Dada una lista enlazada individualmente, encuentre el medio de la lista enlazada y establezca el Node medio de la lista enlazada al principio de la lista enlazada.
Ejemplos:
Input: 1 2 3 4 5 Output: 3 1 2 4 5 Input: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Output: 4 1 2 3 5 6
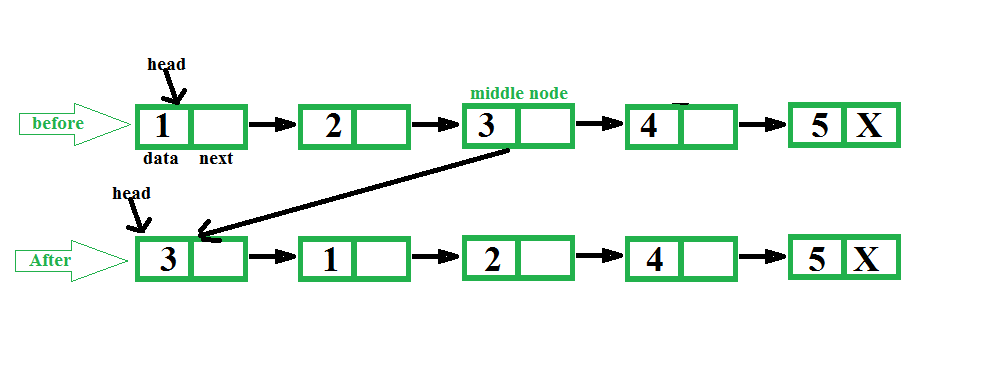
La idea es encontrar primero el medio de una lista enlazada usando dos punteros , el primero se mueve uno a la vez y el segundo se mueve dos a la vez. Cuando el segundo puntero llega al final, el primero llega al medio. También realizamos un seguimiento del anterior del primer puntero para que podamos eliminar el Node medio de su posición actual y convertirlo en la cabeza.
C
// C program to make middle node as
// head of linked list.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Link list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to get the middle and set at
beginning of the linked list*/
void setMiddleHead(struct Node** head)
{
if (*head == NULL)
return;
// To traverse list nodes one by one
struct Node* one_node = (*head);
// To traverse list nodes by skipping
// one.
struct Node* two_node = (*head);
// To keep track of previous of middle
struct Node* prev = NULL;
while (two_node != NULL &&
two_node->next != NULL)
{
// For previous node of middle node
prev = one_node;
// Move one node each time
two_node = two_node->next->next;
// Move two node each time
one_node = one_node->next;
}
// Set middle node at head
prev->next = prev->next->next;
one_node->next = (*head);
(*head) = one_node;
}
// To insert a node at the beginning
// of linked list.
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to the
// new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// A function to print a given linked list
void printList(struct Node* ptr)
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf("");
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Create a list of 5 nodes
struct Node* head = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
push(&head, i);
printf(" list before: ");
printList(head);
setMiddleHead(&head);
printf(" list After: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Producción:
list before: 1 2 3 4 5 list After : 3 1 2 4 5
Complejidad de tiempo : O(n) donde n es el número total de Nodes en la lista enlazada.
Espacio auxiliar : O (1) ya que usa espacio constante
¡ Consulte el artículo completo sobre Hacer la cabeza del Node medio en una lista vinculada para obtener más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA