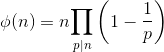Dados tres números enteros L , R y M , la tarea es encontrar la probabilidad de la Función Totient de Euler de que un número en el rango [L, R] sea divisible por M.
La función Totient de Euler es el conteo de números en {1, 2, 3, …, N} que son primos relativos a N, es decir, los números cuyo MCD (Máximo Común Divisor) con N es 1.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: L = 1, R = 5, M = 2
Salida: 0.6
Explicación:
La Función Totient de Euler para N = 1, 2, 3, 4 y 5 es {1, 1, 2, 2, 4} respectivamente.
La cuenta de la función Totient de Euler divisible por M(= 2) es 3.
Por lo tanto, la probabilidad requerida es 3/5 = 0.6Entrada: L = 1, R = 7, M = 4
Salida: 0,142
Explicación:
la función Totient de Euler para N = 1, 2, 3, ….7 es {1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 2, 6} respectivamente .
El conteo de la función Totient de Euler divisible por M(= 4) es 1.
Por lo tanto, la probabilidad requerida es 1/7 = 0.142
Enfoque: la idea es calcular previamente la función Totient de Euler e iterar sobre el rango dado y contar los números divisibles por M para calcular la probabilidad.
Para el cálculo de la función Totient de Euler , utilice la fórmula del producto de Euler :
donde p i es el factor primo de N .
Para cada factor primo i de N ( L <= n <= R) , realice los siguientes pasos:
- Resta todos los múltiplos de i de [1, N] .
- Actualice N dividiéndolo repetidamente por i .
- Si el N reducido es mayor que 1 , elimine todos los múltiplos de N del resultado.
Para el cálculo de los factores primos, utilice el método de la criba de Eratóstenes . La probabilidad en el rango dado será count/(L – R + 1) .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define size 1000001
// Seieve of Erotosthenes
// to compute all primes
void seiveOfEratosthenes(int* prime)
{
prime[0] = 1, prime[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i * i < 1000001; i++) {
// If prime
if (prime[i] == 0) {
for (int j = i * i; j < 1000001;
j += i) {
// Mark all its multiples
// as non-prime
prime[j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
// Function to find the probability of
// Euler's Totient Function in a given range
float probabiltyEuler(int* prime, int L,
int R, int M)
{
int* arr = new int[size]{ 0 };
int* eulerTotient = new int[size]{ 0 };
int count = 0;
// Initializing two arrays
// with values from L to R
// for Euler's totient
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++) {
// Indexing from 0
eulerTotient[i - L] = i;
arr[i - L] = i;
}
for (int i = 2; i < 1000001; i++) {
// If the current number is prime
if (prime[i] == 0) {
// Checking if i is prime factor
// of numbers in range L to R
for (int j = (L / i) * i; j <= R;
j += i) {
if (j - L >= 0) {
// Update all the numbers
// which has prime factor i
eulerTotient[j - L]
= eulerTotient[j - L]
/ i * (i - 1);
while (arr[j - L] % i == 0) {
arr[j - L] /= i;
}
}
}
}
}
// If number in range has a
// prime factor > sqrt(number)
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++) {
if (arr[i - L] > 1) {
eulerTotient[i - L]
= (eulerTotient[i - L] / arr[i - L])
* (arr[i - L] - 1);
}
}
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++) {
// Count those which are divisible by M
if ((eulerTotient[i - L] % M) == 0) {
count++;
}
}
// Return the result
return (1.0 * count / (R + 1 - L));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int* prime = new int[size]{ 0 };
seiveOfEratosthenes(prime);
int L = 1, R = 7, M = 3;
cout << probabiltyEuler(prime, L, R, M);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int size = 1000001;
// Seieve of Erotosthenes
// to compute all primes
static void seiveOfEratosthenes(int []prime)
{
prime[0] = 1;
prime[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i * i < 1000001; i++)
{
// If prime
if (prime[i] == 0)
{
for (int j = i * i; j < 1000001; j += i)
{
// Mark all its multiples
// as non-prime
prime[j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
// Function to find the probability of
// Euler's Totient Function in a given range
static float probabiltyEuler(int []prime, int L,
int R, int M)
{
int[] arr = new int[size];
int []eulerTotient = new int[size];
int count = 0;
// Initializing two arrays
// with values from L to R
// for Euler's totient
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
// Indexing from 0
eulerTotient[i - L] = i;
arr[i - L] = i;
}
for (int i = 2; i < 1000001; i++)
{
// If the current number is prime
if (prime[i] == 0)
{
// Checking if i is prime factor
// of numbers in range L to R
for (int j = (L / i) * i; j <= R; j += i)
{
if (j - L >= 0)
{
// Update all the numbers
// which has prime factor i
eulerTotient[j - L] = eulerTotient[j - L] /
i * (i - 1);
while (arr[j - L] % i == 0)
{
arr[j - L] /= i;
}
}
}
}
}
// If number in range has a
// prime factor > Math.sqrt(number)
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
if (arr[i - L] > 1)
{
eulerTotient[i - L] = (eulerTotient[i - L] / arr[i - L]) *
(arr[i - L] - 1);
}
}
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
// Count those which are divisible by M
if ((eulerTotient[i - L] % M) == 0)
{
count++;
}
}
// Return the result
return (float) (1.0 * count / (R + 1 - L));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int []prime = new int[size];
seiveOfEratosthenes(prime);
int L = 1, R = 7, M = 3;
System.out.print(probabiltyEuler(prime, L, R, M));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Python3
# Python3 program to implement # the above approach size = 1000001 # Seieve of Erotosthenes # to compute all primes def seiveOfEratosthenes(prime): prime[0] = 1 prime[1] = 0 i = 2 while(i * i < 1000001): # If prime if (prime[i] == 0): j = i * i while(j < 1000001): # Mark all its multiples # as non-prime prime[j] = 1 j = j + i i += 1 # Function to find the probability of # Euler's Totient Function in a given range def probabiltyEuler(prime, L, R, M): arr = [0] * size eulerTotient = [0] * size count = 0 # Initializing two arrays # with values from L to R # for Euler's totient for i in range(L, R + 1): # Indexing from 0 eulerTotient[i - L] = i arr[i - L] = i for i in range(2, 1000001): # If the current number is prime if (prime[i] == 0): # Checking if i is prime factor # of numbers in range L to R for j in range((L // i) * i, R + 1, i): if (j - L >= 0): # Update all the numbers # which has prime factor i eulerTotient[j - L] = (eulerTotient[j - L] // i * (i - 1)) while (arr[j - L] % i == 0): arr[j - L] = arr[j - L] // i # If number in range has a # prime factor > Math.sqrt(number) for i in range(L, R + 1): if (arr[i - L] > 1): eulerTotient[i - L] = ((eulerTotient[i - L] // arr[i - L]) * (arr[i - L] - 1)) for i in range(L, R + 1): # Count those which are divisible by M if ((eulerTotient[i - L] % M) == 0): count += 1 # Return the result return (float)(1.0 * count / (R + 1 - L)) # Driver code prime = [0] * size seiveOfEratosthenes(prime) L, R, M = 1, 7, 3 print(probabiltyEuler(prime, L, R, M)) # This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
C#
// C# Program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
static readonly int size = 1000001;
// Seieve of Erotosthenes
// to compute all primes
static void seiveOfEratosthenes(int []prime)
{
prime[0] = 1;
prime[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i * i < 1000001; i++)
{
// If prime
if (prime[i] == 0)
{
for (int j = i * i; j < 1000001; j += i)
{
// Mark all its multiples
// as non-prime
prime[j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
// Function to find the probability of
// Euler's Totient Function in a given range
static float probabiltyEuler(int []prime, int L,
int R, int M)
{
int[] arr = new int[size];
int []eulerTotient = new int[size];
int count = 0;
// Initializing two arrays
// with values from L to R
// for Euler's totient
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
// Indexing from 0
eulerTotient[i - L] = i;
arr[i - L] = i;
}
for (int i = 2; i < 1000001; i++)
{
// If the current number is prime
if (prime[i] == 0)
{
// Checking if i is prime factor
// of numbers in range L to R
for (int j = (L / i) * i; j <= R; j += i)
{
if (j - L >= 0)
{
// Update all the numbers
// which has prime factor i
eulerTotient[j - L] = eulerTotient[j - L] /
i * (i - 1);
while (arr[j - L] % i == 0)
{
arr[j - L] /= i;
}
}
}
}
}
// If number in range has a
// prime factor > Math.Sqrt(number)
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
if (arr[i - L] > 1)
{
eulerTotient[i - L] = (eulerTotient[i - L] / arr[i - L]) *
(arr[i - L] - 1);
}
}
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
// Count those which are divisible by M
if ((eulerTotient[i - L] % M) == 0)
{
count++;
}
}
// Return the result
return (float) (1.0 * count / (R + 1 - L));
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []prime = new int[size];
seiveOfEratosthenes(prime);
int L = 1, R = 7, M = 3;
Console.Write(probabiltyEuler(prime, L, R, M));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to implement
// the above approach
let size = 1000001;
let prime = new Array(size,0);
// Seieve of Erotosthenes
// to compute all primes
function seiveOfEratosthenes()
{
prime[0] = 1;
prime[1] = 0;
for (let i = 2; i * i < 1000001; i++)
{
// If prime
if (prime[i] == 0)
{
for (let j = i * i; j < 1000001; j += i)
{
// Mark all its multiples
// as non-prime
prime[j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
// Function to find the probability of
// Euler's Totient Function in a given range
function probabiltyEuler(L,R, M)
{
let arr = new Array(size,0);
let eulerTotient = new Array(size,0);
let count = 0;
// Initializing two arrays
// with values from L to R
// for Euler's totient
for (let i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
// Indexing from 0
eulerTotient[i - L] = i;
arr[i - L] = i;
}
for (let i = 2; i < 1000001; i++)
{
// If the current number is prime
if (prime[i] == 0)
{
// Checking if i is prime factor
// of numbers in range L to R
for (let j = (L / i) * i; j <= R; j += i)
{
if (j - L >= 0)
{
// Update all the numbers
// which has prime factor i
eulerTotient[j - L] =
eulerTotient[j - L] / i * (i - 1);
while (arr[j - L] % i == 0)
{
arr[j - L] /= i;
}
}
}
}
}
// If number in range has a
// prime factor > Math.Sqrt(number)
for (let i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
if (arr[i - L] > 1)
{
eulerTotient[i - L] =
(eulerTotient[i - L] / arr[i - L]) *
(arr[i - L] - 1);
}
}
for (let i = L; i <= R; i++)
{
// Count those which are divisible by M
if ((eulerTotient[i - L] % M) == 0)
{
count++;
}
}
count/=2;
// Return the result
return 1.0 * count / (R + 1 - L);
}
// Driver Code
seiveOfEratosthenes();
let L = 1;
let R = 7;
let M = 3;
document.write(probabiltyEuler(L, R, M).toFixed(7));
</script>
0.142857
Complejidad de tiempo: O(Nlog(N))
Espacio auxiliar: O(tamaño), donde el tamaño denota el número hasta el cual se calcula el tamiz.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por deepika_sharma y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA