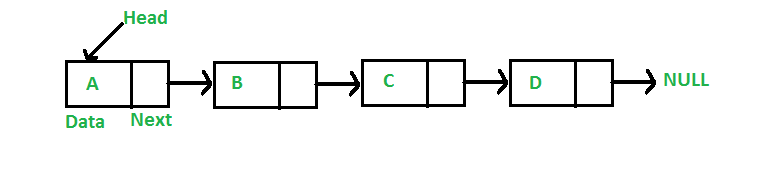
Dada una lista enlazada y un número n, escriba una función que devuelva el valor en el Node n desde el final de la lista enlazada.
Por ejemplo, si la entrada está debajo de la lista y n = 3, entonces la salida es «B»
Método 1 (Usar la longitud de la lista enlazada)
1) Calcular la longitud de la Lista enlazada. Sea la longitud len.
2) Imprima el (len – n + 1) Node desde el principio de la lista enlazada.
Concepto de puntero doble: el primer puntero se usa para almacenar la dirección de la variable y el segundo puntero se usa para almacenar la dirección del primer puntero. Si deseamos cambiar el valor de una variable por una función, le pasamos un puntero. Y si deseamos cambiar el valor de un puntero (es decir, debería empezar a apuntar a otra cosa), pasamos puntero a puntero.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Java
// Simple Java program to find n'th node from end of linked list
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of the list
/* Linked List node */
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to get the nth node from the last of a
linked list */
void printNthFromLast(int n)
{
int len = 0;
Node temp = head;
// 1) count the number of nodes in Linked List
while (temp != null) {
temp = temp.next;
len++;
}
// check if value of n is not more than length of
// the linked list
if (len < n)
return;
temp = head;
// 2) get the (len-n+1)th node from the beginning
for (int i = 1; i < len - n + 1; i++)
temp = temp.next;
System.out.println(temp.data);
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver program to test above methods */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(35);
llist.printNthFromLast(4);
}
} // This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra
35
Complejidad temporal: O(n).
Espacio auxiliar : O (1) ya que usa espacio constante
A continuación se muestra un código C recursivo para el mismo método. Gracias a Anuj Bansal por proporcionar el siguiente código.
Java
static void printNthFromLast(Node head, int n)
{
static int i = 0;
if (head == null)
return;
printNthFromLast(head.next, n);
if (++i == n)
System.out.print(head.data);
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n) donde n es la longitud de la lista enlazada.
Método 2 (Usar dos punteros)
Mantener dos punteros: puntero de referencia y puntero principal. Inicialice tanto los punteros de referencia como los principales en head. Primero, mueva el puntero de referencia a n Nodes desde la cabeza. Ahora mueva ambos punteros uno por uno hasta que el puntero de referencia llegue al final. Ahora el puntero principal apuntará al Node n desde el final. Devuelve el puntero principal.
La imagen de abajo es una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:

A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Java
// Java program to find n'th
// node from end using slow and
// fast pointers
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of the list
/* Linked List node */
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to get the
nth node from end of list */
void printNthFromLast(int n)
{
Node main_ptr = head;
Node ref_ptr = head;
int count = 0;
if (head != null)
{
while (count < n)
{
if (ref_ptr == null)
{
System.out.println(n
+ " is greater than the no "
+ " of nodes in the list");
return;
}
ref_ptr = ref_ptr.next;
count++;
}
if(ref_ptr == null)
{
if(head != null)
System.out.println("Node no. " + n +
" from last is " +
head.data);
}
else
{
while (ref_ptr != null)
{
main_ptr = main_ptr.next;
ref_ptr = ref_ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("Node no. " + n +
" from last is " +
main_ptr.data);
}
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver program to test above methods */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(35);
llist.printNthFromLast(4);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra
Node no. 4 from last is 35
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n) donde n es la longitud de la lista enlazada.
Complejidad espacial : O(1) usando espacio constante
Consulte el artículo completo sobre Programa para el Node n desde el final de una lista vinculada para obtener más detalles.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA