any node have only
// one number then it means
// the number is sorted
else {
sorted_arr[sorted_array_length++]
= root->nxt[i]->arr[0];
}
}
}
}
// Function to calculate the MSD of the
// maximum value in the array
int get_max_exp(int* arr, int n)
{
// Stores the maximum element
int mx = arr[0];
// Traverse the given array
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// Update the value of maximum
if (arr[i] > mx) {
mx = arr[i];
}
}
int exp = 1;
while (mx > 10) {
mx /= 10;
exp *= 10;
}
// Return the resultant value
return exp;
}
// Function to print an array
void print(int* arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Unsorted array
int array[] = { 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790,
95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 };
// Input array length
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
// create the root node
struct node* root = new_node();
// Stores the unsorted array
// in the root node and
// set arr_length
memcpy(root->arr, array, sizeof(array));
root->arr_length = n;
printf("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(root->arr, n);
// Find the optimal longest exponent
int exp = get_max_exp(root->arr, root->arr_length);
// Stores the sorted numbers
int output[n];
int* sorted_arr = &output[0];
// Function Call
msd_sort(root, exp, sorted_arr);
printf("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(sorted_arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of MSD Radix Sort
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// A utility function to print an array
static void print(int[] arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// A utility function to get the digit
// at index d in a integer
static int digit_at(int x, int d)
{
return (int)(x / Math.pow(10, d - 1)) % 10;
}
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
static int[] MSD_sort(int[] arr, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return arr;
}
int count[] = new int[10 + 2];
// temp is created to easily swap Strings in arr[]
HashMap<Integer,Integer> temp = new HashMap<>();
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each integer in count[]
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count[] so that count[] now contains actual
// position of this digits in temp[]
for (int r = 0; r < 10 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
if(temp.containsKey(count+1))
temp.put(count++, arr[i]);
else
temp.put(count++, arr[i]);
}
// Copy all integers of temp to arr[], so that arr[] now
// contains partially sorted integers
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
if(temp.containsKey(i-lo))
arr[i] = temp.get(i - lo);
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// integers set to sort them by their next digit
for (int r = 0; r < 10; r++)
arr = MSD_sort(arr, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1,
d - 1);
return arr;
}
// function find the largest integer
static int getMax(int arr[], int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// Main function to call MSD_sort
static int[] radixsort(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// get the length of the largest integer
int d = (int)Math.floor(Math.log10(Math.abs(m))) + 1;
// function call
return MSD_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, d);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input array
int arr[] = { 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790,
95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 };
// Size of the array
int n = arr.length;
System.out.printf("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(arr, n);
// Function Call
arr = radixsort(arr, n);
System.out.printf("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
C#
// C# implementation of MSD Radix Sort
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
// A utility function to print an array
static void print(int[] arr, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// A utility function to get the digit
// at index d in a integer
static int digit_at(int x, int d) {
return (int) (x / Math.Pow(10, d - 1)) % 10;
}
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
static int[] MSD_sort(int[] arr, int lo, int hi, int d) {
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return arr;
}
int []count = new int[10 + 2];
// temp is created to easily swap Strings in []arr
Dictionary<int, int> temp = new Dictionary<int, int>();
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each integer in []count
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change []count so that []count now contains actual
// position of this digits in []temp
for (int r = 0; r < 10 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
if (temp.ContainsKey(count + 1))
temp.Add(count++, arr[i]);
else
temp.Add(count++, arr[i]);
}
// Copy all integers of temp to []arr, so that []arr now
// contains partially sorted integers
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
if (temp.ContainsKey(i - lo))
arr[i] = temp[i - lo];
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// integers set to sort them by their next digit
for (int r = 0; r < 10; r++)
arr = MSD_sort(arr, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1, d - 1);
return arr;
}
// function find the largest integer
static int getMax(int []arr, int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// Main function to call MSD_sort
static int[] radixsort(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// get the length of the largest integer
int d = (int) Math.Floor(Math.Log10(Math.Abs(m))) + 1;
// function call
return MSD_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, d);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input array
int []arr = { 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790, 95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 };
// Size of the array
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(arr, n);
// Function Call
arr = radixsort(arr, n);
Console.Write("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// javascript implementation of MSD Radix Sort
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
// A utility function to print an array
function print(arr , n) {
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
document.write();
}
// A utility function to get the digit
// at index d in a integer
function digit_at(x , d) {
return parseInt( x / Math.pow(10, d - 1)) % 10;
}
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
function MSD_sort(arr , lo , hi , d) {
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return arr;
}
var count = Array(10 + 2).fill(0);
// temp is created to easily swap Strings in arr
var temp = new Map();
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each integer in count
for (var i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
var c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count so that count now contains actual
// position of this digits in temp
for (var r = 0; r < 10 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
var c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
if (temp.has(count + 1))
temp.set(count++, arr[i]);
else
temp.set(count++, arr[i]);
}
// Copy all integers of temp to arr, so that arr now
// contains partially sorted integers
for (i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
if (temp.has(i - lo))
arr[i] = temp.get(i - lo);
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// integers set to sort them by their next digit
for (r = 0; r < 10; r++)
arr = MSD_sort(arr, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1, d - 1);
return arr;
}
// function find the largest integer
function getMax(arr , n) {
var mx = arr[0];
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// Main function to call MSD_sort
function radixsort(arr , n) {
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
var m = getMax(arr, n);
// get the length of the largest integer
var d = parseInt( Math.floor(Math.log10(Math.abs(m)))) + 1;
// function call
return MSD_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, d);
}
// Driver Code
// Input array
var arr = [ 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790, 95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 ];
// Size of the array
var n = arr.length;
document.write("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(arr, n);
// Function Call
arr = radixsort(arr, n);
document.write("<br/>Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(arr, n);
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
Unsorted array : 9330 9950 718 8977 6790 95 9807 741 8586 5710 Sorted array : 95 718 741 5710 6790 8586 8977 9330 9807 9950
Uso del método Counting Sort(): esta implementación es para las strings basadas en el método Counting Sort() . Como el carácter ASCII de estilo C es de 1 byte . Por lo tanto, la array de tamaño 256 se usa para contar las ocurrencias de caracteres y ordena las strings lexicográficamente.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de MSD Radix Sort usando el método de conteo sort():
Para string:
C++
// C++ implementation of MSD Radix Sort
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// A utility function to print an array
void print(string* str, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// A utility function to get the ASCII value
// of the character at index d in a string
int char_at(string str, int d)
{
if (str.size() <= d)
return -1;
else
return str.at(d);
}
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
void MSD_sort(string* str, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return;
}
int count[256 + 2] = { 0 };
// temp is created to easily swap strings in str[]
// int temp[n] can also be used but,
// it will take more space.
unordered_map<int, string> temp;
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each string in count[]
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count[] so that count[] now contains actual
// position of this digits in temp[]
for (int r = 0; r < 256 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
temp[count++] = str[i];
}
// Copy all strings of temp to str[], so that str[] now
// contains partially sorted strings
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
str[i] = temp[i - lo];
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// strings set to sort them by their next character
for (int r = 0; r < 256; r++)
MSD_sort(str, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1,
d + 1);
}
int main()
{
string str[] = { "midnight", "badge", "bag",
"worker", "banner", "wander" };
int n = sizeof(str) / sizeof(str[0]);
cout << "Unsorted array : ";
// print the unsorted array
print(str, n);
// Function call
MSD_sort(str, 0, n - 1, 0);
cout << "Sorted array : ";
// print the sorted array
print(str, n);
return 0;
}
C
// C program for the implementation
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// A utility function to get the ASCII value
// of the character at index d in a string
int char_at(char* str, int d)
{
if (sizeof(str) / sizeof(str[0]) <= d)
return -1;
else
return str[d];
}
int n;
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
void MSD_sort(char** str, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo + 1) {
return;
}
int count[256 + 2] = { 0 };
// temp is created to easily swap strings in str[]
char temp[n][100];
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each string in count[]
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count[] so that count[] now contains actual
// position of this digits in temp[]
for (int r = 0; r < 256 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
memcpy(temp[count++], str[i],
strlen(str[i]) + 1);
}
// Copy all strings of temp to str[], so that str[] now
// contains partially sorted strings
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
str[i] = strdup(temp[i - lo]);
}
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// strings set to sort them by their next character
for (int r = 0; r < 256; r++)
MSD_sort(str, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1,
d + 1);
}
// Function to print an array
void print(char** str, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%s ", str[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input String
char* str[] = { (char*)"midnight", (char*)"badge",
(char*)"bag", (char*)"worker",
(char*)"banner", (char*)"wander" };
// Size of the string
n = sizeof(str) / sizeof(str[0]);
printf("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(str, n);
// Function Call
MSD_sort(str, 0, n - 1, 0);
printf("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(str, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Utility function to get the ASCII
// value of the character at index d
// in the string
static int char_at(String str, int d)
{
if (str.length() <= d)
return -1;
else
return (int)(str.charAt(d));
}
// Function to sort the array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
static void MSD_sort(String str[], int lo, int hi,
int d)
{
// Recursive break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return;
}
// Stores the ASCII Values
int count[] = new int[256 + 1];
// Temp is created to easily
// swap strings in str[]
HashMap<Integer, String> temp = new HashMap<>();
// Store the occurrences of the most
// significant character from
// each string in count[]
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count[] so that count[]
// now contains actual position
// of this digits in temp[]
for (int r = 0; r < 256; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
temp.put(count++, str[i]);
}
// Copy all strings of temp to str[],
// so that str[] now contains
// partially sorted strings
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
str[i] = temp.get(i - lo);
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each
// partially sorted strings set to
// sort them by their next character
for (int r = 0; r < 256; r++)
MSD_sort(str, lo + count[r],
lo + count[r + 1] - 1, d + 1);
}
// Function to print an array
static void print(String str[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(str[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input String
String str[] = { "midnight", "badge", "bag",
"worker", "banner", "wander" };
// Size of the string
int n = str.length;
System.out.print("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(str, n);
// Function Call
MSD_sort(str, 0, n - 1, 0);
System.out.print("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(str, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Utility function to get the ASCII
// value of the character at index d
// in the string
static int char_at(String str, int d)
{
if (str.Length <= d)
return -1;
else
return(int)(str[d]);
}
// Function to sort the array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
static void MSD_sort(String []str, int lo,
int hi, int d)
{
// Recursive break condition
if (hi <= lo)
{
return;
}
// Stores the ASCII Values
int []count = new int[256 + 1];
// Temp is created to easily
// swap strings in []str
Dictionary<int,
String> temp = new Dictionary<int,
String>();
// Store the occurrences of the most
// significant character from
// each string in []count
for(int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
{
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change []count so that []count
// now contains actual position
// of this digits in []temp
for(int r = 0; r < 256; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for(int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
{
int c = char_at(str[i], d);
temp.Add(count++, str[i]);
}
// Copy all strings of temp to []str,
// so that []str now contains
// partially sorted strings
for(int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
str[i] = temp[i - lo];
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each
// partially sorted strings set to
// sort them by their next character
for(int r = 0; r < 256; r++)
MSD_sort(str, lo + count[r],
lo + count[r + 1] - 1,
d + 1);
}
// Function to print an array
static void print(String []str, int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(str[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input String
String []str = { "midnight", "badge", "bag",
"worker", "banner", "wander" };
// Size of the string
int n = str.Length;
Console.Write("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(str, n);
// Function Call
MSD_sort(str, 0, n - 1, 0);
Console.Write("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(str, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Unsorted array : midnight badge bag worker banner wander Sorted array : badge bag banner midnight wander worker
Para entero:
C++
// C++ implementation of MSD Radix Sort
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// A utility function to print an array
void print(int* arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// A utility function to get the digit
// at index d in a integer
int digit_at(int x, int d)
{
return (int)(x / pow(10, d - 1)) % 10;
}
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
void MSD_sort(int* arr, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return;
}
int count[10 + 2] = { 0 };
// temp is created to easily swap strings in arr[]
unordered_map<int, int> temp;
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each integer in count[]
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count[] so that count[] now contains actual
// position of this digits in temp[]
for (int r = 0; r < 10 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
temp[count++] = arr[i];
}
// Copy all integers of temp to arr[], so that arr[] now
// contains partially sorted integers
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
arr[i] = temp[i - lo];
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// integers set to sort them by their next digit
for (int r = 0; r < 10; r++)
MSD_sort(arr, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1,
d - 1);
}
// function find the largest integer
int getMax(int arr[], int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// Main function to call MSD_sort
void radixsort(int* arr, int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// get the length of the largest integer
int d = floor(log10(abs(m))) + 1;
// function call
MSD_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, d);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input array
int arr[] = { 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790,
95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 };
// Size of the array
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(arr, n);
// Function Call
radixsort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(arr, n);
return 0;
}
C
// C program for the implementation
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// A utility function to print an array
void print(int* arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d, ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// A utility function to get the digit
// at index d in a integer
int digit_at(int x, int d)
{
return (int)(x / pow(10, d - 1)) % 10;
}
// array length
int n;
// function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
void MSD_sort(int* arr, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo || d < 1) {
return;
}
int count[10 + 2] = { 0 };
// temp is created to easily swap strings in arr[]
int temp[n];
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each integer in count[]
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count[] so that count[] now contains actual
// position of this digits in temp[]
for (int r = 0; r < 10 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
temp[count++] = arr[i];
}
// Copy all integer of temp to arr[], so that arr[] now
// contains partially sorted integers
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
arr[i] = temp[i - lo];
}
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// integers set to sort them by their next digit
for (int r = 0; r < 10; r++)
MSD_sort(arr, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1,
d - 1);
}
// function find the largest integer
int getMax(int arr[], int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// Main function to call MSD_sort
void radixsort(int* arr, int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// get the length of the largest integer
int d = floor(log10(abs(m))) + 1;
// function call
MSD_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, d);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input array
int arr[] = { 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790,
95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 };
// Size of the array
n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(arr, n);
// Function Call
radixsort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of MSD Radix Sort
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// A utility function to print an array
static void print(int[] arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// A utility function to get the digit
// at index d in a integer
static int digit_at(int x, int d)
{
return (int)(x / Math.pow(10, d - 1)) % 10;
}
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
static void MSD_sort(int[] arr, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return;
}
int count[] = new int[10 + 2];
// temp is created to easily swap Strings in arr[]
HashMap<Integer,Integer> temp = new HashMap<>();
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each integer in count[]
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change count[] so that count[] now contains actual
// position of this digits in temp[]
for (int r = 0; r < 10 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
temp.put(count++, arr[i]);
}
// Copy all integers of temp to arr[], so that arr[] now
// contains partially sorted integers
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
arr[i] = temp.get(i - lo);
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// integers set to sort them by their next digit
for (int r = 0; r < 10; r++)
MSD_sort(arr, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1,
d - 1);
}
// function find the largest integer
static int getMax(int arr[], int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// Main function to call MSD_sort
static void radixsort(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// get the length of the largest integer
int d = (int)Math.floor(Math.log10(Math.abs(m))) + 1;
// function call
MSD_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, d);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input array
int arr[] = { 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790,
95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 };
// Size of the array
int n = arr.length;
System.out.printf("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(arr, n);
// Function Call
radixsort(arr, n);
System.out.printf("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#
// C# implementation of MSD Radix Sort
// of MSD Radix Sort using counting sort()
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
// A utility function to print an array
static void print(int[] arr, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// A utility function to get the digit
// at index d in a integer
static int digit_at(int x, int d) {
return (int) (x / Math.Pow(10, d - 1)) % 10;
}
// The main function to sort array using
// MSD Radix Sort recursively
static void MSD_sort(int[] arr, int lo, int hi, int d) {
// recursion break condition
if (hi <= lo) {
return;
}
int []count = new int[10 + 2];
// temp is created to easily swap Strings in []arr
Dictionary<int, int> temp = new Dictionary<int, int>();
// Store occurrences of most significant character
// from each integer in []count
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
count++;
}
// Change []count so that []count now contains actual
// position of this digits in []temp
for (int r = 0; r < 10 + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// Build the temp
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = digit_at(arr[i], d);
temp.Add(count++, arr[i]);
}
// Copy all integers of temp to []arr, so that []arr now
// contains partially sorted integers
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
arr[i] = temp[i - lo];
// Recursively MSD_sort() on each partially sorted
// integers set to sort them by their next digit
for (int r = 0; r < 10; r++)
MSD_sort(arr, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1, d - 1);
}
// function find the largest integer
static int getMax(int []arr, int n) {
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// Main function to call MSD_sort
static void radixsort(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// get the length of the largest integer
int d = (int) Math.Floor(Math.Log10(Math.Abs(m))) + 1;
// function call
MSD_sort(arr, 0, n - 1, d);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input array
int []arr = { 9330, 9950, 718, 8977, 6790, 95, 9807, 741, 8586, 5710 };
// Size of the array
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write("Unsorted array : ");
// Print the unsorted array
print(arr, n);
// Function Call
radixsort(arr, n);
Console.Write("Sorted array : ");
// Print the sorted array
print(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Unsorted array : 9330 9950 718 8977 6790 95 9807 741 8586 5710 Sorted array : 95 718 741 5710 6790 8586 8977 9330 9807 9950
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por scorchingeagle y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
