En análisis numérico, la regla de 1/3 de Simpson es un método para la aproximación numérica de integrales definidas. En concreto, es la siguiente aproximación:
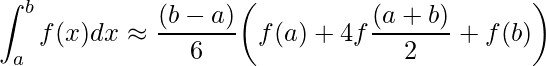
En la regla de 1/3 de Simpson, usamos parábolas para aproximar cada parte de la curva. Dividimos
el área en n segmentos iguales de ancho Δx.
La regla de Simpson se puede derivar aproximando el integrando f (x) (en azul)
por el interpolante cuadrático P(x) (en rojo).

Para integrar cualquier función f(x) en el intervalo (a, b), siga los pasos que se indican a continuación:
1. Seleccione un valor para n, que es el número de partes en que se divide el intervalo.
2. Calcular el ancho, h = (ba)/n
3. Calcular los valores de x0 a xn como x0 = a, x1 = x0 + h, …..xn-1 = xn-2 + h, xn = b.
Considere y = f(x). Ahora encuentra los valores de y(y0 a yn) para los valores correspondientes de x(x0 a xn).
4. Sustituya todos los valores encontrados anteriormente en la fórmula de la regla de Simpson para calcular el valor integral.
El valor aproximado de la integral puede ser dado por la regla de Simpson :

Nota: En esta regla, n debe ser PAR.
Aplicación:
Se utiliza cuando es muy difícil resolver matemáticamente la integral dada.
Esta regla proporciona una aproximación fácilmente sin conocer realmente las reglas de integración.
Ejemplo :
Evaluate logx dx within limit 4 to 5.2.
First we will divide interval into six equal
parts as number of interval should be even.
x : 4 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2
logx : 1.38 1.43 1.48 1.52 1.56 1.60 1.64
Now we can calculate approximate value of integral
using above formula:
= h/3[( 1.38 + 1.64) + 4 * (1.43 + 1.52 +
1.60 ) +2 *(1.48 + 1.56)]
= 1.84
Hence the approximation of above integral is
1.827 using Simpson's 1/3 rule.
C++
// CPP program for simpson's 1/3 rule
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate f(x)
float func(float x)
{
return log(x);
}
// Function for approximate integral
float simpsons_(float ll, float ul, int n)
{
// Calculating the value of h
float h = (ul - ll) / n;
// Array for storing value of x and f(x)
float x[10], fx[10];
// Calculating values of x and f(x)
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
x[i] = ll + i * h;
fx[i] = func(x[i]);
}
// Calculating result
float res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == 0 || i == n)
res += fx[i];
else if (i % 2 != 0)
res += 4 * fx[i];
else
res += 2 * fx[i];
}
res = res * (h / 3);
return res;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
float lower_limit = 4; // Lower limit
float upper_limit = 5.2; // Upper limit
int n = 6; // Number of interval
cout << simpsons_(lower_limit, upper_limit, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for simpson's 1/3 rule
public class GfG{
// Function to calculate f(x)
static float func(float x)
{
return (float)Math.log(x);
}
// Function for approximate integral
static float simpsons_(float ll, float ul,
int n)
{
// Calculating the value of h
float h = (ul - ll) / n;
// Array for storing value of x
// and f(x)
float[] x = new float[10];
float[] fx= new float[10];
// Calculating values of x and f(x)
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
x[i] = ll + i * h;
fx[i] = func(x[i]);
}
// Calculating result
float res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == 0 || i == n)
res += fx[i];
else if (i % 2 != 0)
res += 4 * fx[i];
else
res += 2 * fx[i];
}
res = res * (h / 3);
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String s[])
{
// Lower limit
float lower_limit = 4;
// Upper limit
float upper_limit = (float)5.2;
// Number of interval
int n = 6;
System.out.println(simpsons_(lower_limit,
upper_limit, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Gitanjali
Python3
# Python code for simpson's 1 / 3 rule
import math
# Function to calculate f(x)
def func( x ):
return math.log(x)
# Function for approximate integral
def simpsons_( ll, ul, n ):
# Calculating the value of h
h = ( ul - ll )/n
# List for storing value of x and f(x)
x = list()
fx = list()
# Calculating values of x and f(x)
i = 0
while i<= n:
x.append(ll + i * h)
fx.append(func(x[i]))
i += 1
# Calculating result
res = 0
i = 0
while i<= n:
if i == 0 or i == n:
res+= fx[i]
elif i % 2 != 0:
res+= 4 * fx[i]
else:
res+= 2 * fx[i]
i+= 1
res = res * (h / 3)
return res
# Driver code
lower_limit = 4 # Lower limit
upper_limit = 5.2 # Upper limit
n = 6 # Number of interval
print("%.6f"% simpsons_(lower_limit, upper_limit, n))
C#
// C# program for simpson's 1/3 rule
using System;
public class GfG
{
// Function to calculate f(x)
static float func(float x)
{
return (float)Math.Log(x);
}
// Function for approximate integral
static float simpsons_(float ll, float ul,
int n)
{
// Calculating the value of h
float h = (ul - ll) / n;
// Array for storing value of x
// and f(x)
float[] x = new float[10];
float[] fx= new float[10];
// Calculating values of x and f(x)
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
x[i] = ll + i * h;
fx[i] = func(x[i]);
}
// Calculating result
float res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == 0 || i == n)
res += fx[i];
else if (i % 2 != 0)
res += 4 * fx[i];
else
res += 2 * fx[i];
}
res = res * (h / 3);
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Lower limit
float lower_limit = 4;
// Upper limit
float upper_limit = (float)5.2;
// Number of interval
int n = 6;
Console.WriteLine(simpsons_(lower_limit,
upper_limit, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m
PHP
<?php
// PhP program for simpson's 1/3 rule
// Function to calculate f(x)
function func($x)
{
return log($x);
}
// Function for approximate integral
function simpsons_($ll, $ul, $n)
{
// Calculating the value of h
$h = ($ul - $ll) / $n;
// Calculating values of x and f(x)
for ($i = 0; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
$x[$i] = $ll + $i * $h;
$fx[$i] = func($x[$i]);
}
// Calculating result
$res = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
if ($i == 0 || $i == $n)
$res += $fx[$i];
else if ($i % 2 != 0)
$res += 4 * $fx[$i];
else
$res += 2 * $fx[$i];
}
$res = $res * ($h / 3);
return $res;
}
// Driver program
$lower_limit = 4; // Lower limit
$upper_limit = 5.2; // Upper limit
$n = 6; // Number of interval
echo simpsons_($lower_limit, $upper_limit, $n);
// This code is contributed by ajit.
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScriptprogram for simpson's 1/3 rule
// Function to calculate f(x)
function func(x)
{
return Math.log(x);
}
// Function for approximate integral
function simpsons_(ll, ul, n)
{
// Calculating the value of h
let h = (ul - ll) / n;
// Array for storing value of x
// and f(x)
let x = [];
let fx= [];
// Calculating values of x and f(x)
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
x[i] = ll + i * h;
fx[i] = func(x[i]);
}
// Calculating result
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == 0 || i == n)
res += fx[i];
else if (i % 2 != 0)
res += 4 * fx[i];
else
res += 2 * fx[i];
}
res = res * (h / 3);
return res;
}
// Driver code
// Lower limit
let lower_limit = 4;
// Upper limit
let upper_limit = 5.2;
// Number of interval
let n = 6;
document.write(simpsons_(lower_limit,
upper_limit, n));
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.
</script>
Producción:
1.827847
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Sharad_Bhardwaj y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA