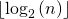Explique la funcionalidad de las siguientes funciones.
Pregunta 1
C++
/* Assume that n is greater than or equal to 1 */
int fun1(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0;
else
return 1 + fun1(n / 2);
}
Java
/* Assume that n is greater than or equal to 1 */
static int fun1(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0;
else
return 1 + fun1(n / 2);
}
Python3
# Assume that n is greater than or equal to 1 */ def fun1(n): if(n == 1): return 0 else: return 1 + fun1(n//2)
C#
/* Assume that n is greater than or equal to 1 */
static int fun1(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0;
else
return 1 + fun1(n / 2);
}
Javascript
<script>
/* Assume that n is greater than or equal to 1 */
function fun1(n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 0
else
return 1 + fun1(Math.floor(n / 2))
}
</script>
Respuesta: La función calcula y devuelve
Por ejemplo, si n está entre 8 y 15, fun1() devuelve 3. Si n está entre 16 y 31, fun1() devuelve 4.
Pregunta 2
C++
/* Assume that n is greater than or equal to 0 */
void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
cout << n%2 << endl;
}
C
/* Assume that n is greater than or equal to 0 */
void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
printf("%d", n%2);
}
Java
/* Assume that n is greater than or equal to 1 */
static void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
System.out.println(n%2);
}
Python3
# Assume that n is greater than or equal to 0 */ def fun2(n): if(n == 0): return fun2(n // 2) print(n % 2, end="")
C#
void fun2(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return;
fun2(n/2);
Console.Write(n%2);
}
Javascript
<script>
// Assume that n is greater than or equal to 1
function fun2(n)
{
if (n == 0)
return;
fun2(Math.floor(n / 2));
document.write(n % 2 + " ")
}
</script>
Respuesta: La función fun2() imprime el equivalente binario de n. Por ejemplo, si n es 21, fun2() imprime 10101.
Nota: Las funciones anteriores son solo para practicar la recursividad, no son la implementación ideal de la funcionalidad que brindan.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra alguna de las respuestas/códigos incorrectos.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA