Dada una array 2D tsp[][] , donde cada fila tiene la array de distancias desde esa ciudad indexada a todas las demás ciudades y -1 indica que no existe un camino entre esas dos ciudades indexadas. La tarea es imprimir el costo mínimo en el ciclo TSP.
Ejemplos:
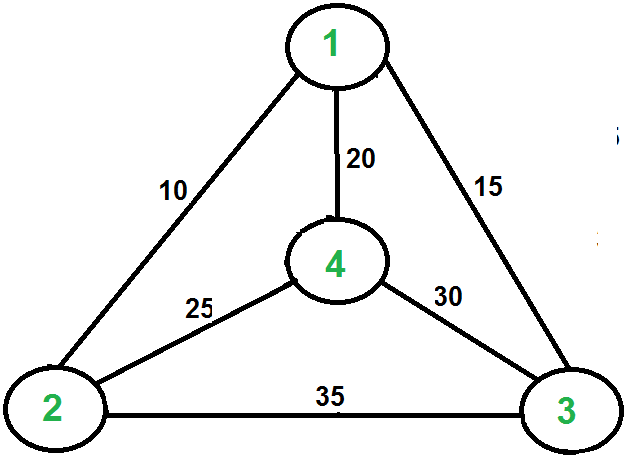
Entrada:
cucharadita[][] = {{-1, 10, 15, 20},
{10, -1, 35, 25},
{15, 35, -1, 30},
{20, 25, 30, – 1}};
A continuación se muestra el gráfico dado:
Salida: 80
Explicación:
Estamos tratando de encontrar el camino/ruta con el costo mínimo tal que se logre nuestro objetivo de visitar todas las ciudades una vez y regresar a la ciudad de origen. El camino a través del cual podemos lograr eso, se puede representar como 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 1. Aquí, comenzamos desde la ciudad 1 y terminamos en la misma visitando todas las demás ciudades una vez en nuestro camino. El costo de nuestro camino/ruta se calcula de la siguiente manera:
1 -> 2 = 10
2 -> 4 = 25
4 -> 3 = 30
3 -> 1 = 15
(Todos los costos se toman de la array 2D dada)
Por lo tanto, costo total = 10 + 25 + 30 + 15 = 80
Entrada:
cucharadita[][] = {{-1, 30, 25, 10},
{15, -1, 20, 40},
{10, 20, -1 , 25},
{30, 10, 20, -1}};
Salida: 50
Presentamos el problema del vendedor ambulante y discutimos las soluciones de programación ingenua y dinámica para el problema en la publicación anterior . Ambas soluciones son inviables. De hecho, no existe una solución de tiempo polinomial disponible para este problema, ya que se trata de un problema NP-Hard conocido. Sin embargo, existen algoritmos aproximados para resolver el problema.
Este problema se puede relacionar con el problema del ciclo hamiltoniano , de manera que aquí sabemos que existe un ciclo hamiltoniano en el gráfico, pero nuestro trabajo es encontrar el ciclo con el costo mínimo. Además, en un gráfico TSP particular, puede haber muchos ciclos hamiltonianos, pero solo necesitamos generar uno que satisfaga nuestro objetivo requerido del problema.
Enfoque: Este problema se puede resolver usandoTécnica codiciosa . A continuación se muestran los pasos:
- Cree dos titulares de datos primarios:
- Una lista que contiene los índices de las ciudades en términos de la array de entrada de distancias entre ciudades.
- Array de resultados que tendrá todas las ciudades que se pueden mostrar en la consola de cualquier manera.
- Realice un recorrido en la array de adyacencia dada tsp[][] para toda la ciudad y si el costo de llegar a cualquier ciudad desde la ciudad actual es menor que el costo actual, actualice el costo.
- Genere el ciclo de ruta mínimo utilizando el paso anterior y devuelva allí el costo mínimo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the minimum
// cost path for all the paths
void findMinRoute(vector<vector<int> > tsp)
{
int sum = 0;
int counter = 0;
int j = 0, i = 0;
int min = INT_MAX;
map<int, int> visitedRouteList;
// Starting from the 0th indexed
// city i.e., the first city
visitedRouteList[0] = 1;
int route[tsp.size()];
// Traverse the adjacency
// matrix tsp[][]
while (i < tsp.size() && j < tsp[i].size())
{
// Corner of the Matrix
if (counter >= tsp[i].size() - 1)
{
break;
}
// If this path is unvisited then
// and if the cost is less then
// update the cost
if (j != i && (visitedRouteList[j] == 0))
{
if (tsp[i][j] < min)
{
min = tsp[i][j];
route[counter] = j + 1;
}
}
j++;
// Check all paths from the
// ith indexed city
if (j == tsp[i].size())
{
sum += min;
min = INT_MAX;
visitedRouteList[route[counter] - 1] = 1;
j = 0;
i = route[counter] - 1;
counter++;
}
}
// Update the ending city in array
// from city which was last visited
i = route[counter - 1] - 1;
for (j = 0; j < tsp.size(); j++)
{
if ((i != j) && tsp[i][j] < min)
{
min = tsp[i][j];
route[counter] = j + 1;
}
}
sum += min;
// Started from the node where
// we finished as well.
cout << ("Minimum Cost is : ");
cout << (sum);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input Matrix
vector<vector<int> > tsp = { { -1, 10, 15, 20 },
{ 10, -1, 35, 25 },
{ 15, 35, -1, 30 },
{ 20, 25, 30, -1 } };
// Function Call
findMinRoute(tsp);
}
// This code is contributed by grand_master.
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class TSPGreedy {
// Function to find the minimum
// cost path for all the paths
static void findMinRoute(int[][] tsp)
{
int sum = 0;
int counter = 0;
int j = 0, i = 0;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
List<Integer> visitedRouteList
= new ArrayList<>();
// Starting from the 0th indexed
// city i.e., the first city
visitedRouteList.add(0);
int[] route = new int[tsp.length];
// Traverse the adjacency
// matrix tsp[][]
while (i < tsp.length
&& j < tsp[i].length) {
// Corner of the Matrix
if (counter >= tsp[i].length - 1) {
break;
}
// If this path is unvisited then
// and if the cost is less then
// update the cost
if (j != i
&& !(visitedRouteList.contains(j))) {
if (tsp[i][j] < min) {
min = tsp[i][j];
route[counter] = j + 1;
}
}
j++;
// Check all paths from the
// ith indexed city
if (j == tsp[i].length) {
sum += min;
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
visitedRouteList.add(route[counter] - 1);
j = 0;
i = route[counter] - 1;
counter++;
}
}
// Update the ending city in array
// from city which was last visited
i = route[counter - 1] - 1;
for (j = 0; j < tsp.length; j++) {
if ((i != j) && tsp[i][j] < min) {
min = tsp[i][j];
route[counter] = j + 1;
}
}
sum += min;
// Started from the node where
// we finished as well.
System.out.print("Minimum Cost is : ");
System.out.println(sum);
}
// Driver Code
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
// Input Matrix
int[][] tsp = {
{ -1, 10, 15, 20 },
{ 10, -1, 35, 25 },
{ 15, 35, -1, 30 },
{ 20, 25, 30, -1 }
};
// Function Call
findMinRoute(tsp);
}
}
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class TSPGreedy{
// Function to find the minimum
// cost path for all the paths
static void findMinRoute(int[,] tsp)
{
int sum = 0;
int counter = 0;
int j = 0, i = 0;
int min = int.MaxValue;
List<int> visitedRouteList = new List<int>();
// Starting from the 0th indexed
// city i.e., the first city
visitedRouteList.Add(0);
int[] route = new int[tsp.Length];
// Traverse the adjacency
// matrix tsp[,]
while (i < tsp.GetLength(0) &&
j < tsp.GetLength(1))
{
// Corner of the Matrix
if (counter >= tsp.GetLength(0) - 1)
{
break;
}
// If this path is unvisited then
// and if the cost is less then
// update the cost
if (j != i &&
!(visitedRouteList.Contains(j)))
{
if (tsp[i, j] < min)
{
min = tsp[i, j];
route[counter] = j + 1;
}
}
j++;
// Check all paths from the
// ith indexed city
if (j == tsp.GetLength(0))
{
sum += min;
min = int.MaxValue;
visitedRouteList.Add(route[counter] - 1);
j = 0;
i = route[counter] - 1;
counter++;
}
}
// Update the ending city in array
// from city which was last visited
i = route[counter - 1] - 1;
for(j = 0; j < tsp.GetLength(0); j++)
{
if ((i != j) && tsp[i, j] < min)
{
min = tsp[i, j];
route[counter] = j + 1;
}
}
sum += min;
// Started from the node where
// we finished as well.
Console.Write("Minimum Cost is : ");
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input Matrix
int[,] tsp = { { -1, 10, 15, 20 },
{ 10, -1, 35, 25 },
{ 15, 35, -1, 30 },
{ 20, 25, 30, -1 } };
// Function call
findMinRoute(tsp);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
from typing import DefaultDict
INT_MAX = 2147483647
# Function to find the minimum
# cost path for all the paths
def findMinRoute(tsp):
sum = 0
counter = 0
j = 0
i = 0
min = INT_MAX
visitedRouteList = DefaultDict(int)
# Starting from the 0th indexed
# city i.e., the first city
visitedRouteList[0] = 1
route = [0] * len(tsp)
# Traverse the adjacency
# matrix tsp[][]
while i < len(tsp) and j < len(tsp[i]):
# Corner of the Matrix
if counter >= len(tsp[i]) - 1:
break
# If this path is unvisited then
# and if the cost is less then
# update the cost
if j != i and (visitedRouteList[j] == 0):
if tsp[i][j] < min:
min = tsp[i][j]
route[counter] = j + 1
j += 1
# Check all paths from the
# ith indexed city
if j == len(tsp[i]):
sum += min
min = INT_MAX
visitedRouteList[route[counter] - 1] = 1
j = 0
i = route[counter] - 1
counter += 1
# Update the ending city in array
# from city which was last visited
i = route[counter - 1] - 1
for j in range(len(tsp)):
if (i != j) and tsp[i][j] < min:
min = tsp[i][j]
route[counter] = j + 1
sum += min
# Started from the node where
# we finished as well.
print("Minimum Cost is :", sum)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Input Matrix
tsp = [[-1, 10, 15, 20], [10, -1, 35, 25], [15, 35, -1, 30], [20, 25, 30, -1]]
# Function Call
findMinRoute(tsp)
Minimum Cost is : 80
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N 2 *log 2 N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)